Idealization in relationships often creates unrealistic expectations that contrast sharply with reality, leading to disappointment and conflict. Explore this dynamic further in this article to understand how balancing idealization and reality fosters healthier connections.
Table of Comparison
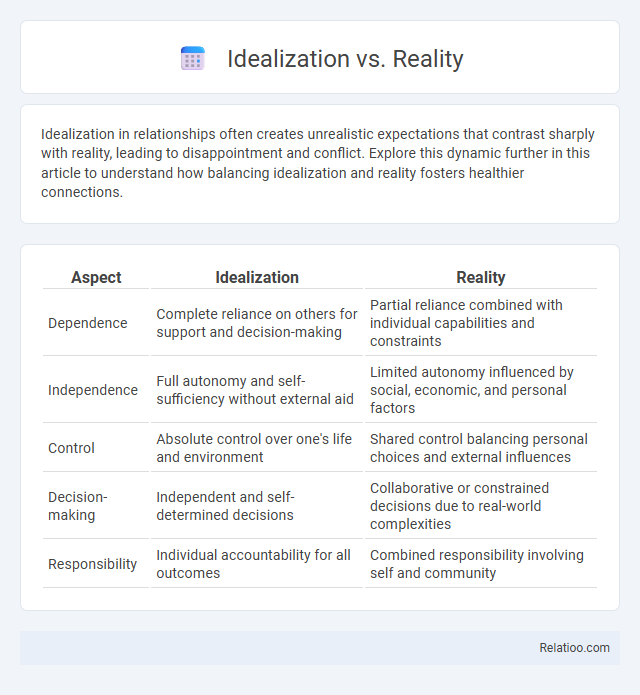
| Aspect | Idealization | Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Dependence | Complete reliance on others for support and decision-making | Partial reliance combined with individual capabilities and constraints |
| Independence | Full autonomy and self-sufficiency without external aid | Limited autonomy influenced by social, economic, and personal factors |
| Control | Absolute control over one's life and environment | Shared control balancing personal choices and external influences |
| Decision-making | Independent and self-determined decisions | Collaborative or constrained decisions due to real-world complexities |
| Responsibility | Individual accountability for all outcomes | Combined responsibility involving self and community |
Understanding Idealization: Definition and Origins
Idealization refers to the cognitive process where individuals attribute exaggeratedly positive qualities to a person, object, or situation, often overlooking flaws and complexities. Originating from psychological theories, idealization is closely linked to defense mechanisms that protect the ego from anxiety and disappointment by creating unrealistic expectations. Understanding your tendency to idealize can help balance perceptions and foster healthier, more grounded relationships and experiences.
The Psychology Behind Idealization
Idealization stems from the psychological tendency to enhance perceptions of people or situations, often linked to defense mechanisms that protect self-esteem and reduce anxiety. Reality confronts these idealized images with factual complexities, highlighting cognitive dissonance when expectations clash with actual experiences. Understanding the interplay between idealization and reality reveals how the mind negotiates emotional needs, balancing fantasy and truth to maintain psychological stability.
Reality: What Does It Truly Mean?
Reality embodies the state of things as they actually exist, grounded in empirical evidence and observable phenomena rather than subjective interpretations or idealized notions. It reflects the complexities, imperfections, and unpredictability inherent in life, contrasting sharply with the simplified or exaggerated expectations often portrayed in idealization. Understanding reality involves embracing uncertainty, acknowledging limitations, and responding adaptively to authentic circumstances rather than clinging to unrealistic ideals.
Idealization in Relationships: Expectations vs. Experience
Idealization in relationships often creates expectations that partner traits and behaviors will perfectly align with one's desires, leading to a constructed image rather than an authentic connection. This phenomenon can result in disappointment when reality reveals imperfections and complexities inconsistent with the idealized vision. Balancing expectations with genuine experiences fosters healthier, more resilient relationships by embracing authentic traits over idealized fantasies.
Media and Pop Culture: Shaping Our Ideals
Media and pop culture heavily influence your perception of reality by presenting idealized versions of beauty, success, and relationships that often contrast with real-life experiences. These idealizations create unrealistic standards that shape societal expectations and personal aspirations, making it challenging to distinguish between authentic experiences and media portrayals. Understanding this dynamic helps you critically evaluate the impact of media on your ideals and promotes a healthier, more balanced perspective.
The Impact of Idealization on Personal Growth
Idealization creates unrealistic standards that can hinder personal growth by fostering disappointment when reality falls short. Confronting reality allows individuals to develop resilience and self-awareness, essential components for meaningful progress. Balancing idealization with acceptance of real-world limitations promotes healthier goal-setting and emotional maturity.
Navigating Disappointment When Reality Falls Short
Idealization often sets unrealistically high expectations, creating a stark contrast when reality falls short and triggers disappointment. Navigating this emotional gap requires recognizing the natural limitations of idealized perceptions and fostering acceptance of imperfection. Developing strategies such as mindset reframing and emotional resilience helps balance idealism with practical reality, reducing dissatisfaction and promoting healthier expectations.
Strategies for Bridging the Gap Between Idealization and Reality
Effective strategies for bridging the gap between idealization and reality include setting realistic goals that align closely with practical constraints, implementing iterative feedback mechanisms to refine expectations, and fostering adaptive mindset shifts that accommodate unforeseen challenges. Emphasizing continuous learning and progress tracking enables individuals and organizations to recalibrate idealized visions based on empirical data and lived experiences. Leveraging collaborative problem-solving and transparent communication cultivates shared understanding that aligns aspirational ideals with achievable realities.
Embracing Imperfection: The Value of Being Realistic
Embracing imperfection allows individuals to bridge the gap between idealization and reality, fostering healthier expectations and emotional resilience. Studies in psychology highlight that accepting flaws promotes authentic self-esteem and reduces anxiety caused by unrealistic standards. A realistic approach encourages continuous growth and adaptability, affirming the value of genuine experiences over unattainable ideals.
Finding Balance: Healthy Perspectives on Idealization and Reality
Finding balance between idealization and reality is crucial for maintaining healthy perspectives in relationships, work, and personal goals. Recognizing the gap between expectations and actual experiences helps you avoid disappointment and fosters realistic optimism. Embracing imperfections while appreciating aspirations creates a sustainable mindset that supports growth and emotional well-being.
Infographic: Idealization vs Reality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com