Idealism in relationships emphasizes perfect harmony and emotional connection, while realism prioritizes practical compatibility and realistic expectations. Discover how balancing these perspectives can improve your relationship in this article.
Table of Comparison
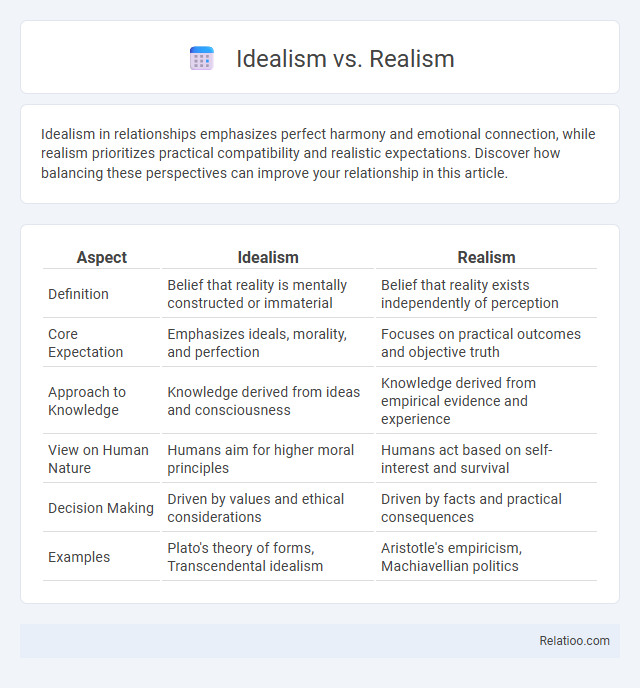
| Aspect | Idealism | Realism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that reality is mentally constructed or immaterial | Belief that reality exists independently of perception |
| Core Expectation | Emphasizes ideals, morality, and perfection | Focuses on practical outcomes and objective truth |
| Approach to Knowledge | Knowledge derived from ideas and consciousness | Knowledge derived from empirical evidence and experience |
| View on Human Nature | Humans aim for higher moral principles | Humans act based on self-interest and survival |
| Decision Making | Driven by values and ethical considerations | Driven by facts and practical consequences |
| Examples | Plato's theory of forms, Transcendental idealism | Aristotle's empiricism, Machiavellian politics |
Introduction to Idealism and Realism
Idealism emphasizes the mind's role in shaping reality, asserting that ideas or consciousness form the foundation of existence. Realism, in contrast, maintains that an external reality exists independently of our perceptions or beliefs. Your understanding of these philosophies influences how you interpret knowledge, truth, and the nature of the world around you.
Historical Origins of Idealism and Realism
Idealism originated in ancient Greek philosophy, notably in the works of Plato, who posited that reality is fundamentally shaped by ideas and forms rather than material objects. Realism emerged as a response to idealism, asserting that objects exist independently of perception, with Aristotle emphasizing empirical observation and the physical world's primacy. The historical development of idealism and realism reflects a fundamental philosophical debate about the nature of reality and knowledge, influencing metaphysics, epistemology, and science throughout history.
Key Philosophical Differences
Idealism emphasizes that reality is fundamentally shaped by the mind and ideas, asserting that your perceptions and consciousness create the essence of existence. Realism, in contrast, maintains that reality exists independently of your thoughts or beliefs, rooted in an objective world accessible through sensory experience. Unlike Idealism, Realism relies on empirical evidence and observation to understand the external world, highlighting a key philosophical difference in how knowledge and existence are perceived.
Core Principles of Idealism
Idealism centers on the belief that reality is fundamentally shaped by ideas, consciousness, or perceptions rather than material objects, emphasizing the primacy of the mind. Core principles include the view that the external world depends on and is inseparable from the mind's activity, asserting that knowledge and reality are intertwined through mental constructs. Understanding Idealism helps you grasp how perceptions influence reality, contrasting with Realism's focus on an objective world independent of individual thoughts.
Core Principles of Realism
Realism centers on the core principles of state sovereignty, national interest, and power politics, asserting that states act primarily to ensure their survival in an anarchic international system. It emphasizes the pragmatic and often competitive nature of international relations, where security and military capabilities dominate decision-making. Your understanding of global politics deepens by recognizing that Realism views conflict as inevitable and prioritizes practical strategies over ideological goals.
Idealism in Modern Thought
Idealism in modern thought emphasizes the primacy of ideas, consciousness, and perception in shaping reality, contrasting sharply with realism's focus on an objective world independent of human experience. Philosophers like Hegel and Berkeley advanced idealism by arguing that reality is mentally constructed or fundamentally shaped by our minds. Contemporary idealist theories influence fields such as epistemology, metaphysics, and cognitive science, underscoring the role of subjective experience in understanding existence.
Realism in Contemporary Context
Realism in the contemporary context emphasizes pragmatic approaches to international relations, prioritizing state sovereignty, power dynamics, and national interest over ideological pursuits. Your understanding of global politics benefits from recognizing how Realism addresses security challenges, economic competition, and diplomatic negotiations amid evolving geopolitical landscapes. This perspective contrasts with Idealism's focus on moral values and international cooperation, highlighting the enduring relevance of Realism in shaping policy decisions and strategic interactions today.
Idealism vs Realism in Politics
Idealism in politics emphasizes the pursuit of ethical principles, international cooperation, and the belief that states should act based on moral values to achieve global peace and justice. Realism focuses on power dynamics, national interest, and the competitive nature of international relations, advocating for pragmatic policies grounded in security and survival. Understanding Your stance between idealism and realism can shape foreign policy strategies, influencing diplomatic interactions and conflict resolutions.
Idealism and Realism in Art and Literature
Idealism in art and literature emphasizes the portrayal of subjects as they could be, highlighting perfection, beauty, and moral values to inspire and elevate the human spirit. Realism, conversely, seeks to depict everyday life and ordinary people with accuracy and truthfulness, focusing on social conditions and objective reality without embellishment. The tension between idealism's aspiration for transcendence and realism's commitment to authenticity shapes much of the artistic and literary discourse, influencing narratives, character development, and thematic exploration.
Conclusion: Balancing Idealism and Realism
Balancing idealism and realism requires integrating visionary goals with practical constraints to create achievable outcomes. Embracing idealism inspires innovation and progress, while realism ensures decisions are grounded in current resources and limitations. This equilibrium fosters sustainable development and effective problem-solving across personal, social, and political domains.
Infographic: Idealism vs Realism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com