Patriarchy enforces systemic male dominance, restricting women's rights and opportunities, while feminism advocates for gender equality and dismantling these oppressive structures. Discover the historical roots and modern implications of this conflict in this article.
Table of Comparison
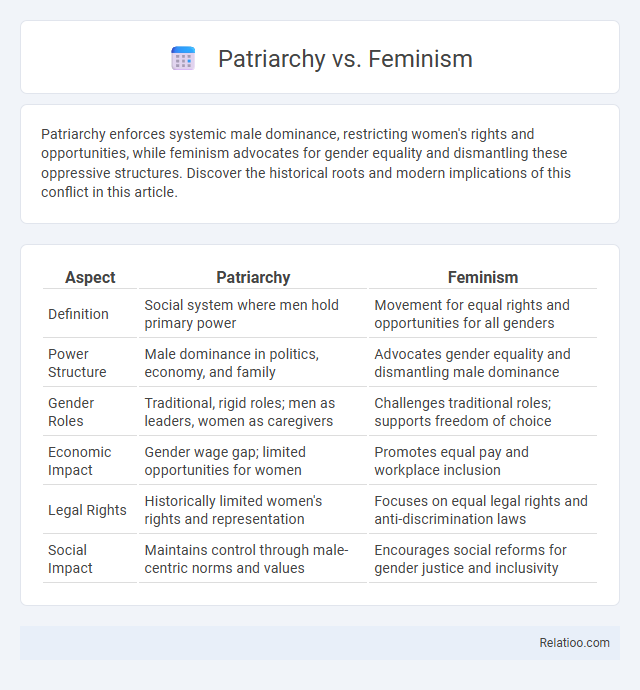
| Aspect | Patriarchy | Feminism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social system where men hold primary power | Movement for equal rights and opportunities for all genders |
| Power Structure | Male dominance in politics, economy, and family | Advocates gender equality and dismantling male dominance |
| Gender Roles | Traditional, rigid roles; men as leaders, women as caregivers | Challenges traditional roles; supports freedom of choice |
| Economic Impact | Gender wage gap; limited opportunities for women | Promotes equal pay and workplace inclusion |
| Legal Rights | Historically limited women's rights and representation | Focuses on equal legal rights and anti-discrimination laws |
| Social Impact | Maintains control through male-centric norms and values | Encourages social reforms for gender justice and inclusivity |
Understanding Patriarchy: Definition and History
Patriarchy is a social system where men hold primary power and predominate in roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property. Its roots trace back to ancient civilizations, evolving through cultural, religious, and legal frameworks that have reinforced male dominance for centuries. Understanding patriarchy helps you recognize its pervasive influence on societal structures and the ongoing feminist efforts to challenge and dismantle these inequities.
The Core Principles of Feminism
Feminism centers on equality, advocating for social, political, and economic rights for all genders, challenging the traditional patriarchal system that often prioritizes male dominance. The core principles emphasize dismantling gender-based oppression, promoting bodily autonomy, and fostering inclusivity across race, class, and sexual orientation. Understanding these values empowers Your ability to recognize and support gender equity in various aspects of society.
Patriarchy’s Influence on Social Structures
Patriarchy shapes social structures by establishing male dominance in political, economic, and family institutions, often restricting women's rights and opportunities. Your access to power and resources is influenced by these deeply ingrained gender hierarchies that prioritize masculine authority. Feminism challenges these norms by advocating for gender equality and dismantling systemic inequalities rooted in patriarchal traditions.
How Feminism Challenges Gender Norms
Feminism challenges gender norms by advocating for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, directly confronting patriarchal structures that enforce traditional roles. It promotes the dismantling of systemic inequalities such as wage gaps, limited political representation, and gender-based violence that patriarchy often perpetuates. You can contribute to this shift by supporting inclusive policies and fostering environments where diverse gender identities are respected and empowered.
Power Dynamics: Male Privilege vs Gender Equality
Patriarchy enforces power dynamics by institutionalizing male privilege, granting men greater access to resources, decision-making, and social status, which perpetuates gender inequality. Feminism challenges these structures by advocating for equal rights, opportunities, and representation for all genders, aiming to dismantle systemic biases and redistribute power more equitably. The conflict between patriarchy and feminism centers on transforming entrenched power imbalances to achieve gender equality and social justice.
The Role of Media in Shaping Gender Narratives
The media plays a pivotal role in shaping and perpetuating gender narratives within the contexts of patriarchy and feminism by reinforcing traditional gender roles or challenging them through diverse representation. Patriarchal media often emphasizes male dominance and female subordination, perpetuating stereotypes that influence societal expectations and behaviors. Your awareness of these media portrayals can empower you to critically evaluate gender norms and support more equitable and inclusive media narratives.
Cultural Perspectives: Patriarchy and Feminism Around the World
Patriarchy manifests differently across cultures, often rooted in historical traditions, religious beliefs, and social hierarchies that prioritize male authority and gender roles. Feminism challenges these structures through diverse global movements advocating for gender equality, women's rights, and social justice, with approaches varying from Western liberal feminism to intersectional and indigenous feminist frameworks. Cultural perspectives shape how societies accept or resist feminist ideologies, influencing legal reforms, educational opportunities, and representation in political and economic spheres worldwide.
Intersectionality: Race, Class, and Gender
Intersectionality examines how overlapping social identities, such as race, class, and gender, shape experiences within patriarchy and feminism by revealing nuanced layers of oppression. You can better understand that patriarchal systems disproportionately marginalize women of color and lower socioeconomic status due to compounded discrimination. Incorporating intersectionality into feminist discourse ensures that advocacy addresses diverse realities, fostering inclusivity beyond a singular focus on gender.
Modern Movements: Progress and Backlash
Modern movements around patriarchy and feminism reveal significant progress in gender equality, with increased advocacy for women's rights, representation, and policy changes combating systemic discrimination. However, these advances also trigger backlash from groups defending traditional patriarchal structures, exemplified by rising anti-feminist rhetoric and efforts to undermine gender-equal legislation. Ongoing debates emphasize the complex interplay between progress toward feminist goals and resistance seeking to maintain established power dynamics.
Toward a Gender-Equal Future: Bridging Patriarchy and Feminism
Toward a gender-equal future requires addressing the entrenched structures of patriarchy that perpetuate gender inequalities by limiting women's social, economic, and political opportunities. Feminism challenges these power imbalances, advocating for equal rights, representation, and dismantling systemic discrimination. Bridging patriarchy and feminism involves fostering dialogue that respects cultural nuances while promoting inclusive reforms to create equitable societies.
Infographic: Patriarchy vs Feminism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com