Consensus fosters collaborative decision-making by prioritizing group agreement and shared understanding, while voting emphasizes majority rule, potentially overlooking minority perspectives. Discover the key differences and implications of Consensus vs Voting in this article.
Table of Comparison
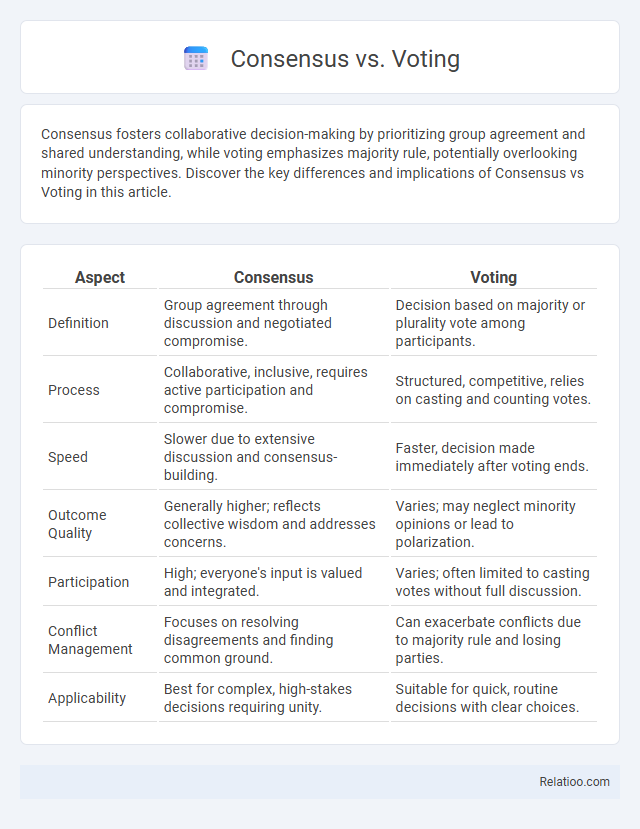
| Aspect | Consensus | Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group agreement through discussion and negotiated compromise. | Decision based on majority or plurality vote among participants. |
| Process | Collaborative, inclusive, requires active participation and compromise. | Structured, competitive, relies on casting and counting votes. |
| Speed | Slower due to extensive discussion and consensus-building. | Faster, decision made immediately after voting ends. |
| Outcome Quality | Generally higher; reflects collective wisdom and addresses concerns. | Varies; may neglect minority opinions or lead to polarization. |
| Participation | High; everyone's input is valued and integrated. | Varies; often limited to casting votes without full discussion. |
| Conflict Management | Focuses on resolving disagreements and finding common ground. | Can exacerbate conflicts due to majority rule and losing parties. |
| Applicability | Best for complex, high-stakes decisions requiring unity. | Suitable for quick, routine decisions with clear choices. |
Understanding Consensus and Voting
Consensus involves collaborative agreement where all participants work towards a common decision, emphasizing mutual understanding and inclusive participation. Voting relies on majority rule, where individuals cast ballots to express preferences, and the option with the most votes prevails, often prioritizing efficiency over unanimity. Understanding consensus requires recognizing its focus on collective harmony and shared purpose, while voting centers on individual choice aggregated to determine an outcome.
Key Differences Between Consensus and Voting
Consensus requires group agreement and collaboration to reach a decision that everyone supports or can accept, while voting relies on majority rule where the option with the most votes wins. Consensus emphasizes mutual understanding and shared outcomes, often leading to more sustainable decisions, whereas voting can result in winners and losers, possibly creating division. The key difference lies in consensus seeking collective agreement versus voting focusing on counting individual preferences.
Advantages of Consensus Decision-Making
Consensus decision-making fosters collaboration by ensuring that all participants contribute their perspectives, leading to more comprehensive and inclusive solutions. This approach enhances group cohesion and commitment, as Your team members feel valued and respected throughout the process. The resulting decisions often reflect a deeper understanding of the issue, reducing conflicts and increasing long-term satisfaction.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Voting
Voting enables clear and quick decision-making, providing a straightforward method to gauge majority preference, which is especially useful in large groups or time-sensitive situations. However, voting may lead to divisiveness and marginalize minority opinions, as it emphasizes majority rule without necessarily fostering collaboration or mutual understanding. The risk of polarization and the potential neglect of nuanced perspectives highlight the limitations of using voting as the sole decision-making mechanism.
Situations Where Consensus Works Best
Consensus works best in collaborative environments where group commitment and mutual understanding are critical, such as community decision-making, project planning, and conflict resolution. It excels when diverse perspectives must be integrated to achieve solutions that satisfy all stakeholders and foster long-term cooperation. Voting is more effective in situations requiring quick, majority-based decisions, while consensus is ideal for complex issues needing collective buy-in.
When Voting is More Effective
Voting is more effective in situations that require a quick decision or when there are diverse opinions without the need for full agreement among participants. It provides a clear, quantifiable outcome, making it ideal for large groups where consensus-building is impractical due to time constraints. In contrast, consensus works best in smaller groups aiming for collective agreement, fostering collaboration and buy-in but often requiring more time and effort.
Impact on Group Dynamics
Consensus fosters collaboration by encouraging active participation and mutual understanding, which strengthens group cohesion and trust. Voting introduces competitive dynamics as members prioritize individual preferences, potentially causing divisions and reduced cooperation. Your choice between consensus and voting significantly shapes the group's communication flow, decision ownership, and long-term effectiveness.
Efficiency and Time Considerations
Consensus requires unanimous agreement, which often leads to high-quality decisions but can be time-consuming and less efficient in large groups. Voting allows quicker decisions by majority rule, improving efficiency and saving time but may result in less thorough agreement. Balancing consensus and voting methods can optimize decision-making by combining inclusivity with time efficiency.
Case Studies: Consensus vs Voting in Action
Case studies reveal that consensus often leads to more durable and inclusive decisions compared to voting, which can produce quick but divisive outcomes. In organizational settings, consensus methods foster collaboration by addressing all stakeholders' concerns, whereas voting might marginalize minority opinions. Your choice between consensus and voting should consider the complexity of the issue and the need for long-term commitment to the decision.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Group
Choosing the right approach for your group depends on the complexity of decisions and the need for collaboration. Consensus fosters collective agreement by integrating diverse viewpoints, ensuring all members feel heard and valued. Voting offers efficiency for straightforward choices but may overlook minority perspectives, while consensus strikes a balance by encouraging dialogue and shared ownership of outcomes.
Infographic: Consensus vs Voting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com