Caretaking involves prioritizing others' needs, often leading to neglect of personal well-being, while self-care emphasizes maintaining one's physical and emotional health to sustain balanced relationships. Explore this article to understand how striking the right balance enhances both personal growth and relationship quality.
Table of Comparison
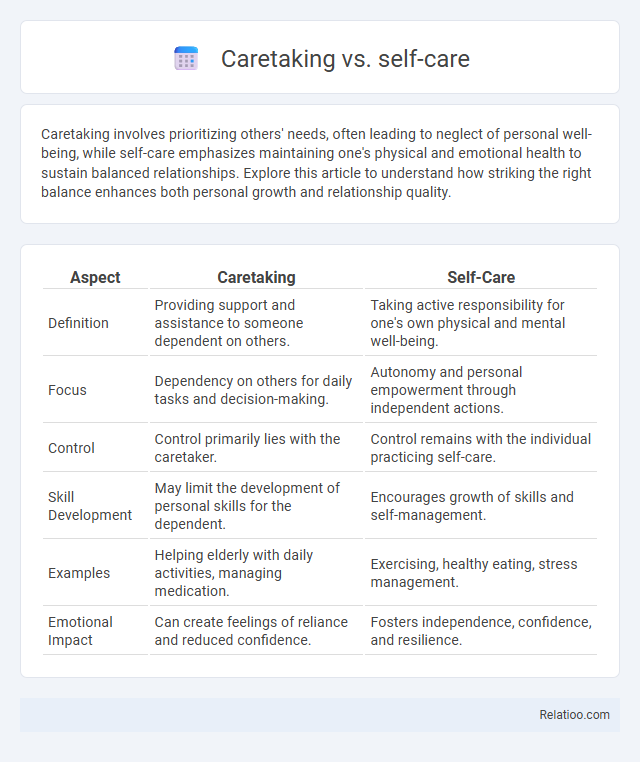
| Aspect | Caretaking | Self-Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing support and assistance to someone dependent on others. | Taking active responsibility for one's own physical and mental well-being. |
| Focus | Dependency on others for daily tasks and decision-making. | Autonomy and personal empowerment through independent actions. |
| Control | Control primarily lies with the caretaker. | Control remains with the individual practicing self-care. |
| Skill Development | May limit the development of personal skills for the dependent. | Encourages growth of skills and self-management. |
| Examples | Helping elderly with daily activities, managing medication. | Exercising, healthy eating, stress management. |
| Emotional Impact | Can create feelings of reliance and reduced confidence. | Fosters independence, confidence, and resilience. |
Understanding Caretaking and Self-Care
Understanding caretaking involves recognizing the responsibilities of providing support and assistance to others, often prioritizing their needs above your own. Self-care emphasizes nurturing your physical, emotional, and mental well-being through activities that restore and maintain balance. Balancing caretaking and self-care ensures sustainable support for others while preserving your health and resilience.
Key Differences Between Caretaking and Self-Care
Caretaking primarily involves providing support and assistance to others, often requiring significant time and emotional investment, while self-care focuses on activities that individuals undertake to maintain their own physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Key differences include the direction of care--caretaking targets others' needs, whereas self-care centers on personal health, recovery, and balance. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for maintaining healthy boundaries, preventing caregiver burnout, and promoting sustainable support systems.
The Psychology Behind Caretaking Behaviors
Caretaking behaviors often stem from deep psychological needs such as a desire for control, approval, or avoidance of personal vulnerability, contrasting with self-care which prioritizes your mental and emotional well-being. In psychology, caretaking can become compulsive, driven by underlying fears or trauma, leading to codependency and emotional exhaustion. Understanding the distinction between caregiving for others and practicing self-care is crucial for maintaining healthy boundaries and promoting psychological resilience.
Benefits of Practicing Self-Care
Practicing self-care enhances mental resilience, reduces stress, and improves overall well-being by prioritizing personal health and emotional balance. Unlike caretaking, which often involves prioritizing the needs of others, self-care ensures sustained energy and focus, enabling individuals to provide more effective support when needed. Regular self-care routines contribute to better physical health, increased productivity, and greater emotional stability.
Common Signs of Caretaking Patterns
Common signs of caretaking patterns include feeling responsible for others' emotions, neglecting your own needs, and constantly seeking approval through helping behaviors. You may experience burnout, resentment, or guilt when boundaries are crossed or self-care is ignored. Recognizing these patterns is essential to balancing caretaking with healthy self-care practices for emotional and mental well-being.
How Caretaking Impacts Mental Health
Caretaking often leads to increased stress and burnout, significantly impacting mental health by causing anxiety, depression, and emotional exhaustion. Unlike self-care, which promotes well-being and resilience, excessive caretaking can deplete personal resources and reduce one's ability to cope effectively. Understanding the balance between caregiving responsibilities and self-care practices is crucial to maintaining mental health and preventing caregiver fatigue.
Building Healthy Self-Care Routines
Building healthy self-care routines involves recognizing the difference between caretaking and self-care, where caretaking often means prioritizing others' needs at the expense of your own well-being. Effective self-care includes setting boundaries and dedicating time to activities that nurture your physical, emotional, and mental health. Your commitment to balanced routines empowers you to maintain resilience, reduce burnout, and promote overall happiness.
Balancing Support for Others with Self-Care
Balancing caretaking and self-care requires recognizing the delicate interplay between supporting others and maintaining personal well-being. Effective caretaking involves setting healthy boundaries to prevent emotional exhaustion while ensuring consistent support for those in need. Prioritizing self-care strategies such as mindfulness, adequate rest, and professional help enables sustained caregiving without compromising mental and physical health.
Overcoming Guilt When Prioritizing Self-Care
Overcoming guilt when prioritizing self-care involves recognizing that Your well-being is essential for effectively supporting others and maintaining healthy relationships. Caretaking often leads to neglecting personal needs, but embracing self-care replenishes your emotional and physical energy without selfishness. Balancing caretaking responsibilities with self-care practices helps reduce guilt and fosters sustainable caregiving dynamics.
Transforming Caretaking Habits for Personal Growth
Transforming caretaking habits requires recognizing the difference between caretaking, which often involves sacrificing your own needs to support others, and self-care, which prioritizes your well-being and personal growth. Shifting from caretaking to self-care empowers you to set healthy boundaries, fostering emotional resilience and enhancing your ability to nurture meaningful relationships. Prioritizing self-care promotes sustainable support for others while ensuring your mental and physical health flourish.
Infographic: Caretaking vs Self-care
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com