Indian relationships often emphasize family bonds and arranged marriages, while American relationships prioritize individual choice and romantic love. Explore more cultural insights and relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
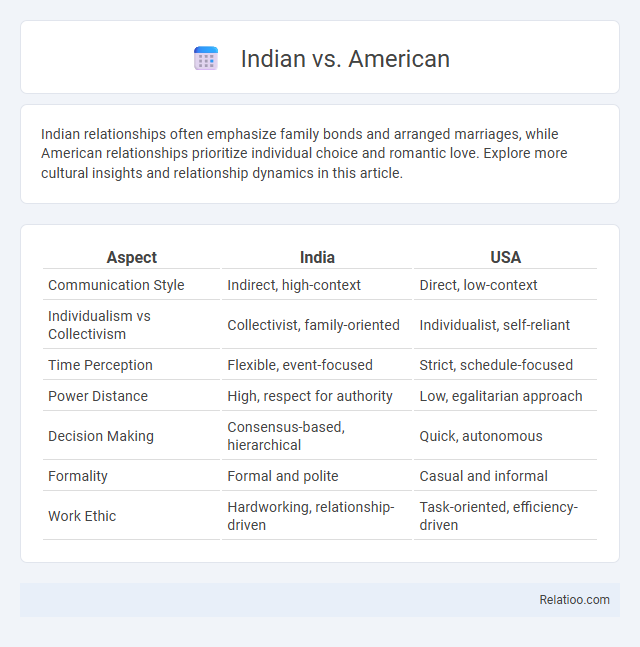
| Aspect | India | USA |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Indirect, high-context | Direct, low-context |
| Individualism vs Collectivism | Collectivist, family-oriented | Individualist, self-reliant |
| Time Perception | Flexible, event-focused | Strict, schedule-focused |
| Power Distance | High, respect for authority | Low, egalitarian approach |
| Decision Making | Consensus-based, hierarchical | Quick, autonomous |
| Formality | Formal and polite | Casual and informal |
| Work Ethic | Hardworking, relationship-driven | Task-oriented, efficiency-driven |
Introduction: Understanding Indian vs American Cultures
Indian culture emphasizes deep-rooted respect for elders, reflecting centuries-old traditions where family hierarchy shapes social interactions. In contrast, American culture values individualism and equality, often encouraging direct communication irrespective of age. Understanding these differences helps you navigate cross-cultural relationships with greater empathy and respect.
Historical Background: India and America
Indian culture places a profound emphasis on elder respect rooted in ancient Hindu traditions, where elders are revered as the embodiments of wisdom and family authority, shaping societal norms through texts like the Manusmriti. In contrast, American elder respect has evolved from European individualistic values, emphasizing personal autonomy and mutual respect without hierarchical obligation, influenced by Enlightenment ideals and a history of democratic structures. Historically, Indian society's collectivist framework contrasts with America's individualistic culture, resulting in differing practices and expectations surrounding elder respect.
Social Structure and Family Dynamics
Indian social structure deeply integrates respect for elders into family dynamics, with multi-generational households emphasizing obedience and care for senior members as a cultural norm. American family systems prioritize individualism and independence, often promoting mutual respect but encouraging children to seek personal autonomy from elders. You will notice that Indian respect for elders is rooted in collective values and tradition, whereas American respect often reflects egalitarian principles and open communication.
Education Systems: India vs America
Indian education emphasizes respect for elders and teachers as integral to learning, fostering hierarchical relationships and disciplined classroom environments. American education encourages open dialogue and critical thinking, promoting equality between students and educators while valuing individual expression. These cultural differences influence classroom dynamics, pedagogical styles, and student-teacher interactions in both countries.
Food Habits and Culinary Traditions
Indian culinary traditions emphasize serving elders first as a sign of respect, reflecting their deep-rooted cultural reverence for age and wisdom. American food habits often prioritize convenience and individuality, with less emphasis on hierarchical serving customs but valuing shared communal meals during holidays. Elder respect in India is intertwined with elaborate food rituals and vegetarian preferences, while American practices focus more on accommodating personal dietary choices, marking a cultural distinction in honoring senior family members through cuisine.
Festivals and Celebrations Compared
Indian festivals like Diwali and Durga Puja emphasize elder respect through rituals that involve seeking blessings from elders and honoring family traditions. In American celebrations such as Thanksgiving, respect for elders is shown through family gatherings and expressing gratitude, highlighting intergenerational bonds without formal rituals. Indian celebrations often integrate cultural heritage and religious practices to honor elders, whereas American festivals focus more on communal togetherness and verbal appreciation.
Communication Styles and Languages
Indian communication often relies on indirect, context-based language, emphasizing respect through honorifics and non-verbal cues, especially towards elders. American communication prefers directness and clarity, valuing open dialogue but still respecting elders with polite forms and attentive listening. Your understanding of these cultural nuances enhances effective interaction by adapting language style and showing appropriate respect across diverse settings.
Work Culture and Professional Life
Indian work culture places significant emphasis on hierarchical respect, where deference to elders and senior colleagues is integral to professional interactions and decision-making processes. In contrast, American professional environments often prioritize meritocracy and individual contribution, with respect earned through performance rather than age or seniority. Elder respect in Indian workplaces fosters strong mentorship and loyalty, whereas American work culture encourages collaboration across age groups, promoting innovation and egalitarian communication.
Fashion and Clothing Differences
Indian elder respect often emphasizes traditional clothing such as sarees, dhotis, and kurta pajamas, symbolizing cultural heritage and reverence in family gatherings. American elder respect generally involves more casual, Western attire like slacks, shirts, or dresses, reflecting individual comfort and modernity while maintaining polite social norms. The fashion contrast highlights India's collective cultural identity through vibrant, formal garments versus America's focus on personal expression and practicality.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap
Indian culture emphasizes deep respect for elders through traditional family hierarchies and daily rituals, while American culture promotes respect based on individual rights and mutual understanding. Both approaches highlight the importance of valuing experience but differ in expression and social norms. Your ability to bridge these cultural perspectives fosters stronger relationships and enriches cross-cultural communication.
Infographic: Indian vs American
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com