Disappointment arises from unmet expectations, while sadness is a broader emotional response to loss or hurt in relationships. Explore the key differences and coping strategies in this article.
Table of Comparison
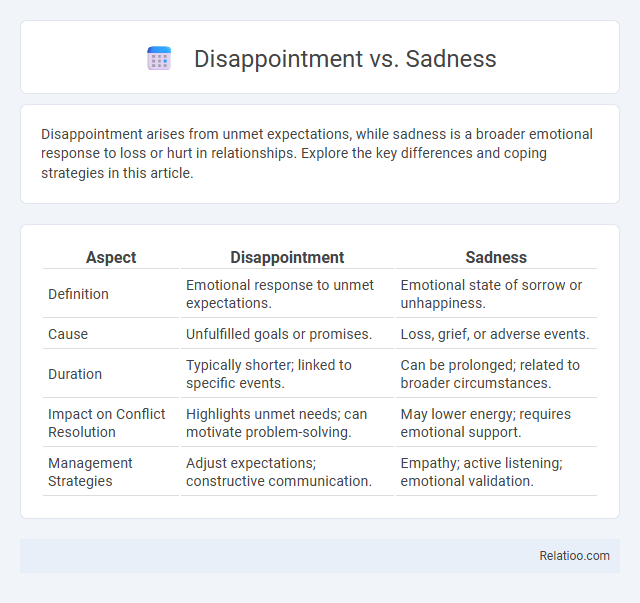
| Aspect | Disappointment | Sadness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response to unmet expectations. | Emotional state of sorrow or unhappiness. |
| Cause | Unfulfilled goals or promises. | Loss, grief, or adverse events. |
| Duration | Typically shorter; linked to specific events. | Can be prolonged; related to broader circumstances. |
| Impact on Conflict Resolution | Highlights unmet needs; can motivate problem-solving. | May lower energy; requires emotional support. |
| Management Strategies | Adjust expectations; constructive communication. | Empathy; active listening; emotional validation. |
Understanding Disappointment: A Brief Overview
Disappointment arises when your expectations are not met, leading to feelings of frustration or letdown, which differ from sadness that stems from loss or grief and from regret that involves wishing things had happened differently. Understanding disappointment involves recognizing it as a temporary emotional response linked to unmet hopes, helping you manage reactions and build resilience. Identifying this distinction allows for healthier emotional processing and clearer communication about your feelings.
Defining Sadness: What Sets It Apart
Sadness is a fundamental human emotion characterized by feelings of loss, helplessness, or sorrow, often linked to specific events or experiences. Unlike disappointment, which arises from unmet expectations, sadness encompasses a broader, deeper emotional state that can persist independently of particular outcomes. This distinction highlights sadness as a more pervasive mood that influences overall emotional well-being beyond the immediate context of failed hopes.
The Emotional Triggers Behind Disappointment
Disappointment stems from unmet expectations or hopes, often triggered by specific events where outcomes fall short of anticipated goals. Sadness is a broader emotional state, arising from various sources such as loss, loneliness, or empathy, and does not necessarily involve broken expectations. Understanding the emotional triggers behind disappointment involves recognizing the cognitive gap between desired and actual results, highlighting its unique link to personal aspirations and future-oriented thinking.
Common Causes of Sadness
Common causes of sadness include experiences such as the loss of a loved one, unfulfilled desires, and feelings of loneliness or rejection. Chemical imbalances in the brain and chronic stress can also contribute to prolonged sadness. Understanding these triggers helps differentiate sadness from disappointment, which typically stems from unmet expectations or specific failures.
Physical and Psychological Symptoms Compared
Disappointment often triggers physical symptoms like muscle tension, headaches, and fatigue, while sadness typically manifests with tearfulness, low energy, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns. Psychologically, disappointment centers on unmet expectations and frustration, whereas sadness involves a deeper sense of loss and emotional pain. Both emotions can lead to decreased motivation, but disappointment usually resolves more quickly, whereas sadness may result in prolonged emotional impact or contribute to depression.
The Role of Expectations in Disappointment
Disappointment arises when your expectations are unmet, creating a gap between anticipated and actual outcomes, while sadness is a broader emotional response to loss or unfavorable situations. Expectations shape the intensity of disappointment, as higher or unrealistic expectations often lead to stronger feelings of letdown. Understanding this dynamic helps manage emotional responses more effectively by adjusting expectations to align with reality.
Coping Mechanisms for Sadness vs Disappointment
Sadness often arises from a personal loss or emotional pain and can be managed through emotional expression, seeking social support, and practicing mindfulness to process feelings. Disappointment typically results from unmet expectations and is effectively addressed by adjusting goals, reframing negative thoughts, and building resilience. Your coping strategy should align with the specific emotional experience, employing reflective techniques for sadness and proactive problem-solving for disappointment.
Impact on Mental Health: Disappointment and Sadness
Disappointment and sadness both significantly impact mental health by influencing emotional resilience and cognitive processing. Disappointment often triggers a sense of unmet expectations, leading to frustration and decreased motivation, while sadness typically manifests as a deeper, more prolonged emotional response that can reduce energy and disrupt daily functioning. Understanding these emotional reactions is crucial for developing coping strategies that mitigate their adverse effects on mental well-being.
How to Address Disappointment and Sadness in Everyday Life
Disappointment and sadness, while often intertwined, stem from different emotional experiences--disappointment arises from unmet expectations, whereas sadness is a broader response to loss or hardship. To address disappointment effectively, focus on adjusting your expectations and engaging in problem-solving strategies to regain control over your situation. Managing sadness involves allowing yourself to feel the emotion fully, seeking social support, and practicing self-care techniques to foster emotional healing and resilience.
When to Seek Help: Recognizing Chronic Emotional Distress
Chronic emotional distress marked by persistent disappointment, sadness, or feelings of hopelessness may indicate a deeper mental health issue requiring professional intervention. When these emotions interfere with daily functioning for weeks or months, manifesting as loss of interest, changes in appetite, or sleep disturbances, seeking help from a mental health specialist is crucial. Early recognition and treatment of conditions like depression or anxiety can significantly improve emotional well-being and quality of life.
Infographic: Disappointment vs Sadness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com