Peacekeeping involves maintaining ceasefires and monitoring conflicts to prevent violence, while peacebuilding focuses on addressing root causes of conflict through social, political, and economic reforms. Explore this article to understand how these strategies complement each other in sustaining long-term peace.
Table of Comparison
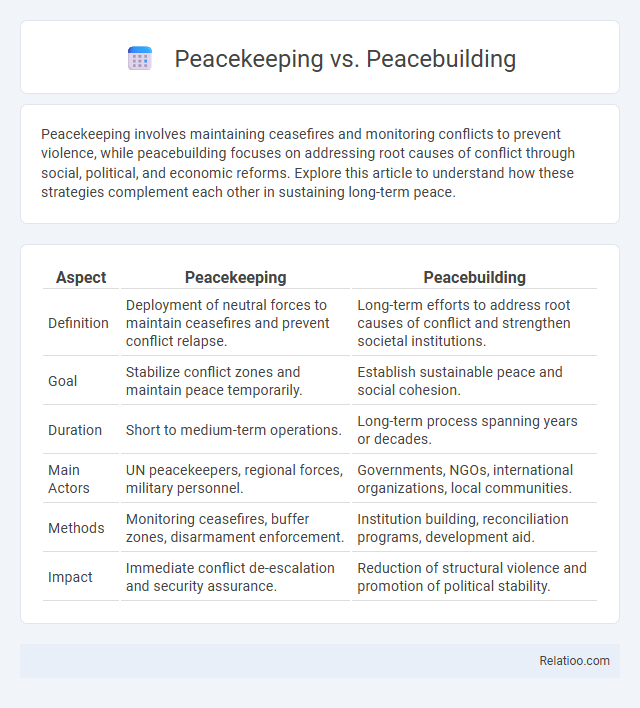
| Aspect | Peacekeeping | Peacebuilding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deployment of neutral forces to maintain ceasefires and prevent conflict relapse. | Long-term efforts to address root causes of conflict and strengthen societal institutions. |
| Goal | Stabilize conflict zones and maintain peace temporarily. | Establish sustainable peace and social cohesion. |
| Duration | Short to medium-term operations. | Long-term process spanning years or decades. |
| Main Actors | UN peacekeepers, regional forces, military personnel. | Governments, NGOs, international organizations, local communities. |
| Methods | Monitoring ceasefires, buffer zones, disarmament enforcement. | Institution building, reconciliation programs, development aid. |
| Impact | Immediate conflict de-escalation and security assurance. | Reduction of structural violence and promotion of political stability. |
Understanding Peacekeeping and Peacebuilding
Peacekeeping involves the deployment of international military and police forces to maintain ceasefires and create a stable environment, preventing the resurgence of conflict. Peacebuilding focuses on addressing the root causes of conflict through political, social, and economic reforms to foster long-term peace and stability. Understanding the distinction clarifies that peacekeeping is primarily a short-term security measure, while peacebuilding aims for sustainable development and reconciliation.
Key Objectives of Peacekeeping
Peacekeeping primarily aims to maintain ceasefires, monitor troop withdrawals, and protect civilians in conflict zones to create a secure environment. Your understanding of peacekeeping's key objectives highlights its role in preventing the resurgence of violence while supporting political processes. This contrasts with peacebuilding, which focuses on addressing root causes of conflict, and reconstruction, which involves rebuilding infrastructure and institutions after hostilities end.
Core Principles of Peacebuilding
Peacebuilding centers on sustainable conflict resolution by addressing root causes, promoting social cohesion, and strengthening governance structures to prevent relapse into violence. Core principles include inclusivity, local ownership, and a holistic approach that integrates political, social, and economic dimensions. Your engagement in peacebuilding efforts ensures long-term stability by fostering accountability, reconciliation, and resilience within affected communities.
Main Actors Involved: Peacekeepers vs. Peacebuilders
Peacekeepers, typically deployed by the United Nations or regional organizations, primarily consist of military personnel, police forces, and observers whose main role is to maintain ceasefires and provide security in conflict zones. Peacebuilders, on the other hand, include international NGOs, development agencies, local governments, and civil society groups focused on addressing root causes of conflict through governance reforms, reconciliation, and economic development. While reconstruction involves governments and international financial institutions working on rebuilding infrastructure and institutions post-conflict, peacekeepers and peacebuilders often collaborate to create a secure environment conducive to sustainable recovery and development.
Operational Approaches: Comparing Strategies
Peacekeeping operations focus on maintaining ceasefires and ensuring security through the deployment of neutral forces, often under the United Nations mandate, emphasizing monitoring and conflict containment. Peacebuilding strategies prioritize long-term stability by addressing root causes of conflict, promoting governance reforms, and supporting social cohesion through inclusive political processes and development programs. Reconstruction involves rebuilding infrastructure, restoring public services, and revitalizing economic activities post-conflict, requiring coordinated efforts among international agencies, governments, and local communities to ensure sustainable recovery aligned with Your region's needs.
Challenges in Implementing Peacekeeping
Implementing peacekeeping operations faces significant challenges such as limited resources, complex mandates, and resistance from local factions, which hinder maintaining stability and security in conflict zones. Your efforts can be complicated by inadequate coordination between international actors and unstable political environments that undermine trust and cooperation. Overcoming these obstacles requires adaptive strategies and robust support to ensure peacekeeping missions effectively lay the groundwork for Peacebuilding and Reconstruction.
Obstacles to Effective Peacebuilding
Obstacles to effective peacebuilding include weak institutional capacity, lack of local ownership, and ongoing political instability that undermine sustainable development efforts. You may encounter challenges such as insufficient funding, fragmented coordination among international actors, and lingering social divisions, which delay the transition from peacekeeping to long-term reconstruction. Addressing these barriers requires a comprehensive approach prioritizing inclusive governance, security sector reform, and socioeconomic recovery.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Failures
Peacekeeping missions like the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH) have shown mixed results, successfully reducing violence but struggling with long-term stability. Peacebuilding efforts in Sierra Leone highlight how community engagement and institution strengthening can prevent relapse into conflict, yet failures in Bosnia revealed the challenges of political fragmentation undermining trust. Your understanding of these case studies is vital for designing effective strategies that balance immediate security with sustainable development and governance reforms.
The Role of International Organizations
International organizations such as the United Nations play a crucial role in peacekeeping by deploying troops and observers to maintain ceasefires and prevent the resurgence of conflict. In peacebuilding, these organizations support governance reforms, economic development, and reconciliation efforts to address root causes of violence and promote long-term stability. During reconstruction, they coordinate humanitarian aid, infrastructure rebuilding, and institutional capacity strengthening to restore normalcy and foster sustainable recovery in post-conflict zones.
Future Trends in Peacekeeping and Peacebuilding
Future trends in peacekeeping and peacebuilding emphasize integrating advanced technology such as AI and remote sensing to improve conflict monitoring and rapid response. You will see increased collaboration between international organizations and local communities to enhance sustainable peace through inclusive governance and economic development. Reconstruction efforts will align more closely with peacebuilding initiatives to address root causes of conflict and promote long-term stability.
Infographic: Peacekeeping vs Peacebuilding
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com