Baby Boomers prioritize emotional connection and active communication in relationships, while the Silent Generation values stability and traditional roles. Discover how these differing expectations shape intergenerational dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
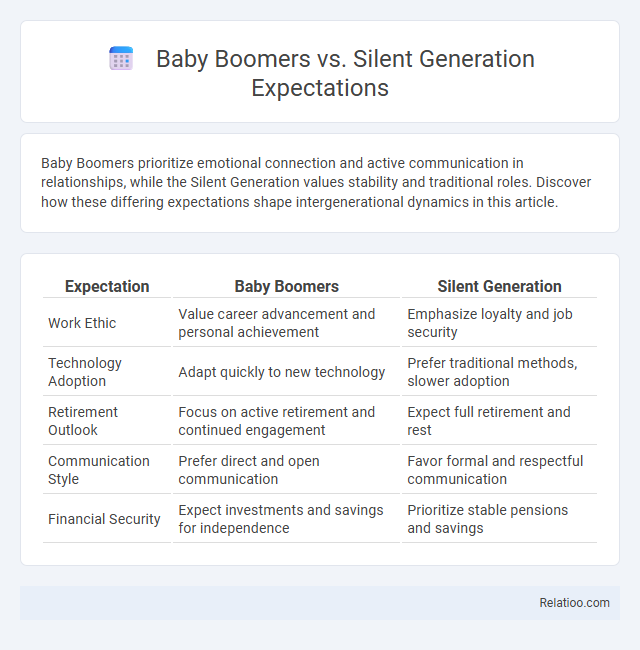
| Expectation | Baby Boomers | Silent Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Work Ethic | Value career advancement and personal achievement | Emphasize loyalty and job security |
| Technology Adoption | Adapt quickly to new technology | Prefer traditional methods, slower adoption |
| Retirement Outlook | Focus on active retirement and continued engagement | Expect full retirement and rest |
| Communication Style | Prefer direct and open communication | Favor formal and respectful communication |
| Financial Security | Expect investments and savings for independence | Prioritize stable pensions and savings |
Defining Baby Boomers and the Silent Generation
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, are characterized by their emphasis on work ethic, economic prosperity, and social activism, whereas the Silent Generation, born between 1928 and 1945, values discipline, loyalty, and conformity shaped by wartime and post-war experiences. These generational differences influence expectations in the workplace, communication styles, and attitudes toward technology and social change. Understanding these core traits is essential for addressing the diverse motivations and behaviors within multigenerational settings.
Historical Context: Shaping Their Worldviews
Baby Boomers, raised during post-World War II economic expansion, prioritize innovation and social change, reflecting the optimistic climate of their youth. The Silent Generation, shaped by the Great Depression and World War II, values stability, discipline, and conformity due to the hardships experienced during their formative years. Your understanding of these historical contexts helps explain the generational differences in expectations regarding work, family, and societal roles.
Core Values and Beliefs Compared
Baby Boomers prioritize achievement, optimism, and individualism, while the Silent Generation values discipline, conformity, and loyalty, reflecting core generational differences in work ethic and social responsibility. Your understanding of these distinctions can enhance communication and collaboration across age groups, as Boomers seek recognition and innovation, whereas the Silent Generation emphasizes tradition and stability. These contrasting values shape expectations in both personal and professional settings, influencing decision-making and relationship dynamics.
Work Ethic and Career Expectations
Baby Boomers prioritize strong work ethic, valuing loyalty, long hours, and job stability, whereas the Silent Generation emphasizes discipline, respect for authority, and a steady career path. Your understanding of generational differences can enhance workplace harmony by adapting communication and motivation strategies to meet each group's career expectations. Companies that recognize these distinctions foster productivity and retain talent across Baby Boomer and Silent Generation employees.
Attitudes Toward Family and Relationships
Baby Boomers prioritize close family bonds and active parenting roles, valuing emotional support and frequent communication with extended family. The Silent Generation tends to emphasize loyalty, stability, and traditional roles within the family, often maintaining more formal boundaries. Generational differences reveal Baby Boomers seek more egalitarian partnerships, while the Silent Generation upholds conventional family expectations shaped by historical socioeconomic conditions.
Technology Adoption and Communication Styles
Baby Boomers tend to adopt technology more gradually, valuing face-to-face and telephone communication, whereas the Silent Generation prefers traditional methods like letters and in-person interactions, reflecting their cautious approach to digital tools. Your communication strategies should consider these generational differences, leveraging email and phone calls for Boomers while respecting the Silent Generation's preference for slower, more personal contact. Understanding these expectations improves engagement by aligning technology use and communication styles with each generation's comfort level and habits.
Financial Priorities and Retirement Planning
Baby Boomers prioritize wealth accumulation and early retirement planning, valuing investments in real estate and stock markets to secure financial independence. The Silent Generation emphasizes preserving capital and steady income streams, often relying on pensions and conservative savings strategies. Understanding these generational financial priorities helps you tailor retirement planning to meet diverse expectations and optimize long-term financial security.
Health, Wellness, and Longevity Perspectives
Baby Boomers prioritize active aging, holistic wellness, and longevity through fitness, nutrition, and preventive healthcare, reflecting their desire to maintain independence. The Silent Generation places greater emphasis on traditional healthcare, medication management, and conservative approaches to health, shaped by their experiences with limited medical advancements. Your wellness strategies should consider these generational differences to effectively address their unique health expectations and lifestyle preferences.
Social Change and Political Involvement
Baby Boomers, shaped by the civil rights movement and Vietnam War protests, expect active social change and prioritize political involvement as a means to influence policy and societal norms. The Silent Generation, raised during the Great Depression and World War II, tends to value stability and incremental change, often participating in politics through traditional voting and community involvement. Your understanding of these generational differences highlights how shifts in social values and political activism reflect broader historical contexts and impact civic engagement today.
Intergenerational Influence and Legacy
Baby Boomers prioritize leaving a legacy of social change and career achievements, while the Silent Generation values stability, discipline, and traditional family roles, shaping distinct expectations for future generations. Your understanding of these generational differences highlights how intergenerational influence shapes attitudes toward work ethic, retirement, and societal contributions. Recognizing these contrasts fosters deeper appreciation of the evolving definitions of success and legacy across age groups.
Infographic: Baby Boomers vs Silent Generation expectations
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com