Formal relationships emphasize structured communication and clear boundaries, often found in professional or official settings. Explore the nuances of formality versus informality in relationships and their impact on interpersonal dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
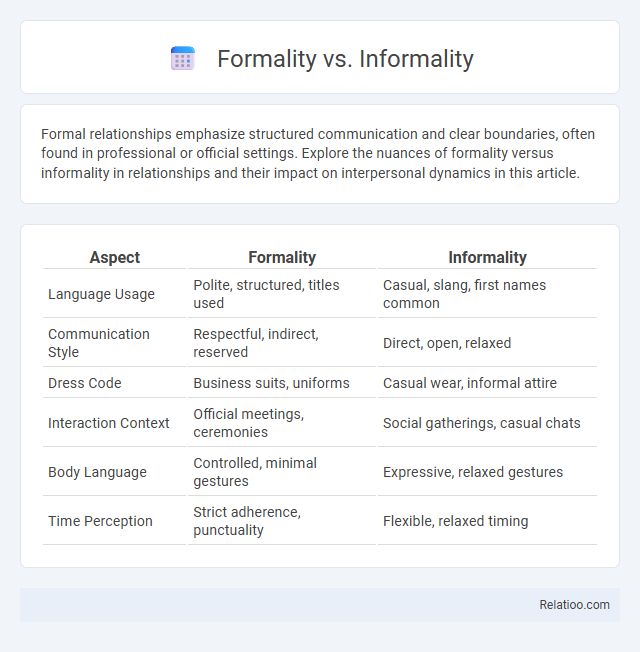
| Aspect | Formality | Informality |
|---|---|---|
| Language Usage | Polite, structured, titles used | Casual, slang, first names common |
| Communication Style | Respectful, indirect, reserved | Direct, open, relaxed |
| Dress Code | Business suits, uniforms | Casual wear, informal attire |
| Interaction Context | Official meetings, ceremonies | Social gatherings, casual chats |
| Body Language | Controlled, minimal gestures | Expressive, relaxed gestures |
| Time Perception | Strict adherence, punctuality | Flexible, relaxed timing |
Understanding Formality and Informality
Formality involves using structured language, respectful titles, and etiquette appropriate for official or professional settings, reflecting clear social hierarchies. Informality allows relaxed, casual communication, often employing slang and first names, which can minimize perceived social distance and foster comfort. Understanding these distinctions helps navigate social contexts effectively by matching language style to the expected social hierarchy and setting.
Historical Context of Formal and Informal Communication
Historical context reveals that formal communication often originated within hierarchical societies where strict social structures dictated language use as a marker of status and respect. Informal communication evolved as a more relaxed, spontaneous interaction style primarily among equals or close associates, reflecting social bonds rather than authority. Understanding this contrast enables you to navigate social hierarchies effectively by choosing appropriate communication styles for different cultural and professional environments.
Key Differences Between Formality and Informality
Formality involves structured communication marked by polite language, adherence to social norms, and professional tone, while informality features casual expressions, relaxed etiquette, and personal interactions. Social hierarchy influences the degree of formality expected; higher-status individuals often receive more formal communication to demonstrate respect and maintain authority. Understanding these key differences helps navigate social contexts and fosters appropriate interpersonal dynamics.
Benefits of Formal Communication
Formal communication enhances clarity and reduces misunderstandings by adhering to established protocols and structured language suited for hierarchical settings. It upholds professionalism and respect in organizational environments, reinforcing authority and role distinctions, which streamline decision-making processes. Such communication fosters accountability through documented exchanges, contributing to efficient information flow and organizational coherence.
Advantages of Informal Communication
Informal communication fosters faster decision-making and enhances creativity by allowing spontaneous exchanges without rigid protocols. It breaks down social hierarchy barriers, promoting inclusivity and stronger interpersonal relationships in your organization. By encouraging open dialogue, informal communication improves employee morale and facilitates a more agile response to challenges.
Common Settings for Formal Interactions
Formal interactions commonly occur in professional environments such as business meetings, academic conferences, and official ceremonies where clear social hierarchy dictates communication styles. In these settings, language tends to be respectful, precise, and devoid of slang, reflecting the roles and status of participants to maintain decorum. Your ability to navigate formality ensures effective communication and reinforces the social structure inherent in these common formal contexts.
Typical Situations for Informal Exchanges
Typical situations for informal exchanges often occur among friends, family members, or colleagues in relaxed environments such as social gatherings, casual meetings, or online chats. Your choice of language reflects familiarity and comfort, using colloquial phrases, slang, and contractions that are generally avoided in formal settings. Understanding these context-specific cues helps navigate social hierarchy appropriately, ensuring conversations remain respectful while fostering genuine connections.
Cultural Perspectives on Formality vs Informality
Cultural perspectives on formality versus informality deeply influence communication styles and social interactions, often reflecting underlying social hierarchies and respect norms. In collectivist societies, such as Japan and South Korea, formal language and rituals emphasize group harmony and hierarchical relationships, whereas individualistic cultures like the United States often favor informal, egalitarian communication to promote personal expression. Understanding these cultural nuances helps you navigate social contexts appropriately, ensuring respectful and effective exchanges across diverse environments.
Impact of Communication Style in the Workplace
Formality in workplace communication reinforces social hierarchy by establishing clear boundaries and respect between roles, enhancing clarity and professionalism. Informal communication fosters collaboration and openness, breaking down hierarchical barriers and encouraging innovation and trust among team members. Balancing formality and informality impacts employee engagement, productivity, and organizational culture by shaping perceptions of authority and inclusiveness.
Choosing the Right Tone: Guidelines and Best Practices
Choosing the right tone involves understanding the levels of formality appropriate for different social hierarchies and contexts to ensure effective communication. Formality often reflects respect and professionalism in hierarchical settings, while informality fosters approachability and relatability in peer-to-peer interactions. Best practices include assessing the audience's role, cultural expectations, and communication purpose to strike a balance that maintains clarity and rapport.
Infographic: Formality vs Informality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com