European relationship norms emphasize individual freedom and gender equality, prioritizing open communication and emotional expression. Middle Eastern relationship norms often focus on family involvement, traditional gender roles, and collective decision-making. Discover the cultural contrasts shaping these relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
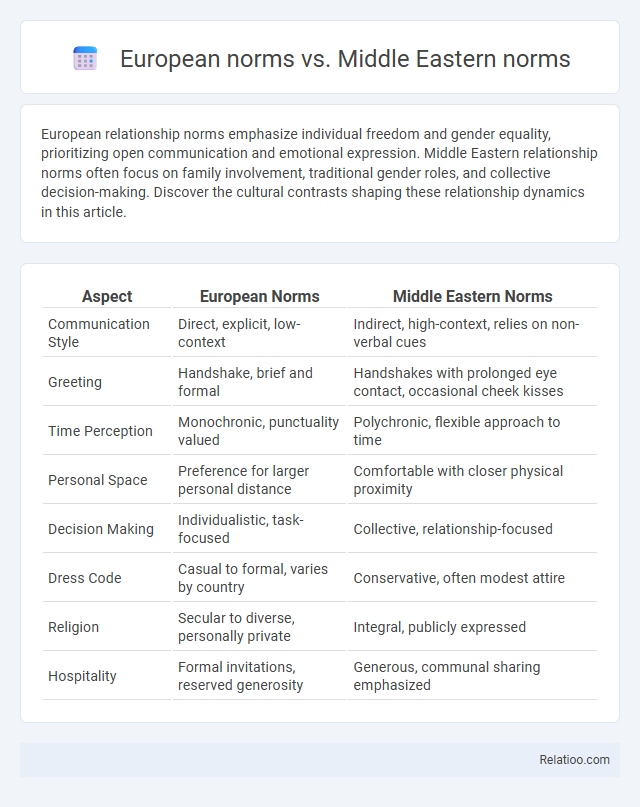
| Aspect | European Norms | Middle Eastern Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Direct, explicit, low-context | Indirect, high-context, relies on non-verbal cues |
| Greeting | Handshake, brief and formal | Handshakes with prolonged eye contact, occasional cheek kisses |
| Time Perception | Monochronic, punctuality valued | Polychronic, flexible approach to time |
| Personal Space | Preference for larger personal distance | Comfortable with closer physical proximity |
| Decision Making | Individualistic, task-focused | Collective, relationship-focused |
| Dress Code | Casual to formal, varies by country | Conservative, often modest attire |
| Religion | Secular to diverse, personally private | Integral, publicly expressed |
| Hospitality | Formal invitations, reserved generosity | Generous, communal sharing emphasized |
Introduction: Understanding European and Middle Eastern Norms
European norms often emphasize individualism, personal freedom, and legal recognition of same-sex relationships, reflecting a broad acceptance of LGBTQ+ rights across many countries. Middle Eastern norms tend to be shaped by traditional values, religious beliefs, and social conservatism, where same-sex relationships are largely unacknowledged or criminalized, creating significant legal and social challenges. Understanding the stark contrasts between these cultural and legal frameworks is essential for grasping the complexities of same-sex relationship recognition and acceptance in diverse regions.
Historical Foundations of Social Norms
European norms regarding same-sex relationships evolved from ancient Greek and Roman acceptance to widespread stigmatization influenced by Christian doctrines during the Middle Ages. In contrast, Middle Eastern norms have been historically shaped by Islamic jurisprudence and cultural practices that generally favor heterosexual unions, with varying interpretations and tolerance levels over time. Understanding these historical foundations helps you grasp why contemporary attitudes toward same-sex relationships differ significantly across these regions.
Family Structure and Roles
European norms regarding family structure and roles in same-sex relationships emphasize legal recognition, equal parental rights, and cohabitation as a legitimate family form, supported by progressive legislation like the European Union's anti-discrimination policies. Middle Eastern norms generally maintain traditional family structures centered on heterosexual marriage, with same-sex relationships often facing legal restrictions and social taboos, resulting in limited recognition and support for non-heteronormative family roles. These divergent approaches reflect broader cultural, religious, and legal frameworks that shape how family responsibilities, parenthood, and societal acceptance are defined and practiced in each region.
Attitudes Toward Gender and Equality
European norms generally emphasize progressive attitudes toward gender equality and strong legal protections for same-sex relationships, reflecting widespread societal acceptance. Middle Eastern norms tend to be more conservative, often influenced by religious and cultural traditions that limit public recognition and rights of same-sex couples and enforce traditional gender roles. These divergent attitudes shape policy frameworks, social acceptance, and individual experiences regarding gender and equality across the two regions.
Approaches to Religion and Secularism
European norms generally emphasize secularism with clear separation between religion and state, promoting legal recognition and protection of same-sex relationships. In contrast, many Middle Eastern societies integrate religious principles into laws, often leading to limited or no legal recognition of same-sex relationships and stronger societal opposition. The tension between traditional religious values and modern secular approaches highlights significant regional disparities in rights and acceptance for LGBTQ+ individuals.
Communication Styles and Politeness
European communication styles in same-sex relationships often emphasize directness and explicit verbal expression, reflecting broader cultural norms of clarity and individualism. Middle Eastern communication tends to be more indirect and context-dependent, with politeness strategies rooted in preserving honor, respect, and social harmony, which can affect openness in discussing same-sex relationships. Understanding these divergent communication patterns and politeness norms is critical for fostering respectful dialogue and inclusivity within diverse cultural contexts.
Hospitality and Social Gatherings
European norms often emphasize inclusivity and open acceptance of same-sex relationships at hospitality events, where guests are welcomed regardless of sexual orientation. Middle Eastern norms typically reflect conservative cultural and religious values, where same-sex relationships may not be openly acknowledged or accepted in social gatherings. In both contexts, the approach to hospitality varies significantly, with Europe leaning towards progressive, inclusive practices and the Middle East maintaining traditional, often private or discreet social interactions.
Work Ethic and Professional Behavior
European norms emphasize punctuality, direct communication, and a balanced work-life approach, fostering professional environments where diversity, including same-sex relationships, is increasingly accepted and protected. Middle Eastern norms often prioritize hierarchical respect and relationship-building, with workplace attitudes influenced by cultural and religious values that may affect openness towards same-sex relationships differently. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate professional behavior effectively across regions while respecting local expectations and inclusivity standards.
Dress Codes and Personal Appearance
European norms on dress codes in same-sex relationships often emphasize individual expression and gender neutrality, reflecting broader societal acceptance and legal protections. Middle Eastern norms tend to be more conservative, with strict dress codes influenced by cultural and religious values that prioritize modesty, often restricting public displays of same-sex relationships. These contrasting dress codes impact personal appearance, where Europeans may adopt diverse styles without social penalty, while Middle Eastern individuals face significant social and legal challenges when expressing identity through clothing.
Conflict Resolution and Negotiation Styles
European norms often emphasize direct communication and collaborative conflict resolution in same-sex relationships, promoting openness and equality. Middle Eastern norms may favor indirect negotiation styles, prioritizing harmony and family approval, which can lead to more discreet conflict handling. The contrast between these approaches highlights the cultural influence on resolving disputes and negotiating boundaries within same-sex partnerships.
Infographic: European norms vs Middle Eastern norms
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com