Conformity in relationships fosters harmony through shared values and behaviors, while independence encourages personal growth and individual expression within the partnership. Discover how balancing conformity and independence can strengthen your relationship in this article.
Table of Comparison
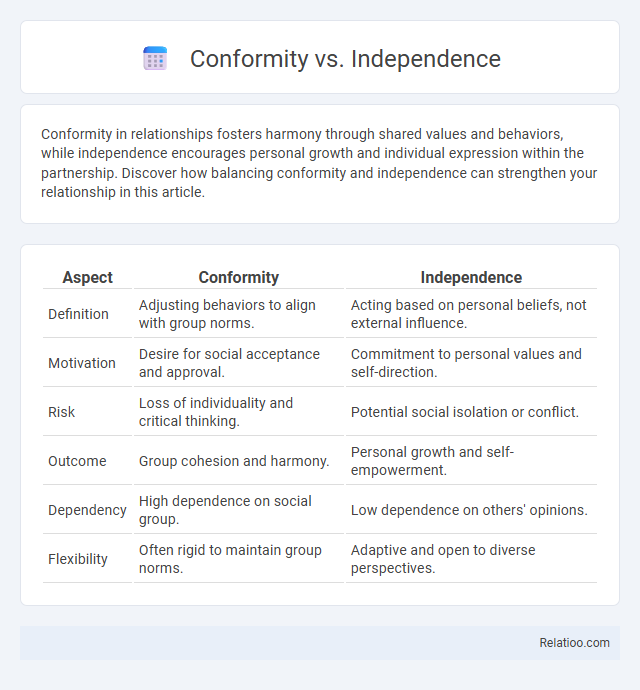
| Aspect | Conformity | Independence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusting behaviors to align with group norms. | Acting based on personal beliefs, not external influence. |
| Motivation | Desire for social acceptance and approval. | Commitment to personal values and self-direction. |
| Risk | Loss of individuality and critical thinking. | Potential social isolation or conflict. |
| Outcome | Group cohesion and harmony. | Personal growth and self-empowerment. |
| Dependency | High dependence on social group. | Low dependence on others' opinions. |
| Flexibility | Often rigid to maintain group norms. | Adaptive and open to diverse perspectives. |
Understanding Conformity: Definition and Types
Conformity involves adjusting behaviors or beliefs to align with group norms, driven by social influence and the desire for acceptance. Types of conformity include normative conformity, which occurs to gain social approval, and informational conformity, where individuals adopt behaviors based on evidence or information from others. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify how social pressures shape individual decision-making and group dynamics.
Defining Independence: What It Truly Means
Independence means making decisions based on your own values, beliefs, and critical thinking rather than blindly following societal norms or peer pressure. It involves self-reliance, personal responsibility, and the courage to stand alone when necessary. True independence empowers you to create authentic paths while respecting but not succumbing to conformity.
Historical Perspectives on Conformity and Independence
Historical perspectives on conformity highlight its roots in social cohesion and cultural stability, often seen in collective societies where adherence to norms ensured survival and order. Independence emerged as a hallmark of enlightenment thinking, emphasizing individual rights, personal freedom, and critical reasoning against traditional conformity. Throughout history, these opposing forces shaped social structures, with conformity often linked to authority and tradition, while independence inspired revolutions and social reforms.
Social Influences: Why People Conform
Social influences drive conformity as individuals adapt behaviors to align with group norms, seeking acceptance and avoiding social rejection. Psychological factors such as normative social influence compel conformity to gain approval, while informational social influence leads people to conform when uncertain, relying on others' knowledge. Independence emerges when individuals resist these pressures, valuing personal beliefs over group consensus despite social demands.
Psychological Benefits of Independence
Independence fosters psychological benefits such as enhanced self-esteem, autonomy, and personal growth by enabling individuals to make decisions aligned with their values and beliefs. Unlike conformity, which may suppress individuality to fit social norms, independence promotes critical thinking and authentic self-expression. This psychological empowerment often leads to greater resilience, creativity, and long-term well-being.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Behavior
Culture profoundly influences whether individuals prioritize conformity or independence in their behavior. Collectivist societies emphasize conformity to group norms and social harmony, while individualistic cultures value personal autonomy and self-expression. Understanding your cultural background helps explain your behavioral tendencies and social interactions within different cultural contexts.
Consequences of Excessive Conformity
Excessive conformity can lead to the suppression of creativity and critical thinking, resulting in groupthink and poor decision-making outcomes. Your ability to express individuality and innovate may be stifled when you prioritize fitting in over independent judgment. This can ultimately decrease personal satisfaction and reduce the group's overall effectiveness in problem-solving and adapting to change.
Striking a Balance: When to Conform, When to Stand Alone
Striking a balance between conformity and independence requires assessing situational factors such as group norms, personal values, and potential consequences. Conforming can foster social harmony and collaboration when aligned with ethical standards, whereas standing alone is crucial for innovation and maintaining integrity in the face of peer pressure. Effective decision-making hinges on discerning when social cohesion outweighs personal dissent and vice versa.
Fostering Independence in Modern Society
Fostering independence in modern society involves promoting critical thinking, self-reliance, and personal accountability while balancing social norms and collective values. Encouraging educational systems and workplaces to support autonomy and creativity enhances individual empowerment without disregarding the importance of societal cohesion. This approach enables people to contribute uniquely to community development while maintaining their authentic identities.
Conformity vs Independence: Impacts on Personal Growth
Conformity often limits your personal growth by encouraging adherence to group norms and suppressing individuality, which can stifle creativity and self-expression. Independence fosters critical thinking, self-discovery, and resilience, empowering you to make authentic choices that align with your values. Balancing conformity and independence influences your ability to develop a unique identity while maintaining social harmony.
Infographic: Conformity vs Independence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com