Western eldercare emphasizes professional services and independent living, while Eastern eldercare prioritizes family involvement and multigenerational support. Explore this article to understand the cultural contrasts shaping eldercare approaches worldwide.
Table of Comparison
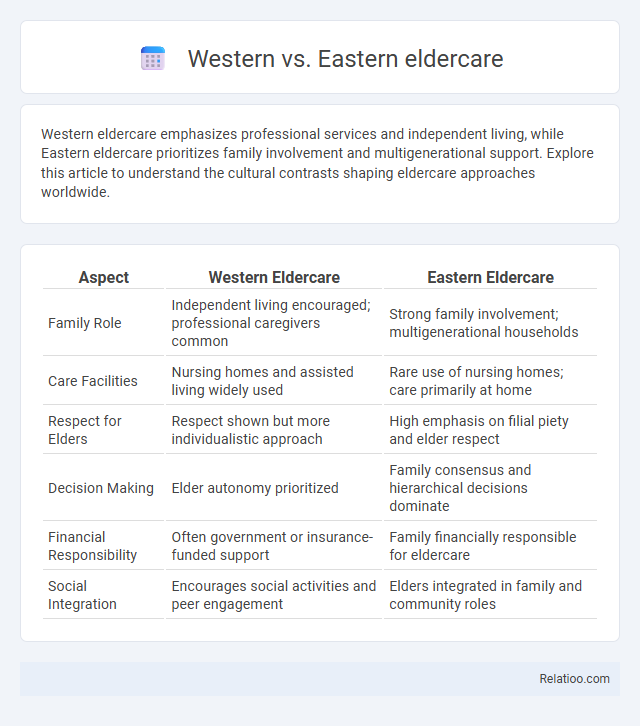
| Aspect | Western Eldercare | Eastern Eldercare |
|---|---|---|
| Family Role | Independent living encouraged; professional caregivers common | Strong family involvement; multigenerational households |
| Care Facilities | Nursing homes and assisted living widely used | Rare use of nursing homes; care primarily at home |
| Respect for Elders | Respect shown but more individualistic approach | High emphasis on filial piety and elder respect |
| Decision Making | Elder autonomy prioritized | Family consensus and hierarchical decisions dominate |
| Financial Responsibility | Often government or insurance-funded support | Family financially responsible for eldercare |
| Social Integration | Encourages social activities and peer engagement | Elders integrated in family and community roles |
Introduction to Western and Eastern Eldercare
Western eldercare emphasizes professional services, structured healthcare systems, and individual autonomy, often integrating advanced medical technology for aging populations. Eastern eldercare centers on familial responsibility, respect for elders, and community support, highlighting multigenerational living and traditional caregiving practices. Your understanding of these contrasting approaches can guide personalized care strategies that blend both Western efficiency and Eastern cultural values.
Historical Context of Eldercare in East and West
Western eldercare historically developed through institutional models like nursing homes and formal healthcare systems, reflecting industrialized societal shifts. Eastern eldercare centers on family-based care rooted in Confucian values emphasizing filial piety and multigenerational households. Understanding these cultural and historical contexts helps you navigate the differing expectations and support structures in eldercare practices worldwide.
Family Roles and Responsibilities
Western eldercare often emphasizes professional caregiving services and institutional care, reflecting a focus on individual independence and formal support systems. Eastern eldercare typically centers on multigenerational family involvement, where respecting and caring for elders is a deeply ingrained cultural value, often placing primary responsibility on adult children. Understanding these differing family roles and responsibilities can help You navigate eldercare decisions that align with your cultural values and personal needs.
Institutional vs Home-Based Care
Western eldercare predominantly emphasizes institutional care, with advanced nursing facilities and assisted living centers designed to provide medical support and social interaction for the elderly. Eastern eldercare favors home-based care rooted in family involvement and cultural respect for elders, promoting intergenerational living and personalized attention. Institutional care in the West offers specialized healthcare infrastructure, while Eastern home-based models leverage familial networks for emotional well-being and daily assistance.
Cultural Attitudes Toward Aging
Western eldercare often emphasizes independence and medical intervention, reflecting a cultural preference for individualism and formal support systems. Eastern eldercare typically centers on familial responsibility and respect for elders, rooted in Confucian values and multigenerational living arrangements. These cultural attitudes toward aging influence caregiving practices, elder support structures, and societal expectations in each region.
Government Policies and Support Systems
Government policies in Western eldercare emphasize formalized support systems, including comprehensive healthcare, pension schemes, and long-term care insurance, ensuring your access to professional services and financial aid. Eastern eldercare relies heavily on family-based care reinforced by cultural values and government programs promoting community support and home-based assistance. Both regions are advancing integrated models combining state resources and family involvement to enhance eldercare quality and accessibility.
Healthcare Approaches in Eldercare
Western eldercare emphasizes advanced medical technology and professional healthcare services, focusing on chronic disease management and individualized treatment plans. Eastern eldercare integrates holistic approaches, combining traditional medicine, family involvement, and community support to address physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being. Both healthcare approaches in eldercare prioritize improving quality of life but differ in balancing clinical intervention with cultural and familial values.
Social Integration and Community Support
Western eldercare often emphasizes individualized care plans and professional healthcare services, prioritizing autonomy and medical support. Eastern eldercare typically integrates multigenerational family involvement and community-based support systems, fostering strong social integration and collective responsibility. Your choice between these approaches can significantly impact social engagement and the quality of community connections for the elderly.
Challenges and Opportunities in Both Systems
Western eldercare faces challenges like high healthcare costs and workforce shortages, yet offers opportunities through advanced medical technologies and institutional care facilities. Eastern eldercare emphasizes familial support and community-based care, contending with demographic shifts and urbanization pressures, while benefiting from strong cultural values around respect for elders. Your choice between these systems depends on balancing personalized familial care with access to professional healthcare services tailored to aging populations.
Future Trends in Global Eldercare
Future trends in global eldercare reveal a shift toward integrating advanced technology such as AI-driven health monitoring and telemedicine, enhancing personalized care across Western and Eastern models. Western eldercare increasingly emphasizes autonomy and home-based care, while Eastern approaches maintain strong family involvement, influencing the development of hybrid care systems worldwide. Cross-cultural innovations and policy adaptations are projected to address the rising demand for sustainable, culturally sensitive eldercare solutions amid aging populations.
Infographic: Western vs Eastern eldercare
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com