High expectations in relationships often promote growth and mutual respect, while low expectations may lead to dissatisfaction and emotional neglect. Discover how balancing expectations can improve your connection in this article.
Table of Comparison
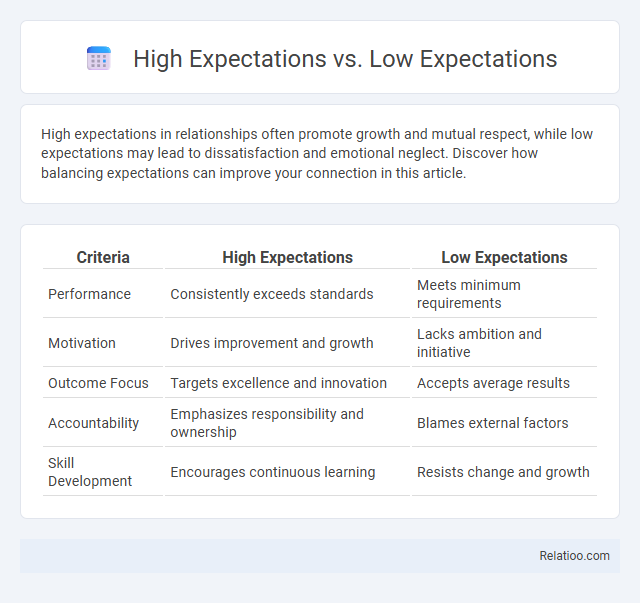
| Criteria | High Expectations | Low Expectations |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Consistently exceeds standards | Meets minimum requirements |
| Motivation | Drives improvement and growth | Lacks ambition and initiative |
| Outcome Focus | Targets excellence and innovation | Accepts average results |
| Accountability | Emphasizes responsibility and ownership | Blames external factors |
| Skill Development | Encourages continuous learning | Resists change and growth |
Understanding the Concept of Expectations
Expectations shape your perceptions and interactions by influencing emotional responses and behavior patterns. High expectations often drive motivation and achievement but can cause stress if unrealistic, while low expectations might reduce pressure but limit potential growth. Temperament affects how individuals interpret and respond to these expectations, making self-awareness vital for balancing ambition with emotional well-being.
Psychological Impact of High vs Low Expectations
High expectations often drive increased motivation and achievement but can also lead to heightened stress, anxiety, and feelings of failure when unmet. Low expectations may reduce pressure and anxiety, fostering a more relaxed mindset yet potentially resulting in lower ambition and diminished personal growth. Temperament influences how individuals perceive and respond to these expectations, with sensitive temperaments more vulnerable to negative psychological impacts from high expectations.
High Expectations: Benefits and Drawbacks
High expectations often drive individuals to achieve greater success by fostering motivation, discipline, and resilience. However, excessively high expectations can lead to stress, anxiety, and burnout, negatively impacting your mental health and overall well-being. Balancing high expectations with realistic goals and understanding one's temperament is essential to maximize benefits while minimizing drawbacks.
Low Expectations: Advantages and Limitations
Low expectations can reduce stress and promote emotional stability by lowering the pressure to achieve unrealistic goals, fostering a more relaxed and content mindset. However, sustained low expectations may limit personal growth and restrict opportunities by discouraging ambition and effort toward self-improvement. Balancing low expectations with awareness of one's temperament ensures mental well-being without stifling potential development.
Effects on Personal Growth and Motivation
High expectations often drive your personal growth by fostering resilience, goal-setting, and motivation to achieve higher standards, while low expectations can lead to complacency and limited development. Temperament plays a crucial role in moderating these effects, as individuals with a positive, adaptable temperament may thrive under high expectations, whereas those with a more sensitive or anxious disposition might experience stress or decreased motivation. Understanding the balance between expectations and temperament helps tailor motivational strategies that promote sustainable personal growth.
Influence on Relationships and Social Interactions
High expectations can create pressure and strain in relationships, often leading to disappointment when others don't meet your standards. Low expectations might foster tolerance and reduce conflict but can also result in unmet personal needs and stagnation. Your temperament shapes how you respond to these expectations, influencing social interactions by affecting communication style, emotional regulation, and conflict resolution.
Expectations in Educational and Workplace Settings
High expectations in educational and workplace settings often drive increased motivation, performance, and goal attainment by fostering a growth mindset and encouraging persistent effort. Low expectations can lead to self-fulfilling prophecies of underachievement, reduced engagement, and diminished confidence among students and employees. Temperament influences how individuals respond to these expectations, with resilient temperaments more likely to thrive under high demands, while sensitive temperaments might require supportive adjustments to optimize outcomes.
Strategies to Set Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic expectations requires understanding the interplay between high expectations, low expectations, and individual temperament. Tailoring strategies to Your specific temperament involves balancing ambition with self-awareness, setting achievable goals based on past performance and emotional resilience. Employing techniques like incremental goal-setting, positive reinforcement, and regular self-assessment helps maintain motivation while avoiding frustration or complacency.
Managing Disappointment and Resilience
High expectations often lead to greater motivation but can increase the risk of intense disappointment when outcomes fall short, requiring robust resilience strategies to manage setbacks effectively. Low expectations may reduce the likelihood of frustration but can limit personal growth and achievement, making it crucial to balance realistic goal-setting with temperament traits such as emotional stability and optimism. Temperament influences how individuals process disappointment and develop resilience, with those exhibiting adaptive coping mechanisms and positive affect typically handling unmet expectations more constructively.
Finding the Balance: Healthy Expectation Setting
Finding the balance between high expectations, low expectations, and temperament is essential for healthy expectation setting, fostering motivation without causing undue stress. High expectations can drive achievement but may overwhelm individuals with sensitive temperaments, while low expectations might limit potential and growth. Tailoring expectations to align with temperament promotes resilience, adaptability, and sustained personal development.
Infographic: High Expectations vs Low Expectations
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com