Eastern education emphasizes collective harmony and respect for authority in relationships, while Western education promotes individual expression and critical thinking. Discover deeper insights into how these educational philosophies shape interpersonal connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
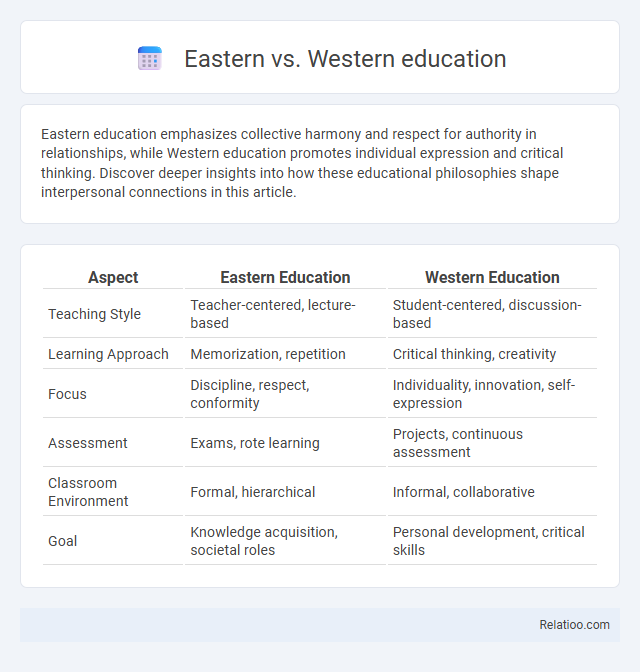
| Aspect | Eastern Education | Western Education |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Style | Teacher-centered, lecture-based | Student-centered, discussion-based |
| Learning Approach | Memorization, repetition | Critical thinking, creativity |
| Focus | Discipline, respect, conformity | Individuality, innovation, self-expression |
| Assessment | Exams, rote learning | Projects, continuous assessment |
| Classroom Environment | Formal, hierarchical | Informal, collaborative |
| Goal | Knowledge acquisition, societal roles | Personal development, critical skills |
Introduction to Eastern and Western Education
Eastern education emphasizes memorization, discipline, and respect for authority, fostering a collective mindset and deep cultural roots. Western education prioritizes critical thinking, creativity, and individual expression, encouraging innovation and personal development. Your choice between these systems impacts learning style and long-term educational expectations.
Historical Background of Educational Systems
The historical background of Eastern education is deeply rooted in Confucian values, emphasizing discipline, rote memorization, and respect for authority to maintain societal harmony. Western education originates from ancient Greek philosophy, prioritizing critical thinking, individualism, and inquiry-based learning as tools for innovation and personal development. Your understanding of these foundational differences helps clarify varied education expectations shaping students' experiences worldwide.
Philosophical Foundations and Core Values
Eastern education emphasizes collectivism, respect for authority, and holistic development rooted in Confucian and Taoist philosophies, while Western education prioritizes individualism, critical thinking, and innovation influenced by Enlightenment and Socratic traditions. Your educational expectations shape whether you value memorization and discipline or creativity and questioning as core values. Both systems aim to cultivate knowledge, but their philosophical foundations lead to distinct approaches in teaching, learning, and personal growth.
Teaching Methods and Classroom Environment
Eastern education emphasizes rote memorization, discipline, and teacher-centered instruction, fostering a structured classroom environment where respect for authority guides learning. Western education values critical thinking, creativity, and student-centered methods, encouraging open discussion and collaboration to enhance engagement. Your ideal education experience depends on preferences for either structured guidance or interactive exploration within the classroom setting.
Role of Teachers and Students
Eastern education emphasizes teacher-centered learning where instructors are authoritative figures imparting knowledge, expecting students to respect hierarchy and diligently absorb information. Western education promotes student-centered approaches, encouraging critical thinking, active participation, and open dialogue between teachers and learners. Your educational expectations may vary based on these cultural frameworks, influencing how you engage with teachers and assume responsibility for your learning process.
Curriculum Structure and Academic Focus
Eastern education emphasizes a rigorous curriculum structure centered on memorization, standardized testing, and mastery of core subjects like mathematics and science. Western education prioritizes a flexible curriculum designed to foster critical thinking, creativity, and interdisciplinary learning across humanities, arts, and sciences. Your educational expectations should align with these differences, choosing a system that best supports your academic goals and learning style.
Assessment, Testing, and Grading Practices
Eastern education systems emphasize high-stakes testing and rigorous assessment methods, prioritizing standardized exams to measure student achievement and rank performance. Western education often incorporates diverse evaluation techniques, including formative assessments, project-based learning, and continuous grading, fostering critical thinking and creativity. Education expectations differ as Eastern approaches typically value rote memorization and exam results, while Western systems aim for holistic development and skill application through varied assessment practices.
Parental and Societal Influence on Education
Parental and societal influence shapes Eastern education through a strong emphasis on discipline, respect for authority, and academic excellence, often driven by collective cultural values. Western education tends to prioritize individualism, creativity, and critical thinking, reflecting societal encouragement of personal expression and innovation. Your educational expectations are molded by these influences, balancing external demands with personal aspirations.
Strengths and Challenges of Each Approach
Eastern education emphasizes discipline, rote memorization, and mastery of foundational knowledge, fostering strong analytical and memorization skills but sometimes limiting creativity and critical thinking. Western education encourages critical thinking, creativity, and individualism, promoting innovation and problem-solving abilities while occasionally lacking depth in core subject mastery. Balancing the structured rigor of Eastern methods with the flexible, student-centered focus of Western education addresses diverse learning needs and expectations in a globalized world.
Future Trends and Global Impact
Eastern education emphasizes rote learning and discipline, cultivating strong foundational knowledge and respect for authority, while Western education promotes critical thinking and creativity, encouraging innovation and individualism. Future trends reveal increasing integration of both systems, leveraging technology and personalized learning to meet evolving global workforce needs. This hybrid approach aims to create adaptable, culturally aware students poised to navigate and influence the interconnected global economy.
Infographic: Eastern vs Western education
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com