Understanding the difference between a trigger and a reaction is essential for improving relationship dynamics. Explore effective strategies to manage triggers and respond thoughtfully in this article.
Table of Comparison
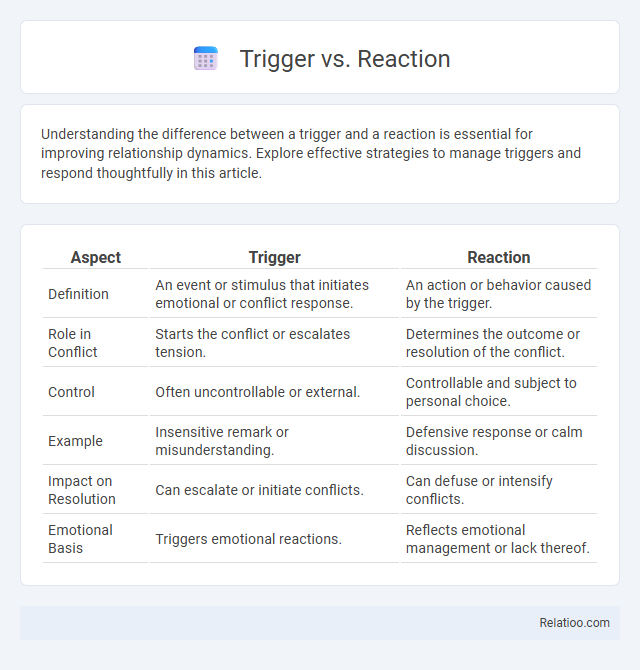
| Aspect | Trigger | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An event or stimulus that initiates emotional or conflict response. | An action or behavior caused by the trigger. |
| Role in Conflict | Starts the conflict or escalates tension. | Determines the outcome or resolution of the conflict. |
| Control | Often uncontrollable or external. | Controllable and subject to personal choice. |
| Example | Insensitive remark or misunderstanding. | Defensive response or calm discussion. |
| Impact on Resolution | Can escalate or initiate conflicts. | Can defuse or intensify conflicts. |
| Emotional Basis | Triggers emotional reactions. | Reflects emotional management or lack thereof. |
Understanding Triggers and Reactions
Understanding triggers involves recognizing specific stimuli or events that provoke emotional or behavioral responses, which are often automatic and subconscious. Reactions refer to the immediate, often instinctive, responses triggered by these stimuli, reflecting individual coping mechanisms or past experiences. Differentiating triggers from reactions is crucial for developing emotional awareness and implementing effective strategies for managing stress, anxiety, and interpersonal conflicts.
Key Differences Between Triggers and Reactions
Triggers are external or internal stimuli that provoke an emotional or behavioral response, whereas reactions are the actual responses to these triggers, often influenced by past experiences and personal coping mechanisms. The key difference lies in the origin and nature: triggers initiate the process by activating memory or emotion, while reactions are the conscious or unconscious behaviors or feelings that follow. Understanding these distinctions helps you manage your responses more effectively by identifying triggers before they lead to overwhelming reactions.
The Psychology Behind Triggers
Triggers activate specific emotional or physiological responses rooted in past experiences, often linked to the brain's amygdala and hippocampus. Your reaction is the immediate, sometimes subconscious, behavior or feeling resulting from that trigger, shaped by learned coping mechanisms and neural pathways. Understanding the psychology behind triggers helps you recognize patterns and develop strategies to manage responses effectively.
How Reactions Manifest Emotionally and Physically
Triggers activate emotional responses by stimulating memories or associations, causing immediate feelings like anxiety, anger, or sadness. Your reaction manifests both emotionally and physically through symptoms such as increased heart rate, muscle tension, sweating, or tears. Recognizing these signs helps manage your response and reduce the impact of emotional triggers effectively.
Common Types of Triggers
Common types of triggers include emotional triggers such as stress, fear, or past trauma that activate strong reactions. Sensory triggers involve sights, sounds, or smells linked to specific memories or experiences, often prompting immediate emotional or physical responses. Behavioral triggers stem from specific actions or environments, causing automatic reactions based on learned associations.
Typical Behavioral Reactions to Triggers
Typical behavioral reactions to triggers vary widely but often include fight, flight, or freeze responses that are instinctively activated by perceived threats. Your reaction may involve increased heart rate, heightened alertness, or impulsive actions aimed at self-preservation or emotional avoidance. Understanding these patterns helps manage your responses more effectively and reduce negative outcomes.
The Role of Awareness in Managing Triggers and Reactions
Awareness plays a crucial role in managing triggers and reactions by enabling individuals to identify specific stimuli that provoke emotional or behavioral responses. Recognizing these triggers allows for conscious intervention before automatic reactions occur, promoting greater self-control and emotional regulation. Developing mindfulness practices enhances this awareness, reducing impulsive responses and fostering healthier coping mechanisms.
Strategies to Identify Your Personal Triggers
Recognizing your personal triggers involves paying close attention to emotional responses and patterns in situations where stress or discomfort arises. Keeping a detailed journal of these incidents, including the context and your reactions, helps you discern specific trigger points. By understanding these triggers, you can develop tailored strategies to manage your reactions and improve emotional resilience effectively.
Techniques to Control and Redirect Your Reactions
Techniques to control and redirect your reactions involve mindfulness practices that help identify triggers before they escalate into emotional responses, enabling a conscious pause to choose healthier actions. Cognitive-behavioral strategies such as reframing negative thoughts and grounding exercises increase emotional regulation by shifting focus away from immediate reactions toward deliberate responses. Consistent use of these methods enhances self-awareness and resilience, reducing the intensity and frequency of reactive behaviors triggered by stress or external stimuli.
Building Resilience: Healthy Responses to Triggers
Building resilience involves recognizing triggers as specific external or internal stimuli that provoke emotional or behavioral reactions. Developing healthy responses requires mindfulness and self-regulation techniques to pause and choose constructive actions rather than automatic reactions. Strengthening resilience enhances emotional stability, reduces stress impact, and fosters adaptive coping mechanisms during challenging situations.
Infographic: Trigger vs Reaction
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com