Fairness emphasizes treating everyone the same, while equity focuses on providing resources based on individual needs to achieve equal outcomes. Explore how balancing fairness and equity strengthens relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
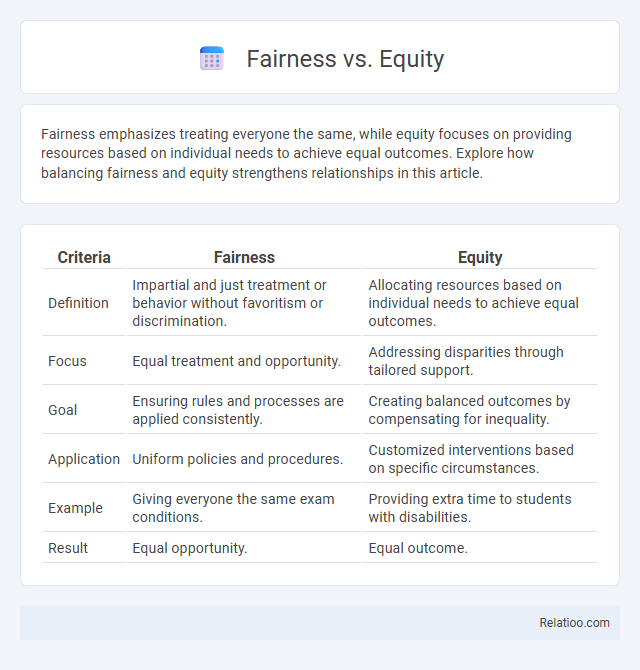
| Criteria | Fairness | Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Impartial and just treatment or behavior without favoritism or discrimination. | Allocating resources based on individual needs to achieve equal outcomes. |
| Focus | Equal treatment and opportunity. | Addressing disparities through tailored support. |
| Goal | Ensuring rules and processes are applied consistently. | Creating balanced outcomes by compensating for inequality. |
| Application | Uniform policies and procedures. | Customized interventions based on specific circumstances. |
| Example | Giving everyone the same exam conditions. | Providing extra time to students with disabilities. |
| Result | Equal opportunity. | Equal outcome. |
Understanding Fairness: Definition and Principles
Fairness involves impartial treatment and just behavior without favoritism, emphasizing equal opportunities for all individuals regardless of background or circumstance. Equity focuses on providing resources and support tailored to individual needs to achieve equal outcomes, recognizing that different approaches are necessary for different people. Understanding fairness requires acknowledging these principles to create environments where justice and equality coexist, balancing universal standards with personalized considerations.
Defining Equity: Meaning and Key Concepts
Equity refers to the principle of fairness by recognizing and addressing individual differences to achieve equal outcomes, rather than providing identical resources or opportunities. It involves tailoring support and interventions based on specific needs, barriers, and circumstances to ensure everyone has access to comparable results. Key concepts include redistribution of resources, removal of systemic obstacles, and promotion of inclusivity to bridge gaps in access and opportunities.
Fairness vs. Equity: Core Differences
Fairness involves treating everyone the same way, ensuring equal treatment and opportunity regardless of individual circumstances. Equity, on the other hand, focuses on tailoring resources and support to meet the unique needs of each individual, aiming to achieve equal outcomes. You must understand that fairness is about equality in process, while equity emphasizes equality in results.
Historical Perspectives on Fairness and Equity
Historical perspectives on fairness and equity reveal evolving understandings of justice, emphasizing fair treatment and impartiality in diverse social contexts. Fairness traditionally centers on equal treatment under the law, while equity addresses the need to consider individual circumstances to achieve true justice. Your approach to policy or social issues benefits from recognizing how historical struggles for equity shaped modern frameworks that balance uniformity with fairness.
Real-World Examples: Fairness in Practice
Fairness in practice often involves treating individuals according to their specific needs, such as providing accessible facilities for people with disabilities to ensure equal participation. Equity goes beyond equal treatment by allocating resources based on varying circumstances, like offering scholarships to underrepresented groups to bridge educational gaps. Understanding these distinctions helps you advocate for policies that address systemic inequalities while promoting just outcomes.
Real-World Examples: Equity in Action
Fairness means treating everyone the same, while equity involves recognizing individual needs and providing resources accordingly to achieve equal outcomes. Real-world examples of equity in action include tailored educational programs for students with learning disabilities, and community health initiatives that allocate more resources to underserved populations. Your understanding of these concepts can help promote just policies that address systemic disparities effectively.
The Role of Policy in Fairness and Equity
Policy plays a critical role in promoting fairness and equity by establishing guidelines and regulations that address systemic disparities and ensure equitable access to resources and opportunities. Fairness emphasizes impartial treatment and justice, while equity focuses on tailored support to achieve equality of outcomes, requiring policies that recognize and respond to diverse needs and structural barriers. Effective policymaking integrates data-driven assessments and stakeholder input to design interventions that balance fairness with equity, fostering inclusive and just societies.
Challenges in Achieving Fairness and Equity
Challenges in achieving fairness and equity often stem from deeply embedded social inequalities and systemic biases, making uniform treatment insufficient for equal outcomes. Fairness requires impartial processes, but equity demands tailored resources and support to address disparities, complicating policy design and implementation. Data limitations and varying definitions of fairness and equity across cultures further hinder consistent measurement and evaluation in social and organizational contexts.
Impacts of Fairness vs. Equity in Society
Fairness emphasizes impartial treatment by applying the same rules to everyone, while equity focuses on distributing resources based on individual needs to achieve equal outcomes. Your understanding of these concepts influences policies that address social disparities, affecting access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. Societal impacts include reduced systemic inequality when equity is prioritized, whereas strict fairness may perpetuate existing advantages for dominant groups.
Moving Forward: Balancing Fairness and Equity
Balancing fairness and equity requires understanding that fairness often means treating everyone the same, while equity involves providing resources and opportunities based on individual needs to achieve equal outcomes. Moving forward, your approach should prioritize flexible policies that address specific disparities without compromising basic justice for all parties. Implementing data-driven strategies can help create environments where fairness and equity coexist, fostering inclusive growth and accountability.
Infographic: Fairness vs Equity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com