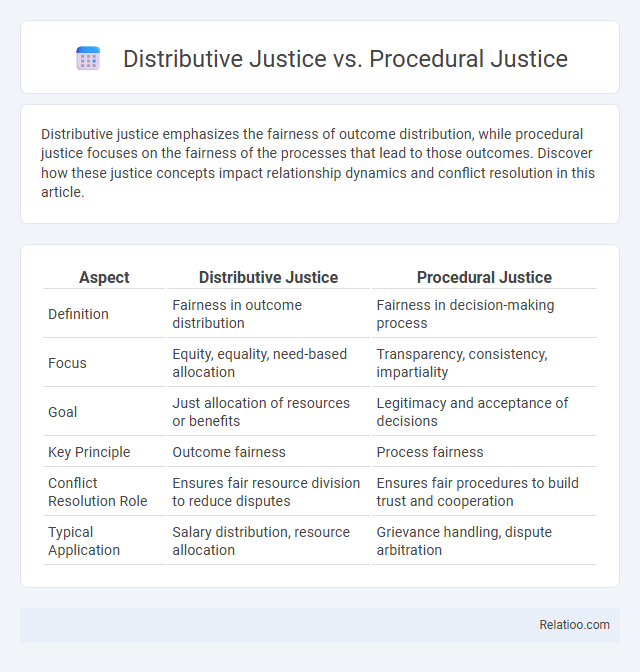
Distributive justice emphasizes the fairness of outcome distribution, while procedural justice focuses on the fairness of the processes that lead to those outcomes. Discover how these justice concepts impact relationship dynamics and conflict resolution in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Distributive Justice | Procedural Justice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fairness in outcome distribution | Fairness in decision-making process |
| Focus | Equity, equality, need-based allocation | Transparency, consistency, impartiality |
| Goal | Just allocation of resources or benefits | Legitimacy and acceptance of decisions |
| Key Principle | Outcome fairness | Process fairness |
| Conflict Resolution Role | Ensures fair resource division to reduce disputes | Ensures fair procedures to build trust and cooperation |
| Typical Application | Salary distribution, resource allocation | Grievance handling, dispute arbitration |
Introduction to Justice in Society
Distributive justice focuses on the fair allocation of resources and benefits among members of society, ensuring that your needs are met according to principles of equity or need. Procedural justice emphasizes the fairness of the processes and methods used to make decisions, highlighting transparency, consistency, and impartiality in societal governance. Equality aims to treat all individuals uniformly, promoting equal rights and opportunities regardless of personal differences or circumstances.
Defining Distributive Justice
Distributive Justice concerns the fair allocation of resources, benefits, and burdens among individuals or groups, ensuring outcomes are equitable based on needs, contributions, or merits. Procedural Justice emphasizes the fairness of the processes and methods used to make decisions rather than the outcomes themselves, while Equality focuses on providing the same level of resources or opportunities to everyone regardless of circumstances. Understanding Distributive Justice helps you evaluate whether resource distribution aligns with ethical principles of fairness and social justice.
Understanding Procedural Justice
Procedural justice emphasizes the fairness of the processes that lead to outcomes rather than the outcomes themselves, ensuring that Your voice is heard and decisions are made transparently and consistently. This type of justice builds trust and legitimacy by focusing on impartiality, consistency, and opportunities for input throughout decision-making. Understanding procedural justice is crucial for creating systems where individuals perceive fairness, regardless of whether they agree with the final distribution of resources or results.
Core Principles of Distributive Justice
Distributive justice centers on the equitable allocation of resources based on principles such as need, contribution, and merit, ensuring fairness in outcome distribution. Procedural justice emphasizes fairness in the processes and methods used to make decisions, safeguarding transparency and impartiality. Understanding these distinctions helps you evaluate justice systems by both how resources are shared and how decisions are made.
Key Elements of Procedural Justice
Key elements of procedural justice include consistency, neutrality, transparency, and the opportunity for voice, which ensure fair processes in decision-making. These components foster trust and legitimacy in institutions by emphasizing unbiased procedures over outcomes. In contrast to distributive justice, which focuses on equitable allocation of resources, and equality, which stresses uniform treatment, procedural justice prioritizes fair methods to achieve just outcomes.
Comparative Analysis: Distributive vs Procedural Justice
Distributive justice centers on the fair allocation of resources and benefits based on outcomes, while procedural justice emphasizes the fairness of the processes that lead to those outcomes, ensuring transparency and impartiality. Your understanding of justice systems improves by comparing these concepts, highlighting that a fair procedure can legitimize decisions even when outcomes are unequal. Studies show organizations with strong procedural justice often experience higher trust and cooperation, whereas distributive justice impacts perceptions of equity and satisfaction.
Examples in Legal and Social Systems
Distributive justice in legal and social systems often involves allocating resources or punishments fairly based on individual needs or contributions, such as sentencing guidelines that weigh the severity of a crime and the offender's background. Procedural justice emphasizes fairness in the processes that lead to decisions, exemplified by transparent court trials and unbiased hearings ensuring Your case is evaluated on evidence and proper protocol. Equality focuses on treating everyone the same, like universal access to public education or equal voting rights, ensuring no one is disadvantaged by systemic biases or discrimination.
Impacts on Social Trust and Fairness
Distributive justice, emphasizing equitable allocation of resources, directly influences perceptions of fairness, which strengthens social trust by ensuring individuals feel their needs are met fairly. Procedural justice, focusing on transparent and unbiased decision-making processes, enhances social trust by fostering legitimacy and respect for authority, regardless of outcomes. Equality promotes uniform treatment and equal opportunity, but without considering individual circumstances, it may weaken perceived fairness and social trust if outcomes are viewed as unjust or inequitable.
Debates and Criticisms
Distributive justice debates center on the fairness of outcome distributions, often criticized for neglecting individual circumstances and perpetuating inequality. Procedural justice challenges focus on whether decision-making processes are transparent and impartial, with critics arguing that fair procedures do not always guarantee just results. Equality discussions highlight tensions between equal treatment and equitable outcomes, questioning if emphasizing sameness overlooks structural disparities affecting Your access to resources and opportunities.
Conclusion: Finding Balance in Justice Systems
Distributive justice emphasizes fair allocation of resources, while procedural justice focuses on fairness in the processes that lead to outcomes, and equality stresses uniform treatment for all individuals. Effective justice systems must integrate these principles to ensure both equitable outcomes and transparent, unbiased procedures. Balancing distributive fairness, procedural integrity, and equal rights creates a comprehensive framework that promotes trust, legitimacy, and social stability.
Infographic: Distributive Justice vs Procedural Justice
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com