Approach-approach dilemmas involve choosing between two desirable relationship options, while avoidance-avoidance dilemmas force a choice between two undesirable relationship outcomes. Discover how these decision-making conflicts impact relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
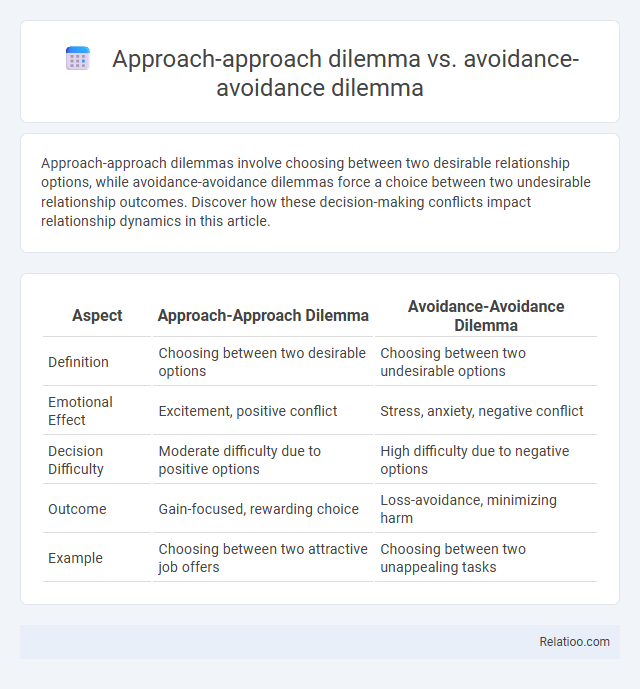
| Aspect | Approach-Approach Dilemma | Avoidance-Avoidance Dilemma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Choosing between two desirable options | Choosing between two undesirable options |
| Emotional Effect | Excitement, positive conflict | Stress, anxiety, negative conflict |
| Decision Difficulty | Moderate difficulty due to positive options | High difficulty due to negative options |
| Outcome | Gain-focused, rewarding choice | Loss-avoidance, minimizing harm |
| Example | Choosing between two attractive job offers | Choosing between two unappealing tasks |
Understanding Approach-Approach and Avoidance-Avoidance Dilemmas
Approach-approach dilemmas involve choosing between two desirable options, while avoidance-avoidance dilemmas force you to decide between two unfavorable outcomes, creating significant psychological stress. Understanding your own decision-making process helps navigate these conflicts by recognizing whether the choices are driven by positive motivations or the need to avoid negative consequences. Effective strategies for managing these dilemmas include weighing the potential benefits in approach-approach scenarios and considering the lesser of two evils in avoidance-avoidance situations.
Defining the Approach-Approach Dilemma
The approach-approach dilemma involves choosing between two equally desirable options, creating a conflict based on positive motivations. This contrasts with the avoidance-avoidance dilemma, where a person must choose between two unpleasant options, and a general dilemma, which refers broadly to any difficult decision requiring a choice between competing alternatives. Understanding the approach-approach dilemma highlights how positive incentives can lead to psychological tension when selecting the best beneficial outcome.
Defining the Avoidance-Avoidance Dilemma
The avoidance-avoidance dilemma occurs when you must choose between two equally unattractive options, causing stress and indecision. Unlike the approach-approach dilemma, where choices are desirable, and general dilemmas involving conflict, avoidance-avoidance situations trap you in a no-win scenario. Understanding this dilemma helps clarify decision-making challenges rooted in fear and avoidance.
Key Psychological Theories Behind Both Dilemmas
Approach-approach dilemmas involve choosing between two desirable outcomes, rooted in Lewin's field theory emphasizing the psychological tension of competing positive goals. Avoidance-avoidance dilemmas force Your decision between two negative options, drawing on Festinger's cognitive dissonance theory, which highlights the discomfort of conflicting avoidant motives. Both dilemmas illustrate the underlying conflict described in decision-making theories, where motivation and emotion interplay to influence behavior.
Real-Life Examples of Approach-Approach Dilemmas
Approach-approach dilemmas involve choosing between two attractive options, such as deciding whether to spend a vacation in Paris or Tokyo, each offering unique cultural experiences and memorable activities. Avoidance-avoidance dilemmas present a choice between two undesirable outcomes, like facing a painful medical procedure or enduring prolonged illness, creating significant stress. Real-life examples of approach-approach dilemmas include selecting between two job offers with excellent benefits and growth opportunities, highlighting the positive yet challenging nature of these decisions in daily life.
Real-Life Examples of Avoidance-Avoidance Dilemmas
Avoidance-avoidance dilemmas occur when individuals face two equally undesirable options, such as choosing between paying a hefty medical bill or risking untreated health issues. In contrast, approach-approach dilemmas involve selecting between two attractive options, like deciding between two exciting job offers. Real-life examples of avoidance-avoidance dilemmas include being stuck between a stressful job or unemployment, or having to choose between costly car repairs and buying a new vehicle.
Cognitive and Emotional Impacts of Each Dilemma
The approach-approach dilemma, involving a choice between two desirable alternatives, typically triggers positive cognitive engagement with minimal emotional distress due to anticipated gains. In contrast, the avoidance-avoidance dilemma, presenting two undesirable options, often leads to heightened anxiety and cognitive conflict as individuals struggle to evade negative outcomes. The general concept of a dilemma intensifies psychological stress by simultaneously activating conflicting motivations, increasing cognitive load, and eliciting ambivalent emotions such as indecision and frustration.
Decision-Making Strategies in Approach-Approach Conflicts
Approach-approach dilemmas involve choosing between two desirable options, making decision-making strategies focus on evaluating the benefits and prioritizing based on personal values or goals. Avoidance-avoidance dilemmas require selecting the lesser of two unfavorable outcomes, often leading to procrastination or stress due to fear of negative consequences. Dilemmas generally present conflicting choices, but in approach-approach conflicts, strategies like cost-benefit analysis, pros and cons lists, and value clarification streamline decision-making by highlighting positive outcomes.
Coping Mechanisms for Avoidance-Avoidance Dilemmas
Avoidance-avoidance dilemmas involve choosing between two undesirable options, creating intense stress and indecision, while approach-approach dilemmas require selecting between two attractive alternatives, and general dilemmas encompass conflicts faced in decision-making. Coping mechanisms for avoidance-avoidance dilemmas often include stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness, cognitive reappraisal to reframe negative perceptions, and problem-focused strategies to identify and pursue viable compromises. These methods help reduce anxiety and facilitate decision-making when all available choices are unappealing.
Comparing Approach-Approach vs Avoidance-Avoidance Dilemmas
Approach-approach dilemmas involve choosing between two equally desirable options, leading to positive conflict but generally easier decision-making due to satisfaction with either choice. Avoidance-avoidance dilemmas require selecting between two unattractive alternatives, creating greater psychological stress and indecision because both outcomes are negative. Comparing the two, approach-approach dilemmas typically result in lower anxiety and quicker resolutions, whereas avoidance-avoidance dilemmas generate higher tension and longer hesitation due to aversion to both options.
Infographic: Approach-approach dilemma vs Avoidance-avoidance dilemma
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com