Kinship care provides children the stability of living with relatives, offering emotional familiarity and cultural continuity, while foster care places children with trained, licensed caregivers outside their family network to ensure safety and well-being. Explore this article to understand the key differences, benefits, and challenges of kinship care versus foster care.
Table of Comparison
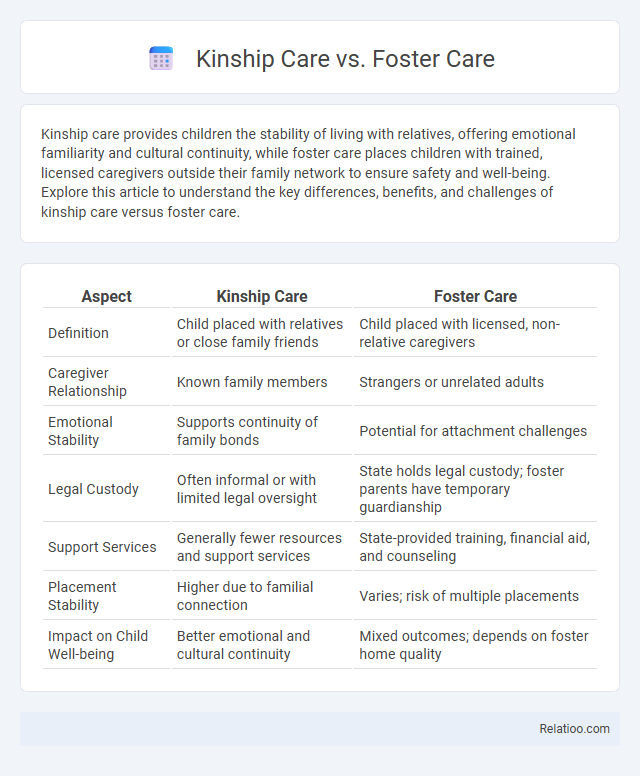
| Aspect | Kinship Care | Foster Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child placed with relatives or close family friends | Child placed with licensed, non-relative caregivers |
| Caregiver Relationship | Known family members | Strangers or unrelated adults |
| Emotional Stability | Supports continuity of family bonds | Potential for attachment challenges |
| Legal Custody | Often informal or with limited legal oversight | State holds legal custody; foster parents have temporary guardianship |
| Support Services | Generally fewer resources and support services | State-provided training, financial aid, and counseling |
| Placement Stability | Higher due to familial connection | Varies; risk of multiple placements |
| Impact on Child Well-being | Better emotional and cultural continuity | Mixed outcomes; depends on foster home quality |
Understanding Kinship Care
Kinship care involves placing children with relatives or close family friends, providing a familiar and stable environment that supports emotional well-being and cultural identity. Unlike traditional foster care, which often places children with certified, non-family caregivers, kinship care prioritizes maintaining family connections and continuity. Understanding kinship care helps you explore alternatives that keep children closer to their roots while ensuring their safety and development.
What Is Foster Care?
Foster care is a temporary arrangement where trained caregivers provide a safe, nurturing environment for children removed from their biological families due to neglect or abuse. Unlike kinship care, which places children with relatives, foster care often involves non-relative adults licensed by child welfare agencies. Your role as a foster parent includes supporting the child's emotional and physical needs while working closely with social services to facilitate family reunification or long-term placement.
Key Differences Between Kinship and Foster Care
Kinship care involves placing children with relatives or close family friends, offering a familiar environment that supports emotional stability. Foster care places children with certified caregivers who may not have a prior relationship with the child, emphasizing safety and structured support. Understanding these key differences helps you make informed decisions about the most suitable care option for a child's unique needs.
Benefits of Kinship Care
Kinship care offers children the advantage of staying within their family network, promoting emotional stability and cultural continuity while maintaining established relationships. Your child benefits from a familiar environment, often resulting in better behavioral and academic outcomes compared to foster care. Kinship caregivers also experience greater satisfaction and reduced stress, strengthening the support system crucial for the child's well-being.
Advantages and Challenges of Foster Care
Foster care offers children a temporary, safe environment with trained caregivers who support emotional and developmental needs, promoting stability and growth during family crises. However, challenges include potential attachment disruptions, varying quality of care, and the emotional complexity for both foster children and foster parents navigating uncertain reunification or adoption processes. Your ability to provide consistent support and understanding plays a crucial role in overcoming these obstacles and fostering positive outcomes for children in foster care.
Emotional Impact on Children
Kinship care often provides children with greater emotional stability due to familiarity and maintained family connections, reducing feelings of abandonment and anxiety. Foster care, while offering safety and shelter, may result in emotional challenges such as attachment difficulties and identity confusion due to frequent transitions and separation from biological family. Fostering emphasizes temporary support, but the uncertainty and changes in caregivers can lead to stress and emotional distress, highlighting the need for consistent emotional nurturing and stability in all care types.
Legal and Financial Aspects
Kinship care involves relatives taking legal guardianship, often resulting in more stable financial support through state benefits tailored for family caregivers. Foster care requires state certification and oversight, with caregivers receiving monthly stipends and possible subsidies for medical and educational needs, but legal rights remain with the state or child welfare agency. Fostering broadly describes the temporary care of children outside their family, where legal custody typically stays with the agency, and financial assistance depends on the fostering program's specific regulations and funding.
Support Services Available
Kinship care offers support services tailored to relatives raising children, including financial assistance, counseling, and specialized parenting programs that respect family bonds. Foster care provides extensive support through trained social workers, access to healthcare, educational resources, and therapeutic services to address diverse child needs. Fostering programs emphasize ongoing training, respite care, and peer support networks to equip foster parents with skills and emotional support for stable placements.
Which Option Is Best for Children?
Kinship care often provides children with a familiar and stable environment by placing them with relatives, promoting emotional security and cultural continuity. Foster care, managed by state agencies, offers professional oversight and access to support services but may lack the familial bonds present in kinship situations. Choosing the best option depends on the child's specific needs, with kinship care favored for maintaining family connections and fostering preferred for structured, therapeutic settings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Care Path
Choosing the right care path depends on the child's best interests and your family's capacity to provide stability and support. Kinship care offers familiarity and continuity by placing a child with relatives, while foster care provides professional oversight and resources from licensed caregivers. Evaluating your ability to meet emotional, financial, and legal needs helps determine whether kinship care, foster care, or becoming a foster parent is the best option for your situation.
Infographic: Kinship Care vs Foster Care
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com