Self-reliance fosters personal growth and emotional stability, while dependence can limit autonomy and create imbalance in relationships. Discover how balancing these dynamics strengthens connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
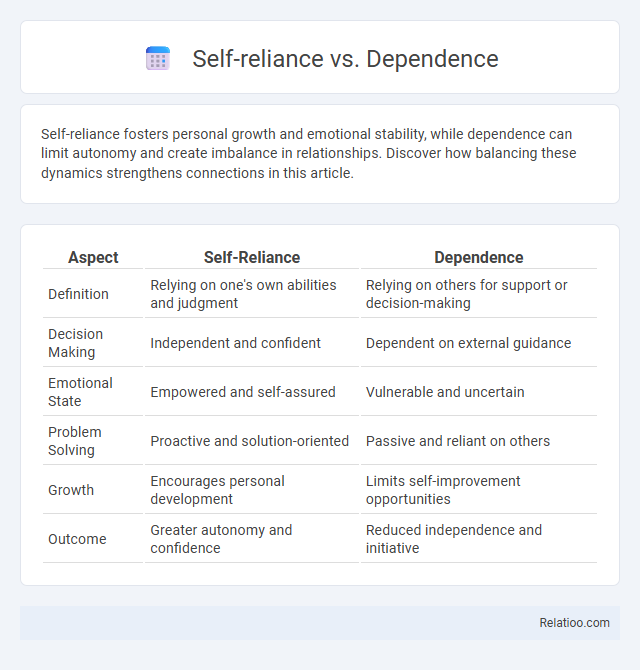
| Aspect | Self-Reliance | Dependence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relying on one's own abilities and judgment | Relying on others for support or decision-making |
| Decision Making | Independent and confident | Dependent on external guidance |
| Emotional State | Empowered and self-assured | Vulnerable and uncertain |
| Problem Solving | Proactive and solution-oriented | Passive and reliant on others |
| Growth | Encourages personal development | Limits self-improvement opportunities |
| Outcome | Greater autonomy and confidence | Reduced independence and initiative |
Understanding Self-Reliance: Meaning and Importance
Self-reliance is the ability to depend on one's own capabilities, judgment, and resources to solve problems and achieve goals, distinguishing it from dependence, which involves relying on others for support and decision-making. Embracing self-reliance fosters personal growth, resilience, and confidence, enabling individuals to navigate challenges independently and make informed choices. This quality is crucial for cultivating autonomy, enhancing problem-solving skills, and building inner strength in both personal and professional contexts.
Defining Dependence: Types and Causes
Dependence can be defined as reliance on others for support, resources, or decision-making, which manifests in various types such as emotional, financial, and social dependence. Emotional dependence often stems from low self-esteem or fear of abandonment, while financial dependence may arise from unemployment or lack of skills, limiting Your ability to achieve independence. Recognizing the causes of dependence, including past trauma, cultural norms, and lack of opportunities, is essential for fostering self-reliance and personal growth.
Historical Perspectives on Self-Reliance and Dependence
Historical perspectives on self-reliance highlight its roots in philosophies emphasizing individual autonomy and personal responsibility, evident in figures like Ralph Waldo Emerson who championed economic and social independence. Dependence, often viewed through the lens of colonial and post-colonial experiences, reflects systemic reliance on external powers or resources, shaping entire societies' development trajectories. Your understanding of these concepts deepens by recognizing how past contexts shape ongoing debates about balancing personal initiative with communal or external support systems.
Psychological Impacts of Self-Reliance
Self-reliance fosters psychological resilience by enhancing individuals' confidence in their problem-solving abilities and promoting emotional autonomy. Dependence on others can lead to increased vulnerability to stress and diminished self-esteem, as individuals may feel powerless without external support. Cultivating self-reliance strengthens mental health by encouraging proactive coping strategies and reducing anxiety linked to uncertainty and lack of control.
Emotional Consequences of Dependence
Dependence often leads to emotional consequences such as increased anxiety, diminished self-esteem, and a lack of personal autonomy, creating a climate of vulnerability and frustration. In contrast, self-reliance fosters emotional resilience, confidence, and a stronger sense of control over one's life and decisions. Balancing self-reliance and healthy interdependence enhances emotional well-being, promoting growth while maintaining supportive relationships.
Social Influences on Individual Autonomy
Social influences significantly shape individual autonomy by either fostering self-reliance or promoting dependence through cultural norms, peer pressure, and family expectations. Communities emphasizing collective goals often encourage dependence, while those valuing personal achievement tend to support self-reliance. Understanding the interplay of societal factors helps reveal how autonomy develops within different social contexts.
Benefits of Fostering Self-Reliance
Fostering self-reliance empowers you to develop critical problem-solving skills and boosts confidence, leading to greater personal and professional success. It reduces dependence on external help, promoting resilience and adaptability in challenging situations. Cultivating self-reliance enhances your ability to take initiative and make informed decisions, ultimately contributing to long-term independence and growth.
Risks and Challenges of Excessive Dependence
Excessive dependence on others can lead to diminished problem-solving skills and reduced personal growth, increasing vulnerability during critical situations. Your ability to adapt and make independent decisions may weaken, resulting in lowered confidence and self-esteem. Balancing self-reliance with constructive support systems is essential to mitigate risks such as burnout, manipulation, or loss of autonomy.
Balancing Self-Sufficiency and Support Systems
Balancing self-sufficiency and support systems involves fostering independence while recognizing the essential role of community and resources in personal growth. Self-reliance emphasizes individual capability and problem-solving, whereas dependence highlights the necessity of external assistance in complex situations. Achieving equilibrium between these aspects enhances resilience, promotes sustainable success, and leverages collaborative strengths without compromising autonomy.
Cultivating Healthy Interdependence
Cultivating healthy interdependence balances self-reliance and dependence by fostering mutual support while maintaining individual autonomy. Emphasizing collaborative problem-solving enhances resilience and personal growth without compromising independence. This approach promotes sustainable relationships where shared responsibilities strengthen community bonds and personal well-being.
Infographic: Self-reliance vs Dependence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com