Dowry refers to the property or money a bride's family gives to the groom or his family before or at marriage, common in South Asian cultures, while Mahr is a mandatory gift or payment from the groom to the bride, as prescribed by Islamic law, ensuring her financial security. Explore this article to understand the cultural, legal, and social distinctions between dowry and mahr and their implications in modern relationships.
Table of Comparison
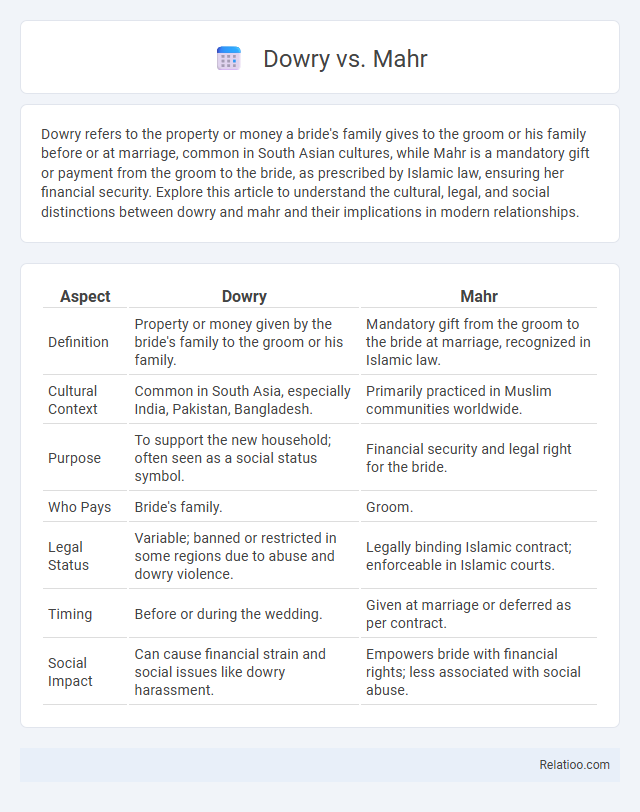
| Aspect | Dowry | Mahr |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Property or money given by the bride's family to the groom or his family. | Mandatory gift from the groom to the bride at marriage, recognized in Islamic law. |
| Cultural Context | Common in South Asia, especially India, Pakistan, Bangladesh. | Primarily practiced in Muslim communities worldwide. |
| Purpose | To support the new household; often seen as a social status symbol. | Financial security and legal right for the bride. |
| Who Pays | Bride's family. | Groom. |
| Legal Status | Variable; banned or restricted in some regions due to abuse and dowry violence. | Legally binding Islamic contract; enforceable in Islamic courts. |
| Timing | Before or during the wedding. | Given at marriage or deferred as per contract. |
| Social Impact | Can cause financial strain and social issues like dowry harassment. | Empowers bride with financial rights; less associated with social abuse. |
Introduction to Dowry and Mahr
Dowry and mahr are culturally and legally distinct practices related to marriage. Dowry refers to the property or wealth transferred from the bride's family to the groom or his family, commonly practiced in South Asia. Mahr is an Islamic marital gift given by the groom directly to the bride, serving as a mandatory and binding contract element to ensure her financial security.
Defining Dowry: Cultural and Legal Perspectives
Dowry refers to the transfer of parental property, gifts, or money at the marriage of a daughter, deeply rooted in various cultural traditions and often regulated by law to prevent exploitation. Mahr, distinct from dowry, is an Islamic legal obligation wherein the groom provides a mandatory gift to the bride, ensuring her financial security and rights. Understanding dowry within both cultural norms and legal frameworks highlights the socio-economic implications and the efforts to distinguish it from Mahr to protect women's rights in matrimonial contexts.
Understanding Mahr in Islamic Tradition
Mahr is an obligatory gift or financial security agreed upon by both parties in an Islamic marriage, distinct from dowry practices found in other cultures. Unlike dowry, which is typically provided by the bride's family to the groom or his family, Mahr is given directly by the groom to the bride as a symbol of respect and commitment. This practice ensures the bride's financial protection and holds significant religious and legal importance in Islamic tradition.
Historical Origins of Dowry and Mahr
Dowry and Mahr have distinct historical origins rooted in different cultural and religious traditions, with dowry traditionally emerging from ancient societies as a transfer of parental property or wealth to a daughter at marriage, often to ensure her security. Mahr, in Islamic law, originates from the Quran as a mandatory gift from the groom to the bride, symbolizing respect and financial security for the wife. The concept of dowry is primarily linked to familial wealth exchange before marriage, whereas mahr functions as a spousal right emphasizing consent and marital responsibility.
Key Differences Between Dowry and Mahr
Dowry involves the transfer of parental property, gifts, or money at the marriage of a daughter and is often negotiable or expected by the bride's family, whereas Mahr is a mandatory gift or payment from the groom to the bride stipulated in Islamic marriage contracts. Dowry can sometimes lead to social issues such as financial strain or dowry-related violence, while Mahr serves as a form of financial security and respect for the bride's rights. Your understanding of these key differences highlights the cultural and legal distinctions essential in marriage practices across various societies.
Legal Implications: Dowry vs. Mahr
Dowry, often considered a cultural gift from the bride's family to the groom, is illegal in many countries, including India, under the Dowry Prohibition Act of 1961, carrying strict legal penalties for both giving and receiving dowry. Mahr, in Islamic law, is a mandatory, specified gift from the groom to the bride, recognized as her lawful property with clear legal enforcement to protect her rights in marriage and divorce. The key legal distinction lies in dowry being a prohibited, often coercive practice contributing to social issues, while mahr is a legally binding entitlement designed to safeguard the bride's financial security.
Societal Impact of Dowry and Mahr Practices
Dowry and Mahr are distinct cultural practices with significant societal impacts; dowry often leads to financial burdens on the bride's family and can perpetuate gender inequality, while Mahr is a mandatory Islamic gift from the groom to the bride, symbolizing financial security and respect. The societal impact of dowry includes increased domestic violence and skewed gender ratios due to dowry-related stresses, whereas Mahr promotes women's empowerment by legally ensuring their financial rights in marriage. Your understanding of these differences highlights the importance of promoting Mahr over dowry to foster more equitable and respectful marital relationships.
Dowry-Related Issues and Controversies
Dowry practices often lead to significant social and legal challenges, including harassment, domestic violence, and financial exploitation against brides, undermining gender equality and human rights. Mahr, a mandatory Islamic marriage gift from the groom to the bride, is intended as a form of financial security and contrasts sharply with dowry demands that burden the bride's family. Understanding the distinct purposes and cultural implications of dowry and mahr helps you navigate and address dowry-related controversies effectively.
Mahr’s Role in Muslim Marriages
Mahr plays a critical role in Muslim marriages as a mandatory gift given by the groom to the bride, symbolizing respect and financial security, distinguishing it from dowry, which is typically provided by the bride's family. Unlike traditional dowry systems that often lead to social pressure and financial burden, Mahr is a voluntary and religiously enshrined obligation that protects the bride's rights and ensures her empowerment within the marriage. Understanding your rights regarding Mahr can strengthen the foundation of a Muslim marriage by emphasizing mutual respect and legal protection.
Towards Reform: Addressing Misconceptions and Promoting Ethical Practices
Dowry, Mahr, and dowry practices differ significantly, with Dowry often linked to social pressure and exploitation, while Mahr is an Islamic mandatory gift from the groom to the bride, ensuring her financial security. Misconceptions around these terms have fueled unethical customs, necessitating reforms that uphold women's rights and align cultural practices with legal frameworks. Your awareness of these distinctions can promote ethical practices and support progressive change in marriage traditions.
Infographic: Dowry vs Mahr
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com