Reappraisal involves changing how you think about a stressful situation in a relationship, while distraction shifts your attention away from the issue to reduce emotional intensity. Discover effective strategies to strengthen your relationship by exploring the benefits and applications of reappraisal and distraction in this article.
Table of Comparison
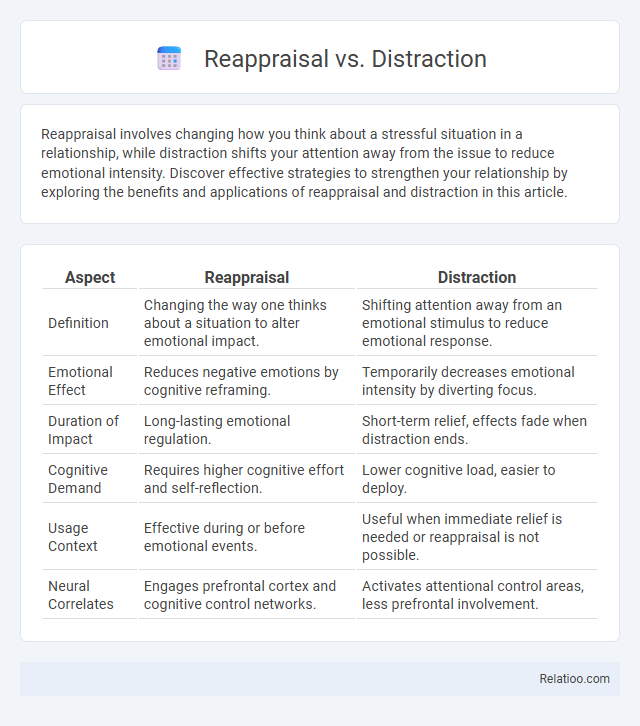
| Aspect | Reappraisal | Distraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changing the way one thinks about a situation to alter emotional impact. | Shifting attention away from an emotional stimulus to reduce emotional response. |
| Emotional Effect | Reduces negative emotions by cognitive reframing. | Temporarily decreases emotional intensity by diverting focus. |
| Duration of Impact | Long-lasting emotional regulation. | Short-term relief, effects fade when distraction ends. |
| Cognitive Demand | Requires higher cognitive effort and self-reflection. | Lower cognitive load, easier to deploy. |
| Usage Context | Effective during or before emotional events. | Useful when immediate relief is needed or reappraisal is not possible. |
| Neural Correlates | Engages prefrontal cortex and cognitive control networks. | Activates attentional control areas, less prefrontal involvement. |
Understanding Reappraisal and Distraction
Reappraisal involves changing the way one interprets a situation to alter its emotional impact, often leading to more adaptive emotional regulation and reduced stress responses. Distraction shifts attention away from emotionally distressing stimuli to neutral or positive activities, providing immediate but sometimes short-lived relief from negative emotions. Understanding the mechanisms and contexts where reappraisal or distraction is more effective helps optimize emotional management strategies for anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders.
Definitions and Psychological Foundations
Reappraisal involves cognitively reframing an emotional stimulus to alter its emotional impact, rooted in the cognitive change strategy of emotion regulation. Distraction shifts attention away from the emotional stimulus to neutral or unrelated thoughts, based on attentional deployment mechanisms within emotion regulation theory. Both strategies engage distinct neural circuits; reappraisal activates prefrontal regions linked to cognitive control, while distraction primarily reduces amygdala responses by diverting attention, highlighting their different psychological foundations.
Key Differences Between Reappraisal and Distraction
Reappraisal involves changing the way you think about a situation to alter its emotional impact, whereas distraction shifts your attention away from the emotional stimulus to reduce its intensity temporarily. Reappraisal leads to longer-lasting emotional regulation by modifying cognitive appraisals, while distraction offers short-term relief without addressing the underlying emotional cause. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the most effective strategy for managing your emotional responses.
Mechanisms of Emotion Regulation
Reappraisal involves cognitive change by altering the interpretation of a situation to reduce emotional impact, engaging prefrontal cortex regions that modulate amygdala activity. Distraction shifts attention away from emotional stimuli, activating dorsal attention networks to inhibit emotional processing and decrease negative affect. Comparing reappraisal and distraction reveals that reappraisal offers longer-lasting regulation by changing emotional meaning, whereas distraction provides immediate but temporary relief through attentional disengagement.
Benefits of Reappraisal Techniques
Reappraisal techniques involve changing the way you interpret a situation to alter its emotional impact, leading to long-term emotional regulation and improved psychological well-being. Unlike distraction, which temporarily shifts attention away from stressors, reappraisal fosters resilience by promoting adaptive thinking patterns and reducing negative emotional responses. Your consistent practice of cognitive reappraisal can enhance emotional control, reduce anxiety, and improve overall mental health outcomes.
Advantages of Distraction Strategies
Distraction strategies effectively reduce negative emotions by redirecting attention away from distressing stimuli, allowing for immediate mood regulation. They are advantageous in high-intensity situations where cognitive resources for reappraisal are limited or when quick emotional relief is necessary. Distraction also prevents rumination, which can exacerbate stress and anxiety, supporting better psychological resilience over time.
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
Reappraisal can be cognitively demanding, potentially leading to increased mental effort and reduced effectiveness under high stress or cognitive load. Distraction might provide immediate relief but often fails to address the root cause of emotional distress, risking avoidance and long-term issues. Combining reappraisal with distraction can sometimes dilute the benefits of each strategy, as frequent shifting between them may hinder the development of consistent emotional regulation skills.
When to Use Reappraisal vs Distraction
Reappraisal involves changing the way you interpret a situation to alter its emotional impact, making it effective for long-term emotional regulation during predictable or ongoing stressors. Distraction redirects your attention away from distressing stimuli, proving useful for immediate relief when emotions are overwhelming or situations are uncontrollable. Your choice between reappraisal and distraction depends on the context and timing: use reappraisal to build resilience over time, and distraction to manage acute emotional distress.
Research Insights and Scientific Evidence
Research insights reveal that reappraisal, an emotion regulation strategy involving cognitive change, effectively reduces negative emotions by altering the meaning of a situation, supported by neuroimaging studies showing prefrontal cortex activation. Distraction, which redirects attention away from emotional stimuli, provides immediate relief but may not foster long-term emotional adjustment, as evidenced by behavioral experiments. Your choice between reappraisal and distraction should consider these scientific findings, emphasizing reappraisal for sustained emotional resilience and distraction for short-term emotional control.
Practical Applications in Everyday Life
Reappraisal involves changing the way you think about a situation to alter its emotional impact, making it effective for managing stress and promoting emotional resilience in daily challenges. Distraction redirects attention away from negative stimuli, useful for temporarily reducing distress during overwhelming moments or acute anxiety episodes. Combining reappraisal and distraction can enhance emotional regulation by providing both immediate relief and long-term cognitive shifts, applicable in contexts like workplace stress, social interactions, and personal decision-making.
Infographic: Reappraisal vs Distraction
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com