Emotional numbing reduces the ability to feel emotions, leading to disconnection in relationships, while dissociation involves detachment from reality, causing gaps in memory and awareness. Explore this article to understand how both affect relational health and ways to address them.
Table of Comparison
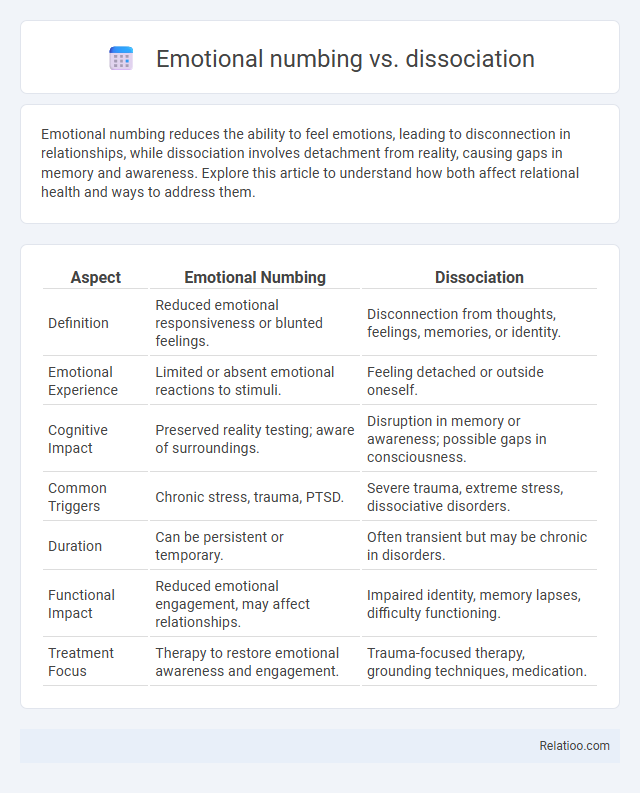
| Aspect | Emotional Numbing | Dissociation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduced emotional responsiveness or blunted feelings. | Disconnection from thoughts, feelings, memories, or identity. |
| Emotional Experience | Limited or absent emotional reactions to stimuli. | Feeling detached or outside oneself. |
| Cognitive Impact | Preserved reality testing; aware of surroundings. | Disruption in memory or awareness; possible gaps in consciousness. |
| Common Triggers | Chronic stress, trauma, PTSD. | Severe trauma, extreme stress, dissociative disorders. |
| Duration | Can be persistent or temporary. | Often transient but may be chronic in disorders. |
| Functional Impact | Reduced emotional engagement, may affect relationships. | Impaired identity, memory lapses, difficulty functioning. |
| Treatment Focus | Therapy to restore emotional awareness and engagement. | Trauma-focused therapy, grounding techniques, medication. |
Understanding Emotional Numbing
Emotional numbing involves a diminished ability to experience emotions, often as a protective response to trauma, whereas dissociation refers to a disconnection from reality, thoughts, or identity as a coping mechanism. Understanding emotional numbing requires recognizing its impact on emotional processing and interpersonal relationships, highlighting symptoms like flat affect and reduced emotional responsiveness. Differentiating emotional numbing from dissociation is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment in conditions such as PTSD and depression.
Defining Dissociation
Dissociation involves a disconnection between thoughts, identity, consciousness, and memory, often serving as a coping mechanism during traumatic experiences. Emotional numbing specifically refers to a reduced ability to experience emotions, resulting in a sense of detachment or flat affect. While emotional numbing is a symptom of dissociation, dissociation encompasses a broader range of experiences including depersonalization, derealization, and identity fragmentation.
Key Differences Between Emotional Numbing and Dissociation
Emotional numbing refers to the reduced ability to feel emotions, often resulting from trauma or depression, while dissociation involves a disconnection from reality or one's sense of self, such as feeling detached from your body or surroundings. Key differences include that emotional numbing primarily affects emotional experience, whereas dissociation affects perception and consciousness. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize whether you're experiencing emotional dullness or a more profound detachment requiring different therapeutic approaches.
Causes and Triggers of Emotional Numbing
Emotional numbing primarily results from prolonged exposure to intense stress or trauma, such as PTSD, where the brain dampens emotional responses to protect against overwhelming feelings. Triggers often include reminders of the traumatic event, chronic stress, or ongoing emotional pain, leading to a reduced ability to experience positive or negative emotions. Unlike dissociation, which involves a detachment from reality or self, emotional numbing specifically refers to a blunted emotional state affecting affective experience.
Causes and Triggers of Dissociation
Dissociation often arises as a psychological response to trauma, extreme stress, or overwhelming emotions, causing a disconnection from reality, memory, or identity. Key triggers include intense fear, abuse, sudden loss, or prolonged exposure to distressing situations, which compel the brain to protect itself by detaching from the present moment. Understanding your triggers can help identify whether you are experiencing dissociation, emotional numbing, or other coping mechanisms that affect emotional processing.
How Emotional Numbing Manifests
Emotional numbing often manifests as a reduced ability to experience feelings, leading to a sense of detachment from your emotions and surroundings. This state differs from dissociation, which involves a disconnection from reality or your sense of self, but both can co-occur in response to trauma or stress. Recognizing how emotional numbing impacts your daily life helps in distinguishing it from dissociation and seeking appropriate therapeutic support.
Common Symptoms of Dissociation
Common symptoms of dissociation include memory loss, a sense of detachment from your body or surroundings, and a feeling of unreality, often described as "spacing out" or "losing time." Emotional numbing, by contrast, involves a reduced ability to experience emotions, leaving you feeling detached or indifferent to events that would typically provoke a response. While emotional numbing specifically targets your emotional reactions, dissociation encompasses a broader disruption in consciousness, identity, or perception.
Emotional Numbing vs. Dissociation: Effects on Daily Life
Emotional numbing reduces your ability to feel emotions, leading to a diminished response to both positive and negative experiences, which can impair relationships and decrease life satisfaction. Dissociation involves a detachment from reality or self, causing disruptions in memory, perception, and identity that can interfere with daily functioning and increase confusion or distress. Understanding these distinctions helps tailor therapeutic approaches, improving emotional regulation and enhancing your overall well-being.
Approaches for Coping and Healing
Approaches for coping with emotional numbing, dissociation, and emotional overwhelm often include mindfulness techniques, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and grounding exercises to help You reconnect with your feelings and the present moment. Professional support, such as trauma-focused therapy or EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing), can facilitate healing by processing underlying trauma and reducing symptoms. Developing self-compassion and practicing regular self-care also enhance emotional regulation and long-term recovery.
When to Seek Professional Help
Emotional numbing, dissociation, and emotional detachment each affect your ability to process feelings but differ in severity and triggers, with dissociation often involving a sense of disconnection from reality. When you notice persistent emotional numbness impacting daily function or dissociation causing memory lapses or identity confusion, it is crucial to seek professional help to prevent worsening mental health. Timely intervention by a mental health professional can offer targeted therapies that improve emotional regulation and overall well-being.
Infographic: Emotional numbing vs dissociation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com