Emotional numbing is a psychological response characterized by a reduced ability to feel emotions, often linked to trauma, whereas alexithymia is a personality construct involving difficulty in identifying and describing one's own emotions. Understanding these distinct emotional challenges can improve relationship dynamics and communication; learn more in this article.
Table of Comparison
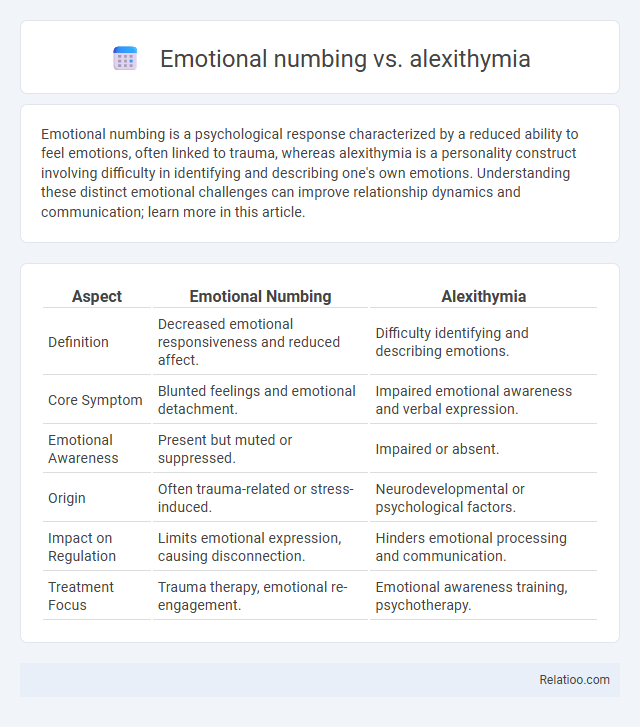
| Aspect | Emotional Numbing | Alexithymia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decreased emotional responsiveness and reduced affect. | Difficulty identifying and describing emotions. |
| Core Symptom | Blunted feelings and emotional detachment. | Impaired emotional awareness and verbal expression. |
| Emotional Awareness | Present but muted or suppressed. | Impaired or absent. |
| Origin | Often trauma-related or stress-induced. | Neurodevelopmental or psychological factors. |
| Impact on Regulation | Limits emotional expression, causing disconnection. | Hinders emotional processing and communication. |
| Treatment Focus | Trauma therapy, emotional re-engagement. | Emotional awareness training, psychotherapy. |
Understanding Emotional Numbing: Definition and Causes
Emotional numbing refers to a reduced ability to experience emotions, often resulting from trauma or chronic stress, which can impair your emotional responsiveness and interpersonal relationships. Unlike alexithymia, characterized by difficulty identifying and describing emotions, emotional numbing primarily involves a blunted emotional experience rather than a cognitive deficit. Understanding emotional numbing involves recognizing its causes, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or depression, which disrupt normal emotional regulation and lead to a protective shutdown of feelings.
What Is Alexithymia? Key Features and Symptoms
Alexithymia is a psychological condition characterized by difficulty in identifying and describing one's emotions, leading to challenges in emotional awareness and self-regulation. Key features include limited emotional insight, reduced ability to distinguish between feelings and bodily sensations, and a tendency toward externally oriented thinking. Unlike emotional numbing, which involves a diminished emotional response often linked to trauma, alexithymia is a chronic trait affecting emotional processing and interpersonal relationships.
Emotional Numbing vs Alexithymia: Core Differences
Emotional numbing involves a diminished ability to feel emotions often linked to trauma or depression, while alexithymia is characterized by difficulty identifying and describing one's emotions, stemming from neurological or psychological factors. Emotional numbing primarily affects the intensity of emotional experience, whereas alexithymia disrupts emotional awareness and verbalization. These core differences impact diagnosis and treatment approaches, with emotional numbing responding better to trauma-focused therapies and alexithymia requiring interventions targeting emotional recognition skills.
Common Triggers of Emotional Numbing
Emotional numbing often arises from trauma, chronic stress, or overwhelming grief, causing a diminished ability to feel emotions. Alexithymia differs as it involves difficulty identifying and describing emotions rather than an absence of feeling. Your awareness of common triggers like PTSD, anxiety, or prolonged emotional distress can help differentiate emotional numbing from alexithymia and guide effective coping strategies.
Root Causes of Alexithymia: Biological and Psychological Factors
Alexithymia stems from a combination of biological factors such as genetic predispositions and neurological differences in brain regions like the anterior cingulate cortex and insula, which affect emotional processing. Psychological factors include early childhood trauma, attachment issues, and chronic stress that impair emotional awareness and expression. In contrast, emotional numbing is often a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder or depression, characterized by reduced emotional responsiveness rather than the fundamental inability to identify or describe emotions seen in alexithymia.
Emotional Expression: How Each Condition Impacts Communication
Emotional numbing reduces the ability to express feelings openly, leading to muted or flat emotional responses that hinder effective communication. Alexithymia specifically impairs the capacity to identify and describe emotions, resulting in vague or limited emotional expression that complicates interpersonal understanding. In contrast, emotional suppression involves consciously inhibiting emotional displays, which can create disconnects between internal feelings and outward communication, ultimately affecting relational dynamics.
Mental Health Implications of Emotional Numbing and Alexithymia
Emotional numbing and alexithymia both involve difficulties in experiencing or expressing emotions, but emotional numbing primarily reflects a reduced capacity to feel emotions often linked to trauma or depression, while alexithymia is characterized by a profound difficulty in identifying and describing feelings. These conditions can severely impact your mental health, leading to challenges in emotional regulation, impaired interpersonal relationships, and increased risk for anxiety and depressive disorders. Understanding the distinct mechanisms of emotional numbing and alexithymia is crucial for effective intervention and fostering emotional awareness and resilience.
Diagnosis and Assessment: Identifying Each Condition
Diagnosing emotional numbing, alexithymia, and typical emotional numbness requires specific assessment tools and clinical interviews to differentiate the conditions accurately. Emotional numbing often appears in PTSD and is evaluated through symptom checklists like the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS), while alexithymia is identified using self-report measures such as the Toronto Alexithymia Scale (TAS-20) focusing on difficulties in identifying and describing emotions. Your healthcare provider may conduct a thorough psychological evaluation to discern these conditions by examining emotional awareness, response patterns, and cognitive processing during the diagnostic process.
Treatment Approaches: Emotional Numbing vs Alexithymia
Treatment approaches for emotional numbing commonly include trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy to help patients reconnect with suppressed emotions. In contrast, alexithymia treatment often involves mindfulness-based therapy and emotion-focused interventions designed to improve emotional awareness and expression. Both conditions benefit from psychotherapeutic support, but targeting emotional identification is particularly crucial for alexithymia, whereas emotional numbing treatments emphasize processing trauma-related affective shutdown.
Coping Strategies and Support for Affected Individuals
Emotional numbing, alexithymia, and emotional disengagement require distinct coping strategies tailored to your specific emotional processing challenges. Techniques like mindfulness meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and expressive arts therapy can help improve emotional awareness and regulation for those experiencing alexithymia or emotional numbing. Support groups, consistent professional counseling, and developing strong social connections enhance resilience and provide necessary emotional validation for affected individuals.
Infographic: Emotional numbing vs alexithymia
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com