Static expectations assume future behaviors remain consistent with past interactions, while dynamic expectations adapt based on ongoing experiences and changes within the relationship. Discover how balancing these outlooks impacts relationship growth and satisfaction in this article.
Table of Comparison
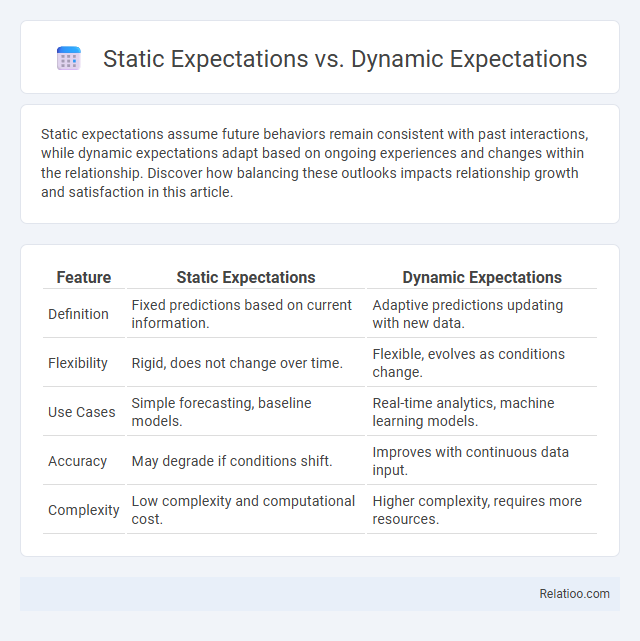
| Feature | Static Expectations | Dynamic Expectations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed predictions based on current information. | Adaptive predictions updating with new data. |
| Flexibility | Rigid, does not change over time. | Flexible, evolves as conditions change. |
| Use Cases | Simple forecasting, baseline models. | Real-time analytics, machine learning models. |
| Accuracy | May degrade if conditions shift. | Improves with continuous data input. |
| Complexity | Low complexity and computational cost. | Higher complexity, requires more resources. |
Introduction to Static and Dynamic Expectations
Static expectations assume individuals form their forecasts based solely on past information without adjusting for anticipated policy changes, leading to predictable economic reactions. Dynamic expectations incorporate agents' forward-looking behavior, where expectations adapt as new information and potential future policies are considered, allowing for more accurate economic modeling. This distinction is crucial in macroeconomic theory, as dynamic models better capture real-world economic decision-making compared to static approaches.
Defining Static Expectations
Static expectations refer to the assumption that economic agents predict future variables based solely on current or past information without adjusting for changes in policy or economic conditions. Your decisions may be less responsive under static expectations, potentially leading to systematic forecast errors when environments shift. Understanding static expectations is critical for comparing how dynamic models, which incorporate evolving information and adaptive learning, differ in predicting economic behavior.
Understanding Dynamic Expectations
Dynamic expectations evolve based on continuously updated information and shifting economic conditions, allowing for more accurate predictions of future events compared to static expectations, which assume fixed, unchanging forecasts. Understanding dynamic expectations helps you anticipate market trends and policy impacts by incorporating new data and behavioral responses into economic models. This approach enhances decision-making by reflecting realistic adjustments in expectations over time, crucial for effective financial planning and economic analysis.
Key Differences Between Static and Dynamic Expectations
Static expectations assume that your future behavior and economic variables remain constant over time, ignoring changes in policy or environment. Dynamic expectations incorporate anticipated changes and adjust predictions based on new information, capturing evolving economic conditions. The key difference lies in static models' rigidity versus dynamic models' flexibility in forecasting and decision-making processes.
The Role of Assumptions in Economic Forecasting
In economic forecasting, static expectations assume agents predict future variables based solely on current or past information, often leading to inaccurate models during structural changes. Dynamic expectations incorporate anticipated future policy shifts and economic changes, enhancing forecast reliability by aligning predictions with evolving economic conditions. The role of assumptions is crucial as dynamic models better capture how rational agents adjust behavior over time, improving the accuracy of macroeconomic and financial forecasts.
Impact of Expectations on Market Outcomes
Static expectations assume agents predict future variables based solely on past and current information, often leading to systematic forecasting errors and market inefficiencies. Dynamic expectations incorporate evolving information and adaptation, enabling more accurate predictions that enhance market adjustment and stability. Fully dynamic models, integrating forward-looking behavior and real-time updates, significantly influence asset pricing, inflation rates, and investment decisions, promoting more efficient and responsive market outcomes.
Behavioral Influences on Expectation Formation
Static expectations are formed based on past experiences without adjusting for new information, leading to potential rigidity in your decision-making process. Dynamic expectations continuously update as new data emerges, reflecting a more flexible and responsive approach, while dynamic behavioral influences incorporate psychological factors like biases and heuristics that shape how expectations evolve. Understanding these behavioral influences helps optimize forecast accuracy by recognizing how emotion, cognitive limitations, and social context impact your expectation formation.
Case Studies: Static vs Dynamic Approaches
Case studies comparing static expectations and dynamic expectations highlight significant variances in forecasting accuracy across economic models. Static approaches rely on fixed assumptions without accounting for evolving market information, often resulting in less adaptive predictions, whereas dynamic expectations incorporate real-time data updates and behavioral adjustments, enhancing model responsiveness. Empirical evidence from business cycle analyses and inflation forecasting demonstrates that dynamic models consistently outperform static ones by capturing feedback mechanisms and expectation adjustments in agent behavior.
Applications in Policy and Business Strategy
Static expectations assume that agents predict future variables based solely on past and current information without anticipating changes in policy or environment, making them suitable for short-term planning but limited in adapting to shifts. Dynamic expectations incorporate forecasts of future policies and events into decision-making, enhancing strategic responsiveness in both macroeconomic policy formulation and business investment strategies. Dynamic models further optimize outcomes by continuously updating expectations with new data, enabling governments and companies to implement adaptive policies and flexible business strategies that respond effectively to evolving market conditions.
Conclusion: Navigating Future Expectations
Static expectations assume a fixed future based on past trends, while dynamic expectations adapt as new information emerges, reflecting a more realistic understanding of economic changes. Dynamic models better capture the uncertainty and complexity of market behavior, helping You make informed decisions in fluctuating environments. Navigating future expectations requires embracing dynamic frameworks to anticipate shifts and optimize strategic responses.
Infographic: Static Expectations vs Dynamic Expectations
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com