Hard Negotiators prioritize firm boundaries and leverage, seeking clear wins in relationship conflicts, while Soft Negotiators emphasize empathy and compromise to maintain harmony. Discover effective strategies to balance these negotiation styles and strengthen your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
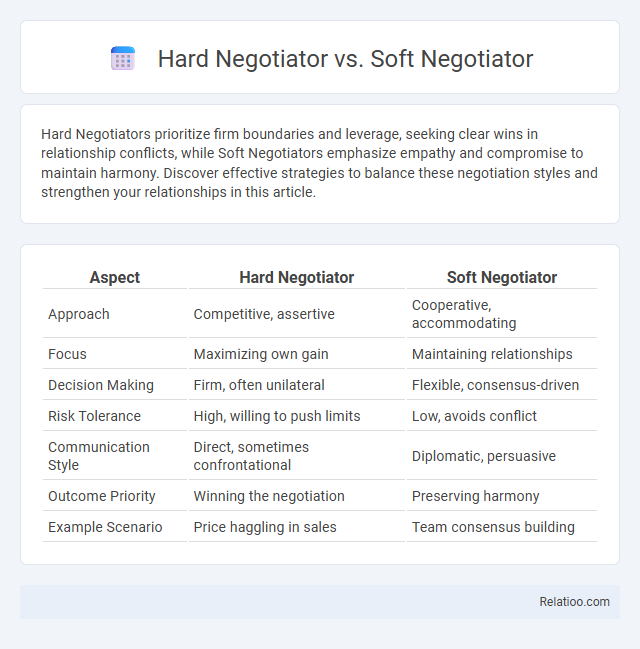
| Aspect | Hard Negotiator | Soft Negotiator |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Competitive, assertive | Cooperative, accommodating |
| Focus | Maximizing own gain | Maintaining relationships |
| Decision Making | Firm, often unilateral | Flexible, consensus-driven |
| Risk Tolerance | High, willing to push limits | Low, avoids conflict |
| Communication Style | Direct, sometimes confrontational | Diplomatic, persuasive |
| Outcome Priority | Winning the negotiation | Preserving harmony |
| Example Scenario | Price haggling in sales | Team consensus building |
Understanding Hard vs Soft Negotiation Styles
Understanding hard vs soft negotiation styles reveals distinct approaches: a hard negotiator prioritizes assertiveness and clear demands, often using pressure tactics, while a soft negotiator emphasizes relationship-building and compromise to reach a mutually acceptable outcome. Your negotiation strategy should align with the context, as hard negotiation suits high-stakes or deadline-driven scenarios, whereas soft negotiation fosters long-term partnerships and trust. Recognizing these differences allows you to adapt and balance strategies effectively for optimal results.
Key Characteristics of Hard Negotiators
Hard negotiators prioritize firm positions, often employing aggressive tactics and strict demands to dominate the negotiation process. They emphasize clear boundaries, minimal concessions, and leverage power to achieve their objectives efficiently. Success for hard negotiators hinges on control, assertiveness, and maintaining a strong bargaining stance throughout discussions.
Defining Traits of Soft Negotiators
Soft negotiators prioritize relationship-building and mutual satisfaction, often willing to make concessions to maintain harmony. They emphasize empathy, active listening, and open communication to create a collaborative atmosphere. This approach contrasts with hard negotiators who focus on assertiveness and winning, while general negotiators balance assertiveness and cooperation depending on context.
Advantages of a Hard Negotiation Approach
The hard negotiation approach emphasizes assertiveness and firmness, enabling negotiators to secure favorable terms and protect their interests effectively. This style often results in clear, decisive outcomes by applying pressure and leveraging power dynamics to achieve maximum value. Hard negotiators are skilled at setting boundaries and resisting concessions, which can prevent exploitation and yield advantageous agreements.
Strengths of a Soft Negotiation Strategy
The strengths of a soft negotiation strategy lie in its emphasis on maintaining positive relationships and fostering trust, which can lead to long-term collaboration and mutual satisfaction. Soft negotiators prioritize empathy and active listening, allowing them to uncover underlying interests and create win-win solutions that satisfy all parties. Your ability to remain flexible and open to compromise enhances communication, reduces conflict, and promotes sustainable agreements.
Common Pitfalls of Hard Negotiators
Hard negotiators often face challenges such as damaging relationships due to their unyielding stance and excessive focus on winning at all costs. Your insistence on rigid demands can result in missed opportunities for mutually beneficial agreements and create resistance from the opposing party. Recognizing these pitfalls helps balance firmness with flexibility to achieve more effective negotiation outcomes.
Risks Associated With Soft Negotiators
Soft negotiators often face higher risks due to their tendency to prioritize relationships over assertiveness, potentially leading to unfavorable agreements and exploitation. Your willingness to compromise easily can result in lost value and diminished leverage during critical discussions. Understanding these risks is essential to balancing empathy with effective negotiation strategies and avoiding suboptimal outcomes.
When to Use Hard Negotiation Techniques
Hard negotiation techniques are most effective when the situation demands clear boundaries, fixed outcomes, or when dealing with parties unwilling to compromise, such as in high-stakes business deals or legal disputes. You should employ hard negotiation when protecting critical interests, maintaining leverage, or establishing authority is essential for achieving your goals. Applying these tactics requires confidence, a firm stance, and strategic concessions to prevent concessions that could weaken your position.
Scenarios Favoring Soft Negotiation Methods
Soft negotiation methods excel in scenarios where maintaining long-term relationships and fostering trust are crucial, such as partnerships, family disputes, or collaborative projects. Your ability to emphasize empathy and open communication helps create win-win outcomes, reducing the risk of conflict escalation. These techniques prioritize mutual understanding over competition, making them ideal for resolving issues with ongoing interaction.
Balancing Hard and Soft Negotiation Tactics
Balancing hard and soft negotiation tactics requires understanding the strengths of each approach: hard negotiators prioritize assertiveness and leverage, while soft negotiators emphasize empathy and relationship building. Your ability to blend assertiveness with flexibility enables you to achieve favorable outcomes while maintaining positive rapport with counterparts. Effective negotiators adapt their style to the context, ensuring a strategic balance that maximizes agreement value and minimizes conflict.
Infographic: Hard Negotiator vs Soft Negotiator
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com