Emotional flooding occurs when overwhelming feelings block rational responses, while emotional reactivity involves immediate, intense reactions to triggers in relationships. Discover how managing these emotional states can improve your connection in this article.
Table of Comparison
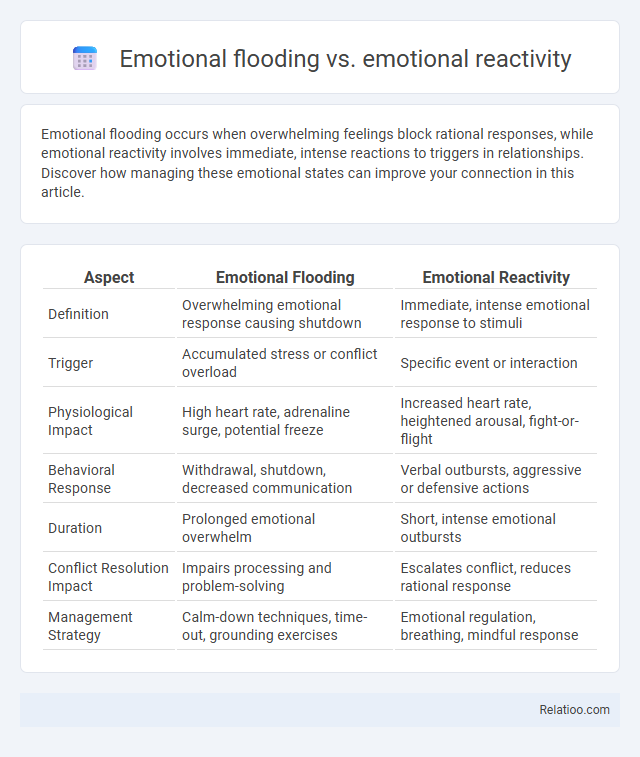
| Aspect | Emotional Flooding | Emotional Reactivity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overwhelming emotional response causing shutdown | Immediate, intense emotional response to stimuli |
| Trigger | Accumulated stress or conflict overload | Specific event or interaction |
| Physiological Impact | High heart rate, adrenaline surge, potential freeze | Increased heart rate, heightened arousal, fight-or-flight |
| Behavioral Response | Withdrawal, shutdown, decreased communication | Verbal outbursts, aggressive or defensive actions |
| Duration | Prolonged emotional overwhelm | Short, intense emotional outbursts |
| Conflict Resolution Impact | Impairs processing and problem-solving | Escalates conflict, reduces rational response |
| Management Strategy | Calm-down techniques, time-out, grounding exercises | Emotional regulation, breathing, mindful response |
Understanding Emotional Flooding
Emotional flooding occurs when an individual experiences an overwhelming surge of intense emotions, impairing their ability to think clearly or respond rationally. This state differs from emotional reactivity, which involves immediate and often impulsive reactions to emotional stimuli without the depth of being overwhelmed. Understanding emotional flooding is crucial for managing stress and improving emotional regulation, as it highlights the need to recognize early signs to prevent escalation in relationships and mental health challenges.
Defining Emotional Reactivity
Emotional reactivity refers to the intensity and speed with which an individual responds to emotional stimuli, often characterized by immediate and heightened emotional responses. Distinct from emotional flooding, which involves being overwhelmed by emotions to the point of cognitive impairment, emotional reactivity emphasizes the sensitivity and quickness of the emotional response rather than the level of overwhelming experience. Understanding emotional reactivity is crucial for managing interpersonal conflicts and improving emotional regulation strategies.
Key Differences Between Emotional Flooding and Reactivity
Emotional flooding involves an overwhelming surge of intense emotions that can incapacitate rational thinking, while emotional reactivity is characterized by immediate, often impulsive responses to emotional stimuli without necessarily losing control. Key differences between emotional flooding and reactivity include the level of emotional intensity, duration, and the impact on cognitive functioning; flooding typically results in prolonged emotional overwhelm and impaired decision-making, whereas reactivity may be brief and less disruptive. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for managing emotional responses effectively in clinical psychology and interpersonal communication contexts.
Causes of Emotional Flooding
Emotional flooding occurs when overwhelming stress triggers an intense surge of emotions, often caused by traumatic experiences, chronic stress, or unresolved conflict, leading to a loss of rational control. Emotional reactivity, by contrast, refers to a heightened sensitivity to emotional stimuli but may not reach the intensity of flooding. Your ability to recognize triggers such as personal vulnerability, threat perception, or high-pressure situations is crucial in managing emotional flooding effectively.
Triggers of Emotional Reactivity
Emotional reactivity is often triggered by perceived threats, unresolved past trauma, or high stress levels, leading to intense, immediate emotional responses. In contrast, emotional flooding occurs when these triggers overwhelm an individual's coping capacity, causing a flood of physiological and psychological reactions that impair rational thinking. Understanding specific triggers such as criticism, rejection, or reminders of past emotional wounds can help differentiate between emotional reactivity and the more intense state of emotional flooding.
Signs and Symptoms of Emotional Flooding
Emotional flooding manifests as intense overwhelm marked by rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and difficulty concentrating, often leading to shut down or aggressive responses. Emotional reactivity is characterized by impulsive reactions, heightened sensitivity, and mood swings triggered by external stimuli. Signs of emotional flooding include physical symptoms like sweating, muscle tension, and cognitive impairments such as memory lapses and distorted thinking patterns.
How Emotional Reactivity Manifests
Emotional reactivity manifests through intense, immediate responses to stimuli, often characterized by heightened physiological arousal, such as increased heart rate and rapid breathing. Your reactions may include impulsive behaviors, difficulty regulating emotions, and a tendency to perceive situations as more threatening than they are. Understanding these signs helps differentiate emotional reactivity from emotional flooding, where the overwhelming emotional experience can incapacitate rational thinking.
Impact on Relationships and Communication
Emotional flooding causes overwhelming feelings that disrupt effective communication and damage trust in relationships by triggering defensive or avoidant behaviors. Emotional reactivity, characterized by impulsive responses to perceived threats, often escalates conflicts and hinders problem-solving efforts between partners. Managing both emotional flooding and reactivity is crucial for maintaining healthy relationships and fostering open, constructive dialogue.
Coping Strategies for Emotional Flooding
Emotional flooding occurs when intense emotions overwhelm cognitive processing, leading to diminished problem-solving abilities and heightened physiological arousal, whereas emotional reactivity refers to automatic, often impulsive emotional responses to stimuli. Coping strategies for emotional flooding include deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, and grounding techniques that help reduce autonomic nervous system activation and restore emotional regulation. Implementing time-outs and cognitive restructuring can prevent escalation by allowing individuals to process emotions before reacting.
Effective Ways to Manage Emotional Reactivity
Emotional reactivity involves intense, immediate responses to triggers, while emotional flooding refers to being overwhelmed by these emotions to the point of losing rational control, often leading to destructive behavior. Effective ways to manage emotional reactivity include practicing mindfulness to increase self-awareness, using deep-breathing techniques to calm the nervous system, and developing cognitive restructuring skills to challenge and change unhelpful thought patterns. Your ability to regulate emotions improves by consistently applying these strategies, fostering resilience during emotionally charged situations.
Infographic: Emotional flooding vs Emotional reactivity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com