Suppression involves consciously pushing away unwanted thoughts or feelings in a relationship, while repression occurs unconsciously, burying emotions deeper within the subconscious. Explore the differences and impacts of suppression vs repression on relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
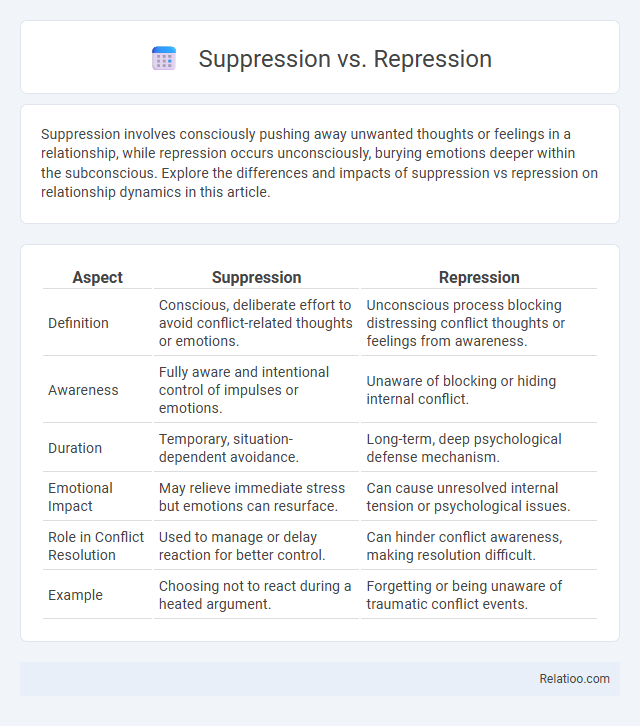
| Aspect | Suppression | Repression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conscious, deliberate effort to avoid conflict-related thoughts or emotions. | Unconscious process blocking distressing conflict thoughts or feelings from awareness. |
| Awareness | Fully aware and intentional control of impulses or emotions. | Unaware of blocking or hiding internal conflict. |
| Duration | Temporary, situation-dependent avoidance. | Long-term, deep psychological defense mechanism. |
| Emotional Impact | May relieve immediate stress but emotions can resurface. | Can cause unresolved internal tension or psychological issues. |
| Role in Conflict Resolution | Used to manage or delay reaction for better control. | Can hinder conflict awareness, making resolution difficult. |
| Example | Choosing not to react during a heated argument. | Forgetting or being unaware of traumatic conflict events. |
Understanding Suppression and Repression
Suppression involves the conscious decision to push unwanted thoughts or feelings out of immediate awareness, allowing temporary control over emotional responses. Repression, in contrast, is an unconscious defense mechanism where disturbing memories or desires are blocked from conscious access, often influencing behavior without awareness. Understanding the distinction is crucial in psychology, as suppression permits deliberate emotional regulation while repression can lead to unresolved psychological conflicts.
Defining Psychological Suppression
Psychological suppression involves the conscious effort to push distressing thoughts or feelings out of your awareness, distinguishing it from repression, which operates unconsciously. Suppression allows you to temporarily control emotions or memories, enabling focus on immediate tasks without being overwhelmed by negative experiences. Understanding suppression helps in managing emotional responses while maintaining mental clarity and intentional self-regulation.
Defining Psychological Repression
Psychological repression refers to the unconscious process by which distressing thoughts, memories, or desires are pushed out of conscious awareness to reduce anxiety and protect the individual from psychological harm. Unlike suppression, which is a deliberate and conscious effort to avoid certain thoughts or emotions, repression operates automatically without conscious control. Understanding repression is crucial in psychoanalytic theory, as it explains how unresolved conflicts influence behavior and emotional health.
Key Differences Between Suppression and Repression
Suppression involves the conscious decision to delay or avoid certain thoughts or feelings, allowing temporary control over unwanted emotions, whereas repression is an unconscious process where the mind automatically blocks distressing memories or desires from awareness. Suppression is deliberate and accessible to the individual's awareness, while repression operates involuntarily, often influencing behavior without the person realizing it. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial in psychological treatment, as suppression can be addressed through conscious effort, whereas repression may require therapeutic intervention to uncover hidden conflicts.
Mechanisms Behind Suppression
Suppression involves the conscious effort to push unwanted thoughts or feelings out of awareness, while repression is an unconscious process where distressing memories are automatically excluded from conscious mind. The mechanism behind suppression is deliberate cognitive control that allows you to decide which information to keep out of focus temporarily. This active management of thoughts helps in coping with immediate stressors but requires continuous mental effort to maintain.
Mechanisms Behind Repression
Repression involves the unconscious mechanism where distressing memories or desires are buried deep within the subconscious mind to protect Your emotional well-being from anxiety or trauma. Unlike suppression, which is a conscious effort to avoid thinking about uncomfortable thoughts, repression operates involuntarily, preventing awareness of painful experiences altogether. This dynamic process is central to theories of psychodynamics and can influence behavior without Your direct control or realization.
Suppression vs Repression: Real-Life Examples
Suppression and repression differ in conscious awareness; suppression is a deliberate effort to avoid certain thoughts, while repression occurs unconsciously, burying distressing memories deep in the subconscious. For example, you may consciously choose to suppress anxiety before a presentation, yet traumatic childhood memories may be repressed without your awareness, influencing behavior unknowingly. Understanding these distinctions helps in therapeutic contexts to identify whether a person's distress is a result of suppressed or repressed emotions.
Effects on Mental Health
Suppression involves consciously avoiding distressing thoughts, which can temporarily reduce anxiety but may lead to increased stress if overused. Repression unconsciously blocks traumatic memories, potentially causing unresolved emotional conflicts and symptoms like anxiety or depression. Understanding these mechanisms can help you recognize how they impact your mental health and guide effective coping strategies.
Therapeutic Approaches to Suppression and Repression
Therapeutic approaches to suppression focus on conscious techniques like mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help you intentionally manage distressing thoughts or emotions. In contrast, repression involves unconscious processes, addressed through psychoanalytic methods such as free association and dream analysis to uncover and resolve hidden conflicts. Understanding these mechanisms allows therapists to tailor interventions that promote emotional awareness and healing.
Choosing Healthier Coping Strategies
Choosing healthier coping strategies involves understanding the differences between suppression, repression, and avoidance; suppression is a conscious effort to delay processing emotions, allowing for intentional reflection and emotional regulation. Repression, an unconscious defense mechanism, blocks distressing thoughts from awareness, often leading to unresolved psychological tension. Avoidance, actively steering clear of stressors or emotions, can hinder emotional growth and prolong distress, making conscious suppression or therapeutic processing more adaptive for mental well-being.
Infographic: Suppression vs Repression
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com