Mindfulness enhances emotional awareness by promoting present-moment focus, while Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) restructures negative thought patterns to improve relationship dynamics. Discover how integrating these approaches can transform your relationships in this article.
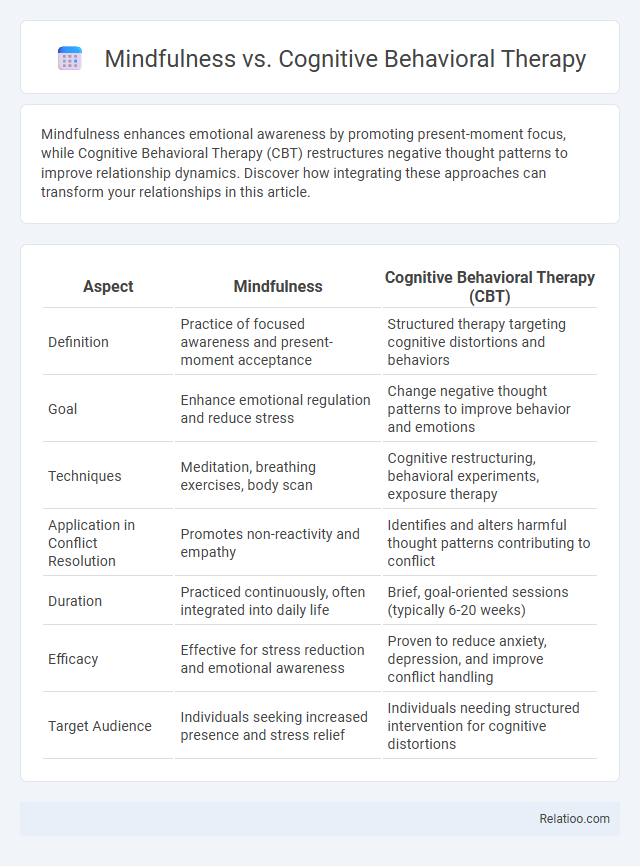
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mindfulness | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practice of focused awareness and present-moment acceptance | Structured therapy targeting cognitive distortions and behaviors |
| Goal | Enhance emotional regulation and reduce stress | Change negative thought patterns to improve behavior and emotions |
| Techniques | Meditation, breathing exercises, body scan | Cognitive restructuring, behavioral experiments, exposure therapy |
| Application in Conflict Resolution | Promotes non-reactivity and empathy | Identifies and alters harmful thought patterns contributing to conflict |
| Duration | Practiced continuously, often integrated into daily life | Brief, goal-oriented sessions (typically 6-20 weeks) |
| Efficacy | Effective for stress reduction and emotional awareness | Proven to reduce anxiety, depression, and improve conflict handling |
| Target Audience | Individuals seeking increased presence and stress relief | Individuals needing structured intervention for cognitive distortions |
Introduction to Mindfulness and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Mindfulness is a practice centered on present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance of thoughts and feelings, promoting emotional regulation and stress reduction. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a structured, goal-oriented psychotherapeutic approach that targets dysfunctional thinking patterns to change behavior and emotional states. Your mental health journey can benefit from integrating Mindfulness techniques with the evidence-based strategies of CBT to enhance self-awareness and cognitive restructuring.
Defining Mindfulness: Concepts and Practices
Mindfulness is the practice of maintaining present-moment awareness with a non-judgmental attitude, often cultivated through meditation, breathing exercises, and body scans. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) integrates mindfulness to help you recognize and reframe negative thought patterns by fostering conscious awareness of your mental processes. Understanding mindfulness as both a standalone practice and a component of CBT highlights its role in enhancing emotional regulation and cognitive flexibility.
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a structured, evidence-based approach that helps you identify and challenge negative thought patterns to improve emotional regulation and behavior. Unlike mindfulness, which emphasizes present-moment awareness and acceptance, CBT actively targets cognitive distortions to foster healthier thinking habits. Combining both methods can enhance mental health by blending mindfulness's awareness techniques with CBT's problem-solving strategies.
Core Principles: Mindfulness vs CBT
Mindfulness centers on present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance of thoughts and feelings, fostering emotional regulation through increased self-awareness. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) emphasizes identifying and challenging distorted cognitive patterns to change behaviors and emotional responses effectively. Both approaches enhance mental health, with mindfulness cultivating observation skills while CBT targets cognitive restructuring for symptom relief.
How Mindfulness Works in Mental Health
Mindfulness enhances mental health by promoting present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance, which reduces stress and emotional reactivity. Unlike Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which targets changing negative thought patterns, mindfulness cultivates a detached observation of thoughts and feelings, leading to increased emotional regulation and resilience. Scientific studies show mindfulness practice increases gray matter density in brain regions associated with attention, self-awareness, and emotional processing, supporting its benefits for anxiety and depression.
Mechanisms of Action in CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) operates through structured mechanisms targeting dysfunctional thought patterns by promoting cognitive restructuring and behavioral activation to alleviate psychological distress. Mindfulness enhances present-moment awareness and acceptance, reducing automatic reactivity and emotional suppression without direct cognitive modification. While both therapies improve mental health, CBT actively challenges and changes negative beliefs, whereas mindfulness fosters non-judgmental observation and cognitive defusion for emotional regulation.
Similarities Between Mindfulness and CBT
Mindfulness and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) both emphasize present-moment awareness and the identification of unhelpful thought patterns to improve mental health outcomes. Both approaches use techniques to increase self-awareness and promote adaptive thinking, leading to reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression. Integrating mindfulness practices within CBT enhances emotional regulation and cognitive restructuring, making treatment more effective.
Key Differences: Mindfulness and CBT Approaches
Mindfulness emphasizes present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance of thoughts and feelings to reduce stress and enhance emotional regulation. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) targets identifying and restructuring negative thought patterns and behaviors to alleviate psychological distress and promote healthier thinking. While mindfulness cultivates observation without reaction, CBT actively challenges and modifies cognitive distortions for lasting behavioral change.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right approach between mindfulness and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) depends on your specific mental health needs, goals, and preferences. Mindfulness emphasizes present-moment awareness and stress reduction, which can benefit anxiety and depression management, while CBT targets cognitive distortions and behavior patterns for lasting change. Factors such as symptom severity, therapy duration, and your comfort with introspective or structured techniques influence the optimal choice for effective treatment.
Integrative Strategies: Combining Mindfulness and CBT
Integrative strategies that combine Mindfulness and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) harness the strengths of both approaches to enhance emotional regulation and reduce stress. By incorporating mindfulness practices into CBT, individuals can increase awareness of their thoughts and feelings, allowing your therapeutic process to become more effective at identifying and restructuring negative thought patterns. This synergy improves mental health outcomes by fostering present-moment awareness alongside cognitive flexibility, making the combined approach a powerful tool for managing anxiety, depression, and other psychological challenges.
Infographic: Mindfulness vs Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com