Permissive parenting is characterized by warmth and leniency, often resulting in children with low self-discipline, while uninvolved parenting involves emotional detachment and neglect, leading to poor social and academic outcomes. Discover more about how these parenting styles impact relationships and child development in this article.
Table of Comparison
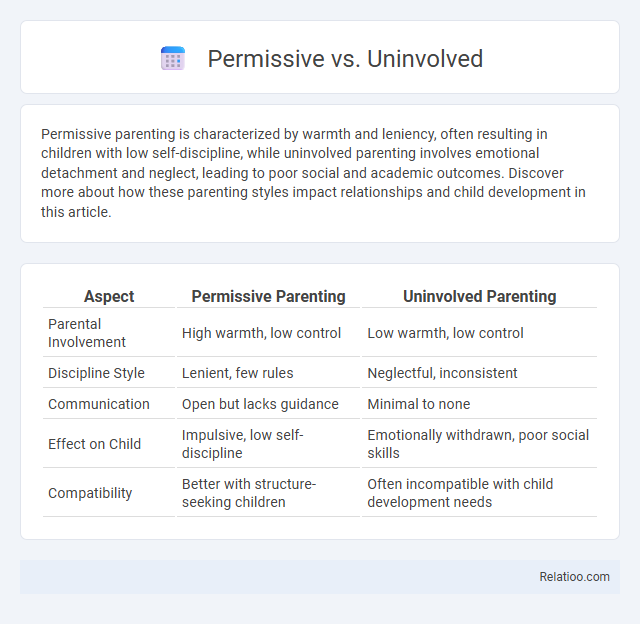
| Aspect | Permissive Parenting | Uninvolved Parenting |
|---|---|---|
| Parental Involvement | High warmth, low control | Low warmth, low control |
| Discipline Style | Lenient, few rules | Neglectful, inconsistent |
| Communication | Open but lacks guidance | Minimal to none |
| Effect on Child | Impulsive, low self-discipline | Emotionally withdrawn, poor social skills |
| Compatibility | Better with structure-seeking children | Often incompatible with child development needs |
Understanding Parenting Styles: Permissive vs Uninvolved
Permissive parenting is characterized by high responsiveness and low demands, where parents are warm and accepting but set few rules or boundaries, often leading to children with poor self-discipline. Uninvolved parenting exhibits low responsiveness and low demands, marked by neglect and minimal interaction, resulting in children who may struggle with emotional regulation and social competence. Understanding these differences highlights how varying degrees of parental engagement impact child development, with permissive styles fostering indulgence and uninvolved styles often causing neglect.
Key Characteristics of Permissive Parenting
Permissive parenting is characterized by high responsiveness and low demandingness, where parents are nurturing and indulgent but set few boundaries or rules. Your child may experience a lack of discipline and guidance, leading to challenges in self-regulation and responsibility. This style contrasts with uninvolved parenting, which is low in both responsiveness and demandingness, and authoritative parenting, which balances warmth and firm control.
Defining the Uninvolved Parenting Approach
The uninvolved parenting style is characterized by low responsiveness and low demands, where parents provide minimal emotional support and supervision. This approach often leads to children experiencing neglect, resulting in difficulties with self-esteem and social competence. Understanding your child's needs requires more engagement than the uninvolved style typically offers, as it lacks both nurturing and guidance.
Emotional Impacts on Children
Permissive parenting often leads to children struggling with self-discipline and experiencing higher levels of emotional insecurity due to inconsistent boundaries. Uninvolved parenting typically results in children feeling neglected, which can cause issues with attachment, low self-esteem, and emotional withdrawal. In contrast, authoritative parenting supports emotional resilience by providing clear guidelines and emotional support, fostering healthy emotional regulation and social competence in children.
Effects on Academic Performance
Permissive parenting, characterized by high warmth but low discipline, often results in children exhibiting lower academic achievement due to a lack of structure and guidance. Uninvolved parenting, marked by neglect and minimal responsiveness, typically leads to the poorest academic outcomes, as children miss essential support and encouragement. In contrast, authoritative parenting, which balances responsiveness with firm expectations, consistently promotes higher academic performance by fostering self-discipline and motivation.
Social Development Differences
Permissive parenting often results in children with high social confidence but poor self-discipline, leading to challenges in peer relationships and authority acceptance. Uninvolved parenting typically impairs social development, causing children to exhibit low self-esteem, social withdrawal, and difficulty forming healthy attachments. In contrast, authoritative parenting promotes balanced social competence, emotional regulation, and positive interpersonal skills, fostering well-adjusted social behavior.
Long-Term Behavioral Outcomes
Permissive parenting often leads to children exhibiting higher levels of impulsivity and poor self-discipline, whereas uninvolved parenting is linked to increased behavioral problems, such as aggression and emotional detachment. Authoritative parenting, contrastingly, promotes long-term positive behavioral outcomes including social competence, academic success, and emotional regulation. Understanding these differences can help you adopt strategies that foster healthier development and better life outcomes for your child.
Identifying Warning Signs in Parenting
Permissive parenting often displays warning signs such as lack of consistent discipline and overly lenient boundaries, leading to children who may struggle with self-regulation and authority. Uninvolved parenting is marked by neglect, emotional detachment, and minimal responsiveness, which can result in developmental delays and low self-esteem in children. Recognizing these patterns early allows for intervention strategies to promote healthier family dynamics and improved child outcomes.
Strategies for Healthier Parenting Alternatives
Permissive parenting often leads to lack of boundaries, while uninvolved parenting results in minimal guidance, both negatively impacting child development. Implementing firm yet nurturing strategies like setting consistent rules and actively engaging with Your child's emotional needs fosters healthier relationships and improved behavioral outcomes. Choosing authoritative parenting, which balances warmth and structure, promotes resilience and self-discipline effectively.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Approach for Child Development
Choosing the best parenting style for child development depends on balancing emotional support with clear boundaries, as permissive parenting risks fostering entitlement while uninvolved parenting often leads to emotional neglect. Authoritative parenting, which combines warmth and structure, consistently promotes positive social, academic, and emotional outcomes in children. Prioritizing responsiveness and consistent discipline optimizes healthy growth and resilience in young individuals.
Infographic: Permissive vs Uninvolved
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com