High Power Distance cultures emphasize hierarchical relationships and centralized authority, while Low Power Distance cultures promote equality and decentralized decision-making. Discover how these differences impact communication and workplace dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
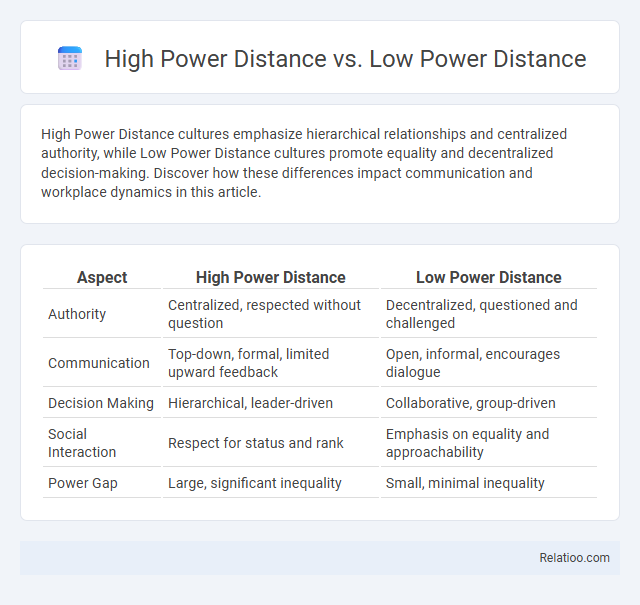
| Aspect | High Power Distance | Low Power Distance |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | Centralized, respected without question | Decentralized, questioned and challenged |
| Communication | Top-down, formal, limited upward feedback | Open, informal, encourages dialogue |
| Decision Making | Hierarchical, leader-driven | Collaborative, group-driven |
| Social Interaction | Respect for status and rank | Emphasis on equality and approachability |
| Power Gap | Large, significant inequality | Small, minimal inequality |
Understanding Power Distance: Definition and Origin
Power distance refers to the extent to which less powerful members of a society accept and expect unequal power distribution, a concept introduced by Dutch social psychologist Geert Hofstede in his cultural dimensions theory. High power distance societies emphasize hierarchical order and centralized authority, while low power distance cultures value equality and participative decision-making. Understanding power distance is crucial for analyzing organizational behavior, leadership styles, and communication patterns across different cultural contexts.
Key Characteristics of High Power Distance Cultures
High power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical structures, where authority and power are centralized, and subordinates are expected to accept their roles without question. Communication in these societies is often top-down, with limited interaction or feedback from lower-level members, reinforcing respect and obedience to superiors. This cultural trait influences organizational behavior by promoting clear chains of command and strong distinctions between social classes.
Traits and Values of Low Power Distance Societies
Low power distance societies value equality, participative decision-making, and open communication, where hierarchy is minimized and power is decentralized. Traits include a strong emphasis on individual autonomy, informal interactions between different social levels, and trust in equal rights. Your interactions in such cultures prioritize collaboration, inclusiveness, and transparency, promoting mutual respect regardless of status.
Communication Styles in High vs Low Power Distance Environments
High power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical communication, where subordinates often use indirect language and show deference to authority, while superiors communicate in a top-down manner with limited feedback. In low power distance environments, communication tends to be more egalitarian, encouraging openness, directness, and collaborative dialogue between all levels of the organizational hierarchy. Understanding these distinct communication styles is crucial for effective cross-cultural interaction and organizational leadership in global settings.
Leadership Approaches: Authoritarian vs Egalitarian
Power distance reflects the extent to which unequal power distribution is accepted within a culture, influencing leadership approaches. High power distance cultures tend to favor authoritarian leadership, where decision-making is centralized and hierarchical, reinforcing clear authority and control. Low power distance cultures promote egalitarian leadership, encouraging participation, collaboration, and shared power in decision-making processes that empower your team.
Impact on Workplace Dynamics and Team Collaboration
High power distance environments often result in hierarchical workplace dynamics where employees may hesitate to challenge authority, limiting open communication and collaborative problem-solving. Low power distance cultures promote egalitarian relationships, encouraging team members to share ideas freely and participate actively in decision-making processes. Understanding power distance is crucial for global organizations to foster effective teamwork by adapting leadership styles that align with their cultural context.
Pros and Cons of High Power Distance Systems
High Power Distance systems emphasize hierarchical structures where authority is rarely questioned, fostering clear decision-making and efficient command flow. However, Your organization may face reduced employee empowerment, limited innovation, and potential communication barriers due to the concentration of power and lack of feedback channels. These systems can create stability in roles but risk alienating lower-level employees by minimizing their autonomy and input.
Pros and Cons of Low Power Distance Systems
Low power distance systems promote equality and open communication between different levels of hierarchy, enhancing employee engagement and innovation. Your organization benefits from increased collaboration and empowerment, but decision-making may slow down due to the need for consensus and shared authority. However, the downside includes potential challenges in maintaining clear leadership roles and enforcing discipline.
Strategies for Managing Cultural Differences in Power Distance
Understanding the concept of power distance, which refers to how a culture handles inequalities in power and authority, is crucial for managing cultural differences effectively. In high power distance cultures, emphasizing respect for hierarchy and clear authority lines helps maintain harmony, whereas in low power distance cultures, fostering open communication and collaborative decision-making enhances engagement and trust. Adapting your management approach by recognizing these cultural dimensions enables your team to navigate power disparities smoothly and promotes a more inclusive workplace environment.
Adapting Leadership and Communication Across Power Distance Contexts
High Power Distance cultures expect leaders to maintain clear hierarchical authority, requiring Your leadership style to emphasize respect, formality, and directive communication to effectively guide teams. In Low Power Distance contexts, leaders adopt a more participative approach, encouraging open dialogue and collaborative decision-making to foster inclusion and innovation. Understanding the nuances of Power Distance allows You to adapt communication strategies and leadership behaviors, ensuring alignment with cultural expectations and enhancing team cohesion across diverse environments.
Infographic: High Power Distance vs Low Power Distance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com