Nationalist leaders often challenge imperial rulers by advocating for self-determination and national sovereignty against colonial or imperial control. Explore this article to understand the complex dynamics between nationalist movements and imperial authorities.
Table of Comparison
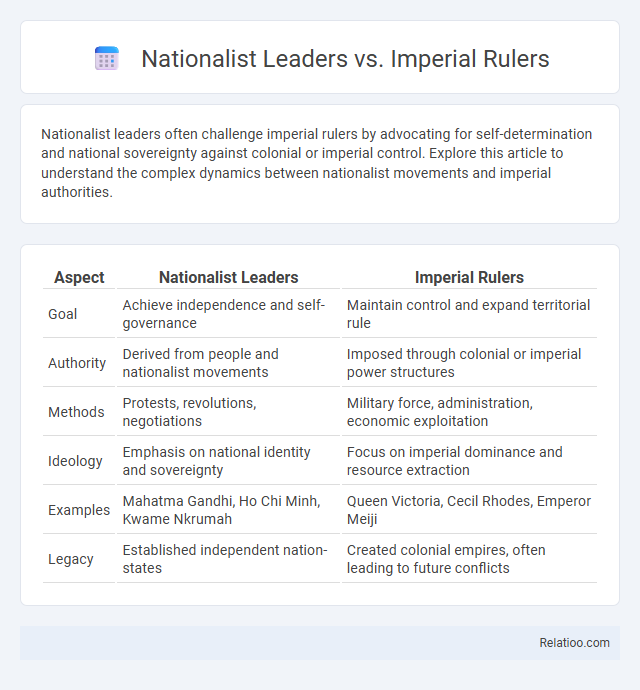
| Aspect | Nationalist Leaders | Imperial Rulers |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Achieve independence and self-governance | Maintain control and expand territorial rule |
| Authority | Derived from people and nationalist movements | Imposed through colonial or imperial power structures |
| Methods | Protests, revolutions, negotiations | Military force, administration, economic exploitation |
| Ideology | Emphasis on national identity and sovereignty | Focus on imperial dominance and resource extraction |
| Examples | Mahatma Gandhi, Ho Chi Minh, Kwame Nkrumah | Queen Victoria, Cecil Rhodes, Emperor Meiji |
| Legacy | Established independent nation-states | Created colonial empires, often leading to future conflicts |
Introduction: Defining Nationalist Leaders and Imperial Rulers
Nationalist leaders are figures who mobilize populations to assert their political sovereignty, cultural identity, and self-determination against foreign domination. Imperial rulers represent centralized authorities governing vast territories, often enforcing control through military power and administrative systems to maintain economic and political dominance. The independence struggle emerges as a dynamic conflict, where nationalist leaders challenge imperial rulers to dismantle colonial structures and achieve national liberation.
Historical Context: The Rise of Nationalism vs Imperialism
Nationalist leaders emerged as pivotal figures challenging imperial rulers during the 19th and 20th centuries, driven by growing demands for self-determination and cultural identity. Imperialism represented the expansionist policies of European powers seeking control over territories and resources, often suppressing indigenous populations and their aspirations for independence. Your understanding of this historical context is crucial for grasping how the struggle for independence was fueled by the clash between nationalist movements advocating autonomy and imperial regimes enforcing foreign dominance.
Ideological Foundations: Core Beliefs and Values
Nationalist leaders emphasized self-determination, cultural identity, and political sovereignty, fostering unity and resistance against imperial domination. Imperial rulers prioritized centralized authority, economic exploitation, and the spread of their political and cultural influence to maintain control over colonies. Your understanding of independence struggles deepens by recognizing these contrasting ideological foundations, highlighting the conflict between the desire for freedom and the imposition of imperial power.
Methods of Governance: Contrasting Approaches to Power
Nationalist leaders prioritized inclusive governance, mobilizing masses through grassroots activism and emphasizing self-rule to dismantle imperial control. Imperial rulers maintained centralized authority, often relying on military force, bureaucratic systems, and economic exploitation to sustain dominance over colonies. Your understanding of these contrasting approaches highlights how nationalist methods sought empowerment and local participation, whereas imperial powers enforced hierarchical, top-down control to suppress independence movements.
Economic Policies: Independence vs Exploitation
Nationalist leaders often championed economic policies that prioritized self-sufficiency, fair trade, and the redistribution of wealth to benefit local populations, contrasting sharply with imperial rulers who prioritized resource extraction and economic exploitation to enrich their own nations. Your understanding of these differing economic approaches highlights the struggle for independence not only as a political fight but also as a demand for economic justice and autonomy. The success of independence movements frequently depended on the ability to implement sustainable economic reforms that reversed the exploitative legacy imposed by imperial powers.
Cultural Identity: Preservation vs Assimilation
Nationalist leaders champion cultural identity preservation by promoting indigenous languages, traditions, and values as a foundation for self-determination, resisting imperial rulers' efforts to enforce assimilation through centralized education and legal systems. Imperial rulers often impose dominant cultural norms to unify diverse populations under a single political entity, aiming to weaken resistance and consolidate power. Your understanding of this dynamic highlights the crucial role cultural identity plays in independence struggles, where maintaining heritage becomes both a form of resistance and a path to national sovereignty.
Key Examples: Prominent Nationalist Leaders and Imperial Rulers
Prominent nationalist leaders such as Mahatma Gandhi in India, Kwame Nkrumah in Ghana, and Ho Chi Minh in Vietnam led powerful independence struggles against imperial rulers like the British Empire, French colonial authorities, and Japanese occupation forces. These leaders employed strategies ranging from nonviolent resistance to armed rebellion, capitalizing on widespread nationalist sentiments to challenge imperial dominance. The clash between nationalist movements and imperial rulers fundamentally reshaped global political boundaries throughout the 20th century, contributing to the decolonization of Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Impact on Society: Social Transformation and Resistance
Nationalist leaders catalyzed social transformation by mobilizing masses and promoting indigenous identities against imperial rulers who enforced hierarchical, exploitative structures to maintain control. Imperial rulers' policies often exacerbated social inequalities, prompting resistance movements that unified diverse social groups in pursuit of independence and social justice. The independence struggle reshaped societal norms, fostering political consciousness, empowerment, and the redefinition of national identity beyond colonial subjugation.
Legacy and Long-term Effects on Nations
Nationalist leaders profoundly shaped national identity and inspired mass movements that dismantled colonial empires, fostering political sovereignty and cultural revival. Imperial rulers imposed centralized control and economic exploitation, leaving legacies of infrastructural development alongside systemic inequalities and divided societies. The independence struggle's long-term effects include the emergence of self-governance, post-colonial state challenges, and enduring debates over national unity versus ethnic diversity.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned from the Nationalist and Imperial Struggle
The struggles between nationalist leaders and imperial rulers reveal that resilience and strategic unity are crucial for achieving independence and self-determination. Your understanding of these historical conflicts underscores the importance of mobilizing grassroots support and fostering a strong national identity to challenge colonial dominance effectively. Lessons learned emphasize that lasting sovereignty arises from the combined efforts of inspired leadership and collective action against imperial power.
Infographic: Nationalist Leaders vs Imperial Rulers
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com