Honor culture emphasizes reputation, social standing, and responding to insults with retaliation, while dignity culture values inherent self-worth and resolving conflicts through legal or social mechanisms. Explore the detailed differences and implications of honor and dignity cultures in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
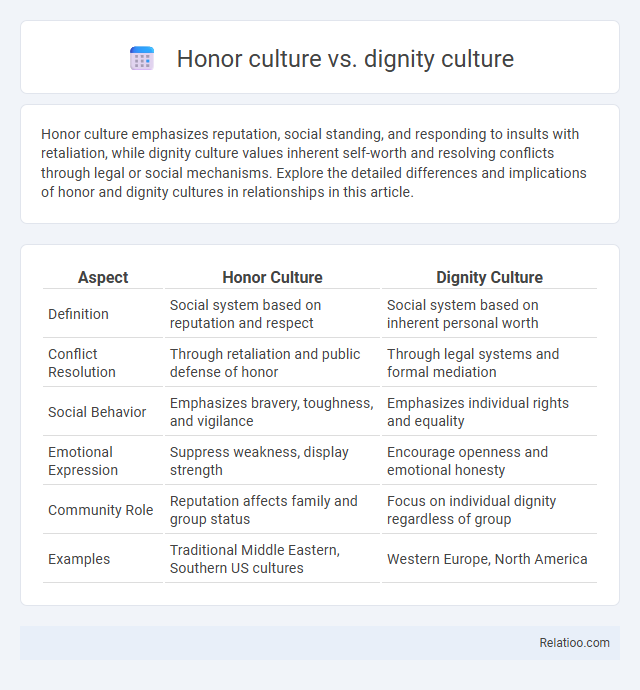
| Aspect | Honor Culture | Dignity Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social system based on reputation and respect | Social system based on inherent personal worth |
| Conflict Resolution | Through retaliation and public defense of honor | Through legal systems and formal mediation |
| Social Behavior | Emphasizes bravery, toughness, and vigilance | Emphasizes individual rights and equality |
| Emotional Expression | Suppress weakness, display strength | Encourage openness and emotional honesty |
| Community Role | Reputation affects family and group status | Focus on individual dignity regardless of group |
| Examples | Traditional Middle Eastern, Southern US cultures | Western Europe, North America |
Understanding Honor Culture: Core Values and Origins
Honor culture emphasizes personal reputation, social standing, and the defense of one's honor through retaliation to perceived slights or insults. Originating primarily in societies with a history of weak centralized authority and frequent conflicts, this culture values courage, loyalty, and social recognition as core principles. Understanding your role within an honor culture allows you to navigate social interactions by recognizing the importance of respect, reputation, and reciprocal behavior.
Defining Dignity Culture: Principles and Evolution
Dignity culture emphasizes inherent individual worth, advocating respect and equality regardless of social status, contrasting with honor culture's focus on reputation and social standing. Founded on principles of mutual respect, empathy, and non-violence, dignity culture has evolved through legal frameworks and human rights movements to promote peaceful conflict resolution. Its development reflects societal shifts toward valuing personal integrity and universal human rights over public reputation and honor-based retaliation.
Honor vs Dignity: Key Differences in Social Behavior
Honor culture centers on reputation and social standing, where individuals actively defend their honor through reputation management and retaliatory behavior. Dignity culture, by contrast, emphasizes intrinsic worth and self-respect, promoting conflict resolution through internal moral standards and legal systems. Your social behavior in an honor culture is shaped by community perception and external validation, whereas in a dignity culture, it is guided by personal integrity and universal rights.
Conflict Resolution: Retaliation or Reconciliation?
Honor culture prioritizes reputation and often resolves conflicts through retaliation to restore social standing, emphasizing personal and family honor. Dignity culture values inherent worth and typically encourages reconciliation and legal means to address disputes, promoting individual rights over social perception. Humility culture fosters conflict resolution through empathy and forgiveness, aiming to maintain social harmony and avoid escalation.
Social Status: Collective Reputation vs Individual Worth
Honor culture emphasizes social status through collective reputation, where your family's or community's honor is paramount and dictates behavior to preserve group standing. Dignity culture prioritizes individual worth, valuing personal integrity and inherent rights independent of external validation. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate social interactions by recognizing whether communal approval or personal respect governs social dynamics.
Impact on Gender Roles and Family Dynamics
Honor culture emphasizes reputation and social standing, often reinforcing strict gender roles where men are protectors and women uphold family honor, which can limit individual autonomy within family dynamics. Dignity culture promotes inherent self-worth and equality, encouraging more fluid gender roles and fostering family relationships based on mutual respect and individual rights. Your understanding of these cultural frameworks can reveal how deeply societal values shape gender expectations and family interactions.
Responses to Insults and Offenses
Honor culture emphasizes reputation and social standing, leading individuals to respond to insults with direct retaliation or public displays of toughness to restore their honor. Dignity culture values inherent self-worth, encouraging restraint and reliance on formal institutions rather than personal revenge when facing offenses. Face culture prioritizes maintaining social harmony and avoiding embarrassment, often responding to insults with subtle, indirect actions to preserve group cohesion.
Influence on Legal and Justice Systems
Honor culture emphasizes reputation and retribution, often leading to legal systems where personal vengeance and social status heavily influence justice outcomes. Dignity culture prioritizes inherent individual worth, promoting impartial legal frameworks that protect personal rights and aim for fair adjudication without bias. Understanding these cultural influences helps you navigate different justice systems by recognizing how societal values shape legal principles and enforcement practices.
Honor and Dignity in Modern Society
Honor culture emphasizes reputation and social standing, where individuals respond to challenges with assertiveness to protect their honor, often valuing public perception and community approval. Dignity culture, predominant in modern society, centers on inherent self-worth and individual rights, promoting internal self-respect rather than external validation. In contemporary contexts, dignity culture encourages legal frameworks and social norms that safeguard personal autonomy and discourage honor-based retaliation, highlighting a shift towards empathy and equality.
Bridging the Gap: Toward a Culture of Mutual Respect
Honor culture emphasizes reputation and social standing, where individuals respond to threats with assertive actions to defend their honor. Dignity culture values inherent human worth, promoting conflict resolution through legal and institutional norms rather than personal retaliation. Bridging the gap between these cultures requires fostering mutual respect by recognizing the importance of both personal honor and universal dignity in Your interactions and community dynamics.
Infographic: Honor culture vs Dignity culture
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com