Balancing obedience and autonomy is crucial for healthy relationships, as respect for individual freedom fosters trust and cooperation while maintaining mutual boundaries ensures harmony. Explore how navigating this dynamic influences relationship success in this article.
Table of Comparison
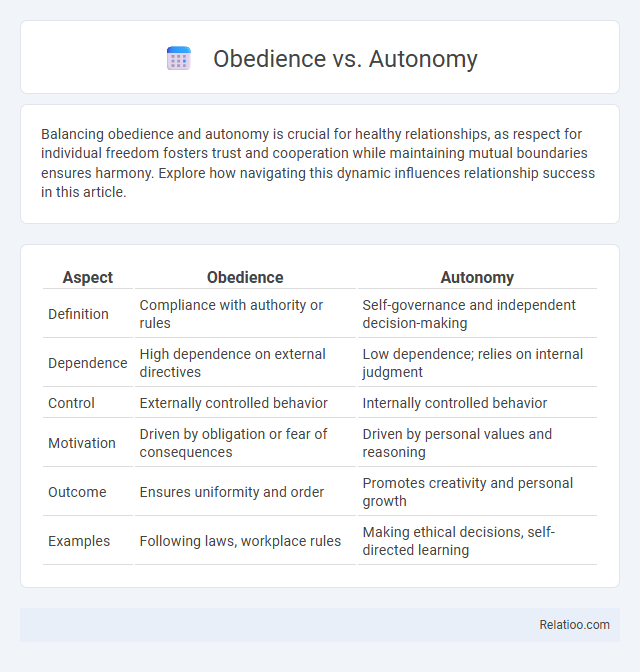
| Aspect | Obedience | Autonomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compliance with authority or rules | Self-governance and independent decision-making |
| Dependence | High dependence on external directives | Low dependence; relies on internal judgment |
| Control | Externally controlled behavior | Internally controlled behavior |
| Motivation | Driven by obligation or fear of consequences | Driven by personal values and reasoning |
| Outcome | Ensures uniformity and order | Promotes creativity and personal growth |
| Examples | Following laws, workplace rules | Making ethical decisions, self-directed learning |
Understanding Obedience and Autonomy
Understanding obedience involves recognizing its role as compliance with authority or rules, often motivated by social or hierarchical pressure, while autonomy emphasizes self-governance and independent decision-making based on personal values and reasoning. Obedience can lead to predictable social order but may suppress individual critical thinking, whereas autonomy fosters innovation and moral responsibility by enabling individuals to act according to their own principles. Balancing obedience and autonomy is crucial in contexts such as organizational behavior, education, and ethical decision-making to maintain both structure and personal freedom.
Historical Perspectives on Obedience
Historical perspectives on obedience reveal a complex interplay between authority and individual behavior, prominently studied in social psychology through Milgram's obedience experiments, which demonstrated that ordinary people could follow harmful orders under authoritative pressure. The rise of totalitarian regimes in the 20th century illustrated the consequences of extreme obedience, where conformity to authoritarian commands often suppressed personal autonomy and moral judgment. These insights highlight how societal structures and power dynamics significantly influence obedience, challenging the balance between individual autonomy and social conformity.
The Psychology Behind Autonomy
The psychology behind autonomy reveals that You thrive when self-determination satisfies intrinsic motivations, promoting personal growth and well-being. Autonomy supports cognitive flexibility and resilience by allowing individuals to make choices aligned with their values instead of merely following rules or social norms associated with obedience and conformity. Neuroscientific studies show that autonomy activates brain regions linked to reward and motivation, reinforcing behaviors that contribute to sustained psychological health.
Cultural Influences on Obedience and Autonomy
Cultural influences play a critical role in shaping obedience and autonomy, with collectivist societies often emphasizing obedience to authority and group norms, while individualistic cultures prioritize personal autonomy and self-expression. Your behavior may conform to societal expectations or assert independence based on cultural values that dictate acceptable levels of conformity and dissent. Understanding these cultural dynamics is essential for interpreting how obedience and autonomy manifest across different social contexts.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Obedience
Obedience fosters structure and efficiency in organizations by ensuring clear hierarchies and prompt compliance with rules, which boosts productivity and safety. However, excessive obedience may suppress creativity, limit critical thinking, and enable unethical behavior by discouraging individuals from questioning authority. Balancing obedience with autonomy is essential to maintain innovation while preserving order.
Advantages and Challenges of Autonomy
Autonomy offers individuals the advantage of enhanced creativity, decision-making power, and personal growth by allowing you to act independently without external control. However, challenges include the risk of isolation, increased responsibility for outcomes, and potential difficulty in coordinating with group expectations or societal norms. Balancing autonomy with social interdependence is crucial to avoid conflicts arising from excessive self-direction or resistance to obedience and conformity pressures.
Obedience vs Autonomy in Education
Obedience in education often emphasizes following rules and teacher instructions, promoting discipline but potentially limiting critical thinking skills. Autonomy encourages students to take responsibility for their learning, fostering creativity, problem-solving abilities, and intrinsic motivation. Balancing obedience with autonomy empowers your students to respect authority while developing independence crucial for lifelong learning.
Workplace Dynamics: Obedience or Autonomy?
Workplace dynamics hinge on balancing obedience and autonomy to enhance productivity and employee satisfaction. Obedience ensures adherence to organizational rules and hierarchical directives, fostering consistency and predictability in operations. Autonomy empowers employees with decision-making freedom, promoting creativity, innovation, and intrinsic motivation, which can lead to improved problem-solving and job engagement.
Navigating the Balance: Striking Harmony
Balancing obedience, autonomy, and conformity requires understanding the context in which each plays a crucial role, such as workplace dynamics or social settings. Your ability to discern when to follow rules, assert independence, or align with group norms determines effective decision-making and relationship management. Striking harmony among these concepts fosters personal growth while maintaining social cohesion and ethical standards.
Future Trends: Shifting Toward Autonomy
Future trends indicate a significant shift toward autonomy as individuals increasingly prioritize personal agency over blind obedience or conformity. Advancements in technology and AI are empowering Your decision-making capabilities, fostering environments where independent thought is valued. Organizations are adapting by promoting autonomy to enhance creativity, innovation, and employee satisfaction.
Infographic: Obedience vs Autonomy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com