Emotional flooding occurs when intense feelings overwhelm the brain's ability to regulate stress, often triggering the fight or flight response during conflict in relationships. Understanding these reactions can improve emotional regulation and communication; learn more in this article.
Table of Comparison
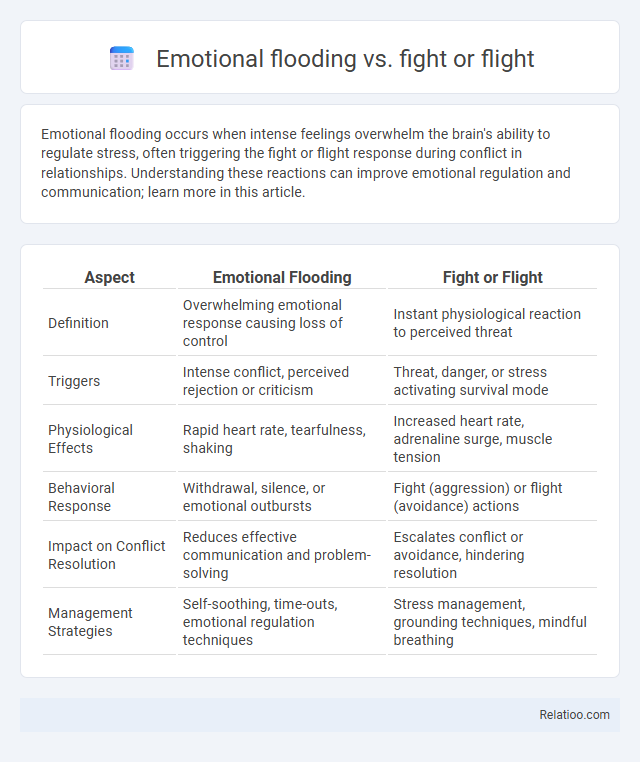
| Aspect | Emotional Flooding | Fight or Flight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overwhelming emotional response causing loss of control | Instant physiological reaction to perceived threat |
| Triggers | Intense conflict, perceived rejection or criticism | Threat, danger, or stress activating survival mode |
| Physiological Effects | Rapid heart rate, tearfulness, shaking | Increased heart rate, adrenaline surge, muscle tension |
| Behavioral Response | Withdrawal, silence, or emotional outbursts | Fight (aggression) or flight (avoidance) actions |
| Impact on Conflict Resolution | Reduces effective communication and problem-solving | Escalates conflict or avoidance, hindering resolution |
| Management Strategies | Self-soothing, time-outs, emotional regulation techniques | Stress management, grounding techniques, mindful breathing |
Understanding Emotional Flooding
Understanding emotional flooding involves recognizing an overwhelming surge of intense feelings that impair rational thinking and escalate stress levels beyond typical fight or flight responses. Unlike the immediate physiological reactions of fight or flight, emotional flooding causes prolonged mental distress, disrupting decision-making and communication. Managing emotional flooding requires strategies to calm the nervous system and restore cognitive control to prevent escalation into reactive or defensive behaviors.
The Science Behind Fight or Flight
The science behind the fight or flight response involves the amygdala detecting threats and triggering the hypothalamus to activate the sympathetic nervous system, releasing adrenaline and cortisol to prepare the body for immediate action. Emotional flooding occurs when intense emotions overwhelm this physiological response, causing cognitive overload and impairing decision-making. Unlike the rapid fight or flight reaction, emotional flooding sustains heightened arousal, often leading to prolonged stress and difficulty in emotional regulation.
Key Differences: Emotional Flooding vs Fight or Flight
Emotional flooding involves an overwhelming surge of intense emotions that impair rational thinking and decision-making, often triggered by stress or trauma. Fight or flight is an automatic physiological response to perceived danger, activating the sympathetic nervous system to prepare the body for immediate action. Key differences lie in emotional flooding's cognitive and emotional overwhelm versus fight or flight's physical readiness for survival.
Triggers of Emotional Flooding
Emotional flooding occurs when overwhelming feelings trigger an intense physiological response, often surpassing your ability to manage emotions effectively. Unlike fight or flight, which activates a survival mechanism to confront or escape threats, emotional flooding is triggered by acute stressors such as criticism, rejection, or conflict that flood the brain with cortisol and adrenaline. Identifying common triggers like relational disputes, perceived threats to self-esteem, or unexpected negative feedback helps in recognizing and managing these intense emotional reactions before they escalate.
Biological Mechanisms of the Fight or Flight Response
The fight or flight response triggers rapid hormonal changes, like adrenaline and cortisol release, activating your sympathetic nervous system for immediate physical reaction. Emotional flooding occurs when overwhelming emotions surpass your brain's regulatory capacity, intensifying the physiological arousal characteristic of fight or flight. Understanding these biological mechanisms helps you manage stress responses more effectively, reducing the impact of emotional flooding on your mental and physical health.
Emotional Flooding in Relationships
Emotional flooding in relationships occurs when overwhelming emotions, such as anger or sadness, trigger a physiological response that impairs your ability to think clearly and communicate effectively. Unlike the fight or flight response, which prepares your body for immediate action in the face of danger, emotional flooding leads to a shutdown or emotional withdrawal, making conflict resolution difficult. Recognizing and managing emotional flooding is crucial for maintaining healthy communication and preventing escalation during relationship conflicts.
Long-term Effects of Chronic Fight or Flight
Chronic activation of the fight-or-flight response leads to prolonged exposure to stress hormones like cortisol, resulting in long-term effects such as impaired immune function, cardiovascular problems, and increased risk of anxiety disorders. Emotional flooding, characterized by overwhelming emotional arousal, can exacerbate the physiological impacts of chronic stress by disrupting emotional regulation and cognitive processing. Persistent emotional flooding combined with ongoing fight-or-flight activation contributes to sustained psychological distress and worsens both mental and physical health outcomes over time.
Coping Strategies for Emotional Flooding
Emotional flooding occurs when overwhelming emotions impair cognitive processing, triggering fight or flight responses that amplify stress and anxiety. Coping strategies for emotional flooding emphasize mindfulness techniques, grounding exercises, and controlled breathing to regain emotional regulation and prevent impulsive reactions. Developing self-awareness through journaling and therapy enhances resilience, enabling individuals to recognize early signs of flooding and employ adaptive responses effectively.
Managing and Calming the Fight or Flight Response
Managing the fight or flight response involves recognizing the physiological signs of emotional flooding, such as increased heart rate and rapid breathing, and employing calming techniques like deep breathing or grounding exercises to restore balance. You can reduce the intensity of emotional flooding by consciously shifting focus away from stress triggers and using mindfulness strategies to calm your nervous system. Effective management of these responses enhances emotional regulation and prevents overwhelming feelings from escalating into reactive behaviors.
Building Emotional Resilience for Both Responses
Emotional flooding occurs when overwhelming emotions exceed your ability to cope, triggering intense stress responses similar to fight-or-flight reactions characterized by adrenaline surges preparing the body for immediate action. Building emotional resilience involves recognizing these physiological and psychological signals early, practicing mindfulness, and developing coping strategies that regulate emotional intensity and improve self-awareness. Strengthening your emotional resilience supports balanced responses to stress, reduces impulsive reactions, and enhances adaptive regulation in both emotional flooding and fight-or-flight situations.
Infographic: Emotional flooding vs Fight or flight
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com