Future-oriented cultures prioritize innovation, planning, and long-term goals, while past-oriented cultures emphasize traditions, history, and established customs in shaping relationships. Explore deeper insights on how these cultural orientations influence interpersonal dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
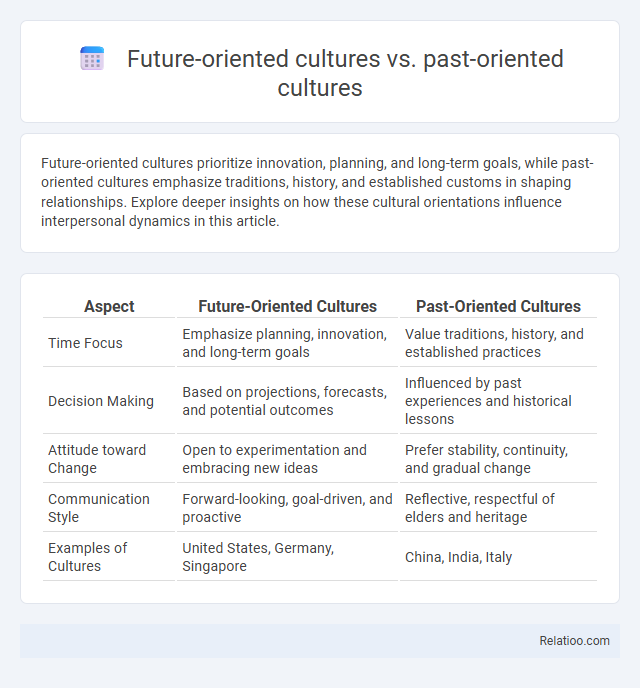
| Aspect | Future-Oriented Cultures | Past-Oriented Cultures |
|---|---|---|
| Time Focus | Emphasize planning, innovation, and long-term goals | Value traditions, history, and established practices |
| Decision Making | Based on projections, forecasts, and potential outcomes | Influenced by past experiences and historical lessons |
| Attitude toward Change | Open to experimentation and embracing new ideas | Prefer stability, continuity, and gradual change |
| Communication Style | Forward-looking, goal-driven, and proactive | Reflective, respectful of elders and heritage |
| Examples of Cultures | United States, Germany, Singapore | China, India, Italy |
Understanding Temporal Orientations in Culture
Understanding temporal orientations in culture reveals how future-oriented cultures prioritize innovation, planning, and long-term goals, while past-oriented cultures emphasize traditions, history, and maintaining established values. Your approach to time shapes decision-making processes, communication styles, and societal expectations in different cultural contexts. Recognizing these distinctions enhances cross-cultural interactions and improves global collaboration by aligning temporal perspectives effectively.
Defining Future-Oriented Cultures
Future-oriented cultures prioritize long-term planning, innovation, and goal-setting, emphasizing progress and adaptability in personal and professional contexts. These societies value delayed gratification and invest in education, technology, and sustainability to ensure future success and societal well-being. Contrasting with past-oriented cultures, which focus on tradition and historical continuity, future-oriented cultures drive economic growth and foster environments conducive to entrepreneurial ventures.
Characteristics of Past-Oriented Cultures
Past-oriented cultures emphasize traditions, customs, and historical continuity, valuing respect for ancestors and long-established social norms. These cultures prioritize preserving heritage and lessons learned from previous generations, often showing reluctance toward rapid change or innovation. Understanding your own or others' time orientation can improve communication and collaboration across diverse cultural contexts.
Time Perception and Its Cultural Impact
Time perception varies significantly between future-oriented and past-oriented cultures, influencing how individuals prioritize goals, traditions, and decision-making processes. Future-oriented cultures emphasize planning, innovation, and progress, encouraging you to focus on long-term achievements, whereas past-oriented cultures value heritage, continuity, and preserving historical knowledge. This cultural time orientation shapes communication styles, business practices, and social interactions by affecting the importance placed on deadlines, flexibility, and respect for tradition.
Decision Making: Past vs Future Focus
In decision making, future-oriented cultures emphasize long-term planning, innovation, and adaptability, often prioritizing potential outcomes and growth opportunities, while past-oriented cultures rely heavily on tradition, experience, and historical context to guide choices. Your approach in a future-focused culture encourages proactive risk assessment and strategic foresight, contrasting with the reflective, stability-seeking decisions typical of past-oriented societies. Understanding the time orientation of a culture enhances your ability to navigate decision-making processes effectively within diverse organizational or social environments.
Influence on Education and Learning Styles
Future-oriented cultures emphasize goal-setting, innovation, and long-term planning, fostering educational environments that encourage critical thinking, adaptability, and technology integration. Past-oriented cultures prioritize tradition, historical knowledge, and respect for established norms, often favoring rote memorization, teacher-centered classrooms, and preservation of cultural heritage in learning styles. Time orientation shapes education by influencing motivation, curriculum design, and pedagogical approaches, impacting how students engage with material and develop cognitive skills.
Approaches to Innovation and Tradition
Future-oriented cultures prioritize innovation by embracing change, investing in new technologies, and encouraging risk-taking to drive progress. Past-oriented cultures emphasize tradition, valuing historical continuity and maintaining established customs as a foundation for social stability. Your approach to innovation or tradition can significantly influence organizational strategies and adaptability within varied time orientation frameworks.
Impacts on Work Ethic and Productivity
Future-oriented cultures emphasize goal-setting, innovation, and long-term planning, leading to proactive work ethics and sustained productivity growth. Past-oriented cultures prioritize tradition, experience, and historical lessons, which can foster stability but may limit adaptability and rapid change in work practices. Time orientation directly impacts workplace motivation, decision-making speed, and the effectiveness of productivity strategies across different cultural contexts.
Cross-Cultural Communication Challenges
Future-oriented cultures prioritize innovation, long-term planning, and adaptability, often embracing change and progress in cross-cultural communication. Past-oriented cultures emphasize tradition, historical values, and stability, which can lead to resistance when confronted with future-focused perspectives. Understanding these time orientations helps mitigate communication challenges by aligning expectations and fostering respect for differing temporal priorities in intercultural interactions.
Balancing Past and Future in Global Societies
Future-oriented cultures prioritize innovation, long-term planning, and adaptability, while past-oriented cultures emphasize tradition, heritage, and preserving established norms. Time orientation in global societies shapes decision-making, communication styles, and organizational behavior, influencing economic development and social cohesion. Balancing past and future perspectives fosters cultural resilience, allowing societies to honor their history while embracing progress and sustainable growth.
Infographic: Future-oriented cultures vs Past-oriented cultures
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com