Complicity in relationships involves active participation and shared responsibility, while compliance refers to passive agreement or submission without genuine engagement. Explore this article to understand how fostering complicity enhances trust and intimacy beyond mere compliance.
Table of Comparison
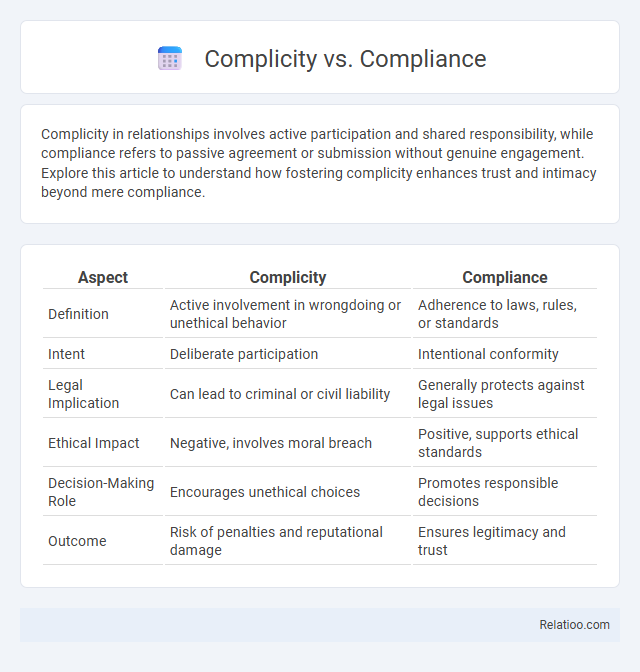
| Aspect | Complicity | Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active involvement in wrongdoing or unethical behavior | Adherence to laws, rules, or standards |
| Intent | Deliberate participation | Intentional conformity |
| Legal Implication | Can lead to criminal or civil liability | Generally protects against legal issues |
| Ethical Impact | Negative, involves moral breach | Positive, supports ethical standards |
| Decision-Making Role | Encourages unethical choices | Promotes responsible decisions |
| Outcome | Risk of penalties and reputational damage | Ensures legitimacy and trust |
Understanding Complicity: Definition and Nuances
Understanding complicity involves recognizing how your actions or inactions contribute to wrongdoing, often by enabling or supporting unethical behavior. Unlike compliance, which requires adherence to laws or rules, complicity implies moral or legal responsibility for participating in or facilitating harmful acts. Grasping these nuances helps you distinguish between passive obedience and active involvement in unethical conduct.
What is Compliance? Key Characteristics
Compliance refers to adhering to laws, regulations, and standards set by authoritative bodies to ensure lawful and ethical behavior within an organization. Key characteristics of compliance include implementation of formal policies, regular monitoring, employee training, and risk management to prevent violations. Understanding compliance helps you maintain integrity and avoid legal consequences in your business operations.
Complicity vs Compliance: Core Differences
Complicity involves actively participating or assisting in wrongdoing, whereas compliance refers to adhering to laws, regulations, or rules without engaging in unethical behavior. The core difference lies in intent and action: complicity implies intentional collaboration in wrongful acts, while compliance emphasizes lawful and ethical conformity. Understanding this distinction is crucial for organizations to prevent legal liability and maintain ethical standards.
Ethical Implications of Complicity
Complicity in unethical actions involves knowingly participating or facilitating wrongdoing, which carries significant moral and legal consequences beyond mere compliance with rules. Compliance refers to adhering to legal and organizational standards, often viewed as a baseline for ethical behavior, but it may fall short when passive behavior enables harmful actions. Understanding the ethical implications of complicity requires recognizing the active responsibility individuals and organizations hold in preventing harm, emphasizing accountability, transparency, and proactive ethical decision-making to avoid contributing to unethical outcomes.
Legal Perspectives on Complicity and Compliance
Legal perspectives on complicity emphasize an individual or entity's involvement in facilitating or enabling a wrongful act, often holding them accountable for crimes committed by others. Compliance refers to adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies designed to prevent legal violations and mitigate risks. Your understanding of these distinctions is crucial for navigating legal responsibilities and avoiding potential liability linked to complicity.
Real-World Examples: Complicity in Organizations
Complicity in organizations often involves knowing participation in unethical or illegal activities, such as covering up financial fraud or ignoring workplace harassment, which contrasts with compliance that entails adhering strictly to legal and regulatory standards. Real-world examples include the Volkswagen emissions scandal where executives were complicit in falsifying test results, or the Wells Fargo fake accounts controversy, highlighting failures in organizational oversight. Your understanding of these distinctions is critical in recognizing how complicity undermines ethical integrity and legal accountability within businesses.
Compliance in Business: Standards and Practices
Compliance in business refers to adhering strictly to established laws, regulations, and internal policies to avoid legal penalties and maintain ethical standards. Your organization must implement comprehensive compliance programs that include regular audits, employee training, and transparent reporting to uphold industry standards and build stakeholder trust. Failure to maintain compliance can lead to severe financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
The Role of Intent: Distinguishing Complicity from Compliance
Complicity involves knowingly participating in wrongdoing, where intent plays a crucial role in distinguishing it from compliance, which is characterized by adherence to rules or orders without intent to support unlawful acts. Compliance reflects lawful obedience to regulations or directives, whereas complicity implies a deliberate choice to assist or enable illegal activities. Understanding intent helps identify complicity by revealing whether an individual consciously supports or facilitates unethical behavior beyond mere compliance.
Preventing Unintentional Complicity in the Workplace
Preventing unintentional complicity in the workplace requires clear policies, thorough employee training, and robust monitoring systems to identify and address unethical behavior promptly. Compliance programs focusing on legal and ethical standards help distinguish between intentional complicity and inadvertent compliance failures. Cultivating a culture of transparency and accountability reduces risks by encouraging employees to report concerns without fear of retaliation.
Building a Culture of Ethical Compliance
Building a culture of ethical compliance requires clear differentiation between complicity, compliance, and complicity, emphasizing individual accountability in upholding organizational standards. Effective training programs and transparent communication channels foster awareness, reducing the risk of complicity in unethical practices and promoting proactive compliance. Integrating robust monitoring systems and leadership commitment ensures sustained adherence to ethical policies, strengthening overall corporate governance.
Infographic: Complicity vs Compliance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com