Understanding the balance between consequence and reward in relationships enhances emotional growth and trust building. Explore how these dynamics shape lasting connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
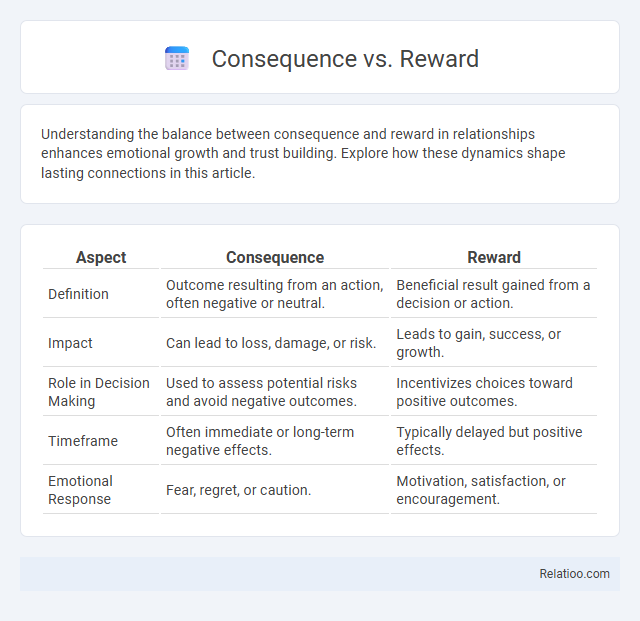
| Aspect | Consequence | Reward |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outcome resulting from an action, often negative or neutral. | Beneficial result gained from a decision or action. |
| Impact | Can lead to loss, damage, or risk. | Leads to gain, success, or growth. |
| Role in Decision Making | Used to assess potential risks and avoid negative outcomes. | Incentivizes choices toward positive outcomes. |
| Timeframe | Often immediate or long-term negative effects. | Typically delayed but positive effects. |
| Emotional Response | Fear, regret, or caution. | Motivation, satisfaction, or encouragement. |
Understanding Consequence and Reward
Understanding consequence and reward is crucial in shaping behavior and decision-making processes. Consequences, whether positive or negative, directly influence future actions by reinforcing or deterring specific behaviors, while rewards serve as incentives that motivate individuals to repeat desirable actions. Recognizing the distinct roles of consequence and reward helps in designing effective behavioral strategies and environments that promote learning and growth.
The Psychology Behind Consequences and Rewards
Understanding the psychology behind consequences and rewards reveals that consequences often motivate behavior through fear of negative outcomes, while rewards encourage positive action by offering desirable incentives. Your brain processes rewards by releasing dopamine, reinforcing habits and making you more likely to repeat the behavior. Consequences activate the brain's threat response, creating a sense of urgency that can either deter or stress you, depending on the severity and context.
Consequence vs Reward: Key Differences
Consequence and reward both serve as outcomes of behavior but differ fundamentally in their nature and impact. Consequences typically involve negative or undesired results aimed at discouraging certain actions, while rewards provide positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. Understanding the key differences between consequence vs reward is crucial for effective behavior management and motivation strategies.
Impact on Behavior and Decision-Making
Consequences shape behavior by providing feedback that reinforces or discourages specific actions, leading to adjustments in decision-making patterns based on outcomes experienced. Rewards act as positive motivators, enhancing the likelihood of repeating behaviors that yield beneficial results, thereby strengthening goal-directed choices. Consistently linking consequences and rewards in decision-making processes improves behavioral adaptation by aligning actions with desired results and long-term objectives.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Effects
Short-term consequences often provide immediate feedback, shaping your behavior quickly, while long-term consequences influence sustained habits and overall life outcomes. Rewards in the short term can motivate actions but may lose effectiveness without alignment to long-term goals, where intrinsic rewards become crucial. Understanding the balance between immediate gratification and future benefits helps optimize decision-making and promotes lasting success.
Real-Life Examples of Consequence and Reward
Real-life examples illustrate how consequences and rewards shape behavior through tangible outcomes; for instance, employees receive bonuses as rewards for exceeding targets, reinforcing positive performance, while facing pay cuts for missing deadlines serves as a consequence that discourages negligence. Understanding this dynamic helps You leverage consequences and rewards effectively in management or personal goal-setting to motivate desired actions. Such strategies align incentives with behavior, driving productivity and accountability.
The Role in Motivation and Learning
Consequences and rewards play crucial roles in shaping motivation and learning by influencing behavior through reinforcement and feedback mechanisms. Positive consequences, such as rewards, encourage repetition of desired actions, while negative consequences discourage undesired behaviors, creating a balance that guides effective learning. Understanding how your responses impact motivation can optimize educational strategies and improve behavioral outcomes.
Balancing Consequence and Reward in Practice
Balancing consequence and reward in practice requires aligning clear expectations with consistent feedback to drive desired behaviors effectively. Effective behavior management involves applying consequences that are proportional to actions while reinforcing positive outcomes through meaningful rewards. This equilibrium fosters motivation, accountability, and sustained performance improvement within organizational or educational settings.
Cultural Perspectives on Consequences and Rewards
Cultural perspectives on consequences and rewards significantly influence how individuals and societies interpret actions and outcomes, shaping behavior and motivation. In some cultures, collective consequences emphasize community harmony and shared responsibility, while rewards often underscore social recognition rather than individual gain. Understanding your cultural context can help you navigate expectations and responses to both consequences and rewards more effectively.
Strategies for Effective Use in Personal Growth
Balancing consequence and reward effectively drives personal growth by reinforcing positive behaviors and correcting negative patterns through strategic application. Establishing clear, consistent consequences promotes accountability, while timely rewards enhance motivation and encourage goal persistence. Implementing a structured approach that aligns consequences with learning outcomes and rewards with milestones maximizes behavioral change and fosters sustained self-improvement.
Infographic: Consequence vs Reward
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com