Rational expectations assume individuals use all available information to forecast future events accurately, while adaptive expectations rely on past experiences to predict future outcomes. Explore this article to understand the impact of these theories on economic decision-making and relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
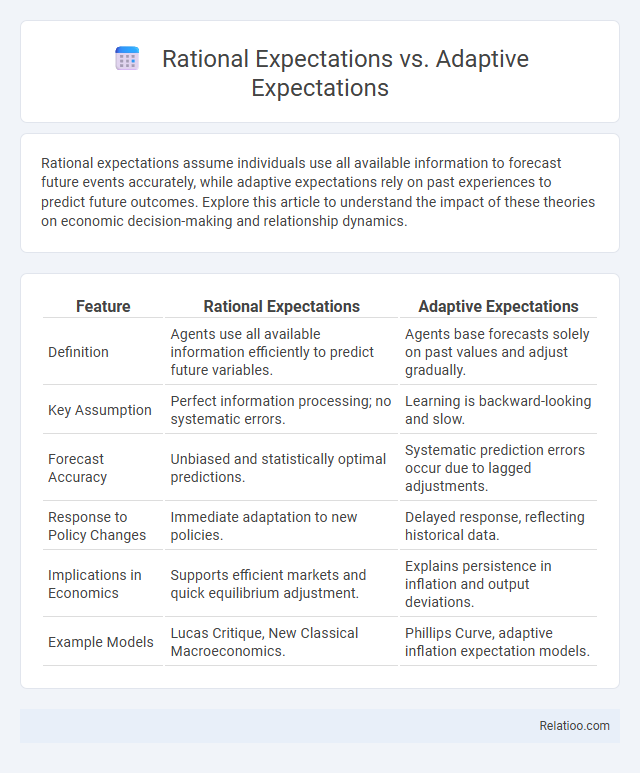
| Feature | Rational Expectations | Adaptive Expectations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agents use all available information efficiently to predict future variables. | Agents base forecasts solely on past values and adjust gradually. |
| Key Assumption | Perfect information processing; no systematic errors. | Learning is backward-looking and slow. |
| Forecast Accuracy | Unbiased and statistically optimal predictions. | Systematic prediction errors occur due to lagged adjustments. |
| Response to Policy Changes | Immediate adaptation to new policies. | Delayed response, reflecting historical data. |
| Implications in Economics | Supports efficient markets and quick equilibrium adjustment. | Explains persistence in inflation and output deviations. |
| Example Models | Lucas Critique, New Classical Macroeconomics. | Phillips Curve, adaptive inflation expectation models. |
Introduction to Expectations in Economics
Rational Expectations theory asserts that individuals form forecasts based on all available information and economic models, making predictions unbiased and efficient. Adaptive Expectations rely on past data and adjust forecasts slowly over time, often lagging behind actual changes in economic variables. Dynamic expectations incorporate changes over time, allowing for more flexible adjustments to future outcomes in response to evolving economic conditions.
Defining Rational Expectations
Rational Expectations theory assumes that Your forecasts of future economic variables are based on all available information and consistent with the actual economic model, contrasting with Adaptive Expectations, which rely solely on past data to predict the future. This approach emphasizes that people do not make systematic errors when predicting the future because they use all relevant and current information efficiently. Dynamic models incorporate Rational Expectations to simulate how economic agents react over time, adjusting their expectations as new information emerges.
Understanding Adaptive Expectations
Adaptive Expectations rely on past experiences to predict future values, adjusting forecasts gradually as new information becomes available. Understanding Adaptive Expectations helps you grasp how individuals or markets update their beliefs based on historical data, often leading to lagging responses to shocks. Unlike Rational Expectations, which assume full use of all available information, Adaptive models emphasize the role of learning and adjustment over time in economic forecasting.
Key Differences Between Rational and Adaptive Expectations
Rational expectations assume that individuals use all available information, including understanding economic models, to forecast future variables accurately, while adaptive expectations rely solely on past data and adjust gradually over time. The key difference lies in the speed and accuracy of adjustment: rational expectations lead to immediate and unbiased predictions, preventing systematic errors, whereas adaptive expectations cause lagged responses, often resulting in systematic forecast errors. Dynamic expectations encompass models incorporating both forward-looking rational components and backward-looking adaptive adjustments to better capture real-world behavior.
Historical Development of Expectation Theories
Rational Expectations Theory, developed in the 1960s by economists like John Muth, revolutionized the understanding of economic forecasting by assuming individuals use all available information efficiently, contrasting with Adaptive Expectations which rely solely on past data to predict future outcomes. The Dynamic Expectation Models emerged to bridge the gap, incorporating both past experiences and forward-looking information, capturing evolving market behavior over time. You can better grasp economic forecasting by analyzing how these expectation theories historically evolved to reflect changes in information processing and decision-making.
Impact on Macroeconomic Policy
Rational Expectations assume individuals use all available information to predict economic variables, leading to policy ineffectiveness when unexpected changes occur. Adaptive Expectations rely on past data trends, causing a lag in response that allows policymakers to exploit short-term trade-offs. Dynamic models incorporate time-varying expectations and adjustments, enhancing the accuracy of policy impact predictions and helping shape effective macroeconomic strategies for Your economic environment.
Role in Inflation Forecasting
Rational Expectations assume individuals use all available information efficiently, leading to accurate inflation forecasting by anticipating policy changes and economic shocks. Adaptive Expectations rely on past inflation data, causing lags in adjusting forecasts and potential errors during rapid economic shifts. Your inflation predictions improve significantly by incorporating dynamic models that blend both approaches, capturing evolving economic trends and behavioral adjustments over time.
Empirical Evidence and Real-World Applications
Empirical evidence shows that Rational Expectations models often outperform Adaptive Expectations in predicting economic variables like inflation and interest rates, as they incorporate all available information rather than relying solely on past data. Dynamic models integrate time-dependent behavior and adjustments, providing a more nuanced understanding of expectations formation in real-world markets such as labor and financial sectors. Applications in macroeconomic policy and asset pricing benefit from dynamic and rational expectations frameworks by improving forecast accuracy and informing decision-making under uncertainty.
Criticisms and Limitations of Each Approach
Rational Expectations assume that individuals use all available information efficiently, but this approach is criticized for its unrealistic assumption of perfect knowledge and computational abilities. Adaptive Expectations rely solely on past data, leading to lagging responses and failing to account for structural changes in the economy, which limits their predictive accuracy. Dynamic models incorporate time and feedback mechanisms but often face complexities in specification and may suffer from overparameterization, making it challenging for You to apply them effectively in real-world scenarios.
Conclusion: Implications for Economic Modeling
Rational expectations assume agents use all available information efficiently, leading to models that better predict policy outcomes and reduce systematic errors. Adaptive expectations rely on past data, causing models to react slowly to changes and often misestimate economic dynamics. Dynamic models incorporating rational expectations enhance the realism and accuracy of economic forecasts, improving policy analysis and decision-making.
Infographic: Rational Expectations vs Adaptive Expectations
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com