Achieved status is a social position earned through personal effort, skills, and accomplishments, while ascribed status is assigned at birth based on factors like family background, ethnicity, or gender. Discover more insights about how these social statuses influence relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
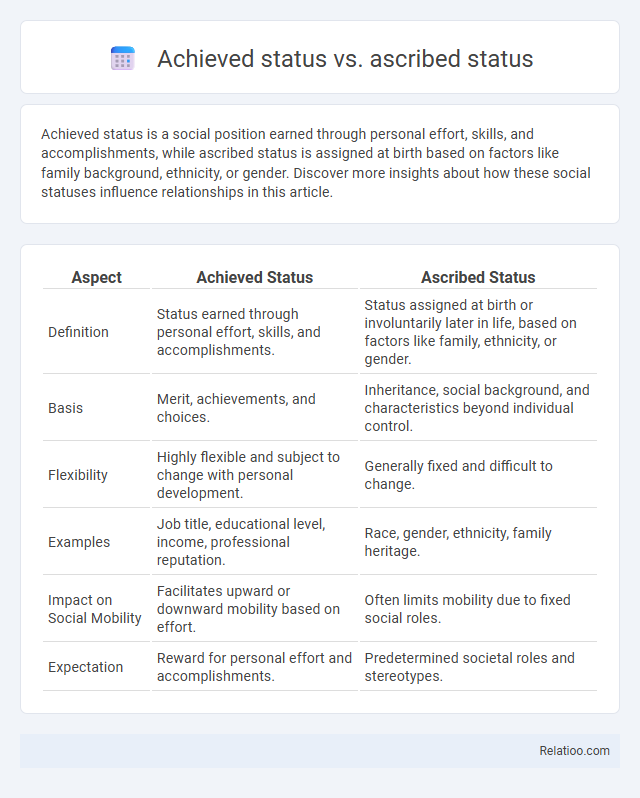
| Aspect | Achieved Status | Ascribed Status |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Status earned through personal effort, skills, and accomplishments. | Status assigned at birth or involuntarily later in life, based on factors like family, ethnicity, or gender. |
| Basis | Merit, achievements, and choices. | Inheritance, social background, and characteristics beyond individual control. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and subject to change with personal development. | Generally fixed and difficult to change. |
| Examples | Job title, educational level, income, professional reputation. | Race, gender, ethnicity, family heritage. |
| Impact on Social Mobility | Facilitates upward or downward mobility based on effort. | Often limits mobility due to fixed social roles. |
| Expectation | Reward for personal effort and accomplishments. | Predetermined societal roles and stereotypes. |
Introduction to Social Status
Social status refers to the social position an individual holds within a group or society, influencing their roles and interactions. Achieved status is earned through personal effort, skills, or accomplishments, such as becoming a doctor or artist. Ascribed status is assigned at birth or involuntarily, including traits like race, gender, or family heritage, shaping opportunities and social expectations.
Defining Ascribed Status
Ascribed status refers to the social position assigned to individuals at birth based on characteristics such as race, ethnicity, gender, or family heritage, which they have no control over. Achieved status, in contrast, is earned through personal effort, skills, or accomplishments, like becoming a doctor or an athlete. Status broadly denotes a person's relative social position within a society, influenced by both ascribed and achieved factors.
Defining Achieved Status
Achieved status refers to the social position a person attains through personal effort, skills, or accomplishments, such as educational attainment or career success. It contrasts with ascribed status, which is assigned at birth based on factors like race, gender, or family background. Understanding achieved status highlights the role of individual agency in shaping social identity, whereas status overall encompasses both achieved and ascribed elements within social hierarchies.
Key Differences Between Achieved and Ascribed Status
Achieved status is earned through individual effort, skills, and accomplishments, reflecting a person's actions and choices, while ascribed status is assigned at birth or involuntarily based on attributes like race, gender, or family background. The key difference lies in control and mobility: achieved status allows social mobility and change over time, whereas ascribed status is fixed and often shapes one's opportunities and societal roles from inception. Understanding this distinction highlights how social stratification and identity formation operate within societies.
Examples of Ascribed Status in Society
Ascribed status refers to social positions assigned at birth or involuntarily acquired, such as race, ethnicity, gender, or family heritage, which shape one's identity and opportunities without personal choice. Examples of ascribed status in society include being born into royalty, inheriting a caste in India, or belonging to a particular racial group. Understanding your ascribed status helps clarify how societal structures influence your social interactions and life chances independently of your achievements or actions.
Examples of Achieved Status in Society
Achieved status refers to social positions earned through individual effort, skills, or accomplishments, such as becoming a doctor, entrepreneur, or Olympic athlete. These statuses contrast with ascribed status, which is assigned at birth, like race, gender, or royal lineage. Examples of achieved status highlight personal agency and mobility within societal structures, demonstrating how education, career success, and talent influence social standing.
The Role of Culture in Status Assignment
Achieved status refers to social positions gained through individual effort, while ascribed status is assigned by cultural factors such as birth, ethnicity, or gender. Your understanding of status varies because cultures define the importance and rigidity of these statuses differently, influencing social mobility and identity. Recognizing how cultural values shape the assignment of achieved and ascribed status highlights the dynamic nature of social hierarchies.
Impacts of Status on Social Mobility
Achieved status, earned through individual effort and skills, directly influences social mobility by allowing individuals to improve their social position based on merit. Ascribed status, determined by birth or inherent characteristics such as race, gender, or family background, often limits social mobility by imposing rigid social barriers. Overall, both achieved and ascribed statuses shape access to resources, opportunities, and social networks, critically impacting the potential for upward or downward social mobility.
Controversies and Debates Surrounding Status
Achieved status refers to positions gained through personal effort, while ascribed status is assigned based on factors like birth or ethnicity, and status encompasses the broader social standing within a hierarchy. Controversies often center on the fairness and rigidity of ascribed status systems, which can perpetuate inequality and limit social mobility. Your understanding of these debates highlights the complex dynamics of power, privilege, and opportunity embedded in social structures.
Conclusion: The Future of Status in Society
The future of status in society increasingly blends achieved status, based on personal accomplishments, with traditional ascribed status linked to birth and social identity. Technological advancements and social mobility expand opportunities for individuals to redefine their social positions beyond inherited characteristics. As societies evolve, understanding the dynamic interplay between achieved and ascribed status remains crucial for addressing inequality and promoting social inclusion.
Infographic: Achieved status vs Ascribed status
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com