2.4 GHz Wi-Fi offers broader coverage and better penetration through walls, while 5 GHz Wi-Fi provides faster speeds and less interference ideal for high-bandwidth activities. Discover the key differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies to optimize your wireless connection in this article.
Table of Comparison
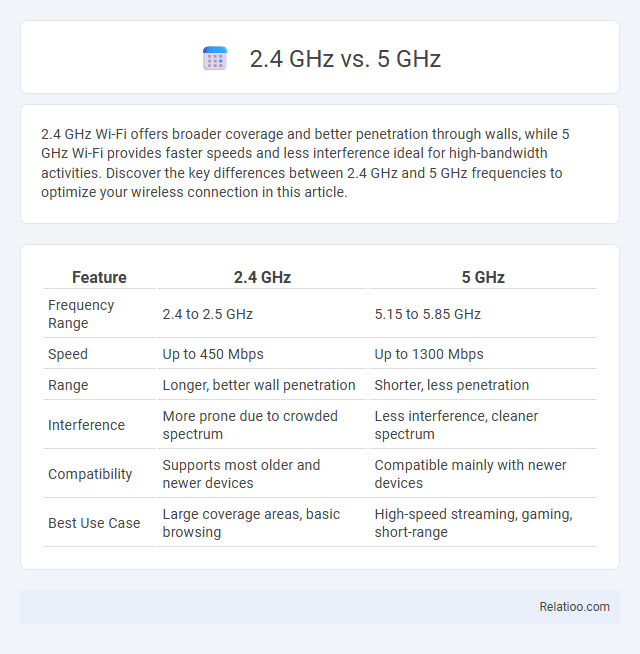
| Feature | 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 2.4 to 2.5 GHz | 5.15 to 5.85 GHz |
| Speed | Up to 450 Mbps | Up to 1300 Mbps |
| Range | Longer, better wall penetration | Shorter, less penetration |
| Interference | More prone due to crowded spectrum | Less interference, cleaner spectrum |
| Compatibility | Supports most older and newer devices | Compatible mainly with newer devices |
| Best Use Case | Large coverage areas, basic browsing | High-speed streaming, gaming, short-range |
Understanding 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi Frequencies
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz are the primary Wi-Fi frequency bands, each offering distinct advantages for wireless connectivity. The 2.4 GHz band provides broader coverage and better penetration through walls, ideal for larger spaces and devices farther from the router. The 5 GHz band supports faster data rates with less interference, making it suitable for high-bandwidth activities such as gaming and streaming in close proximity to the access point.
Key Differences Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Bands
The 2.4 GHz band offers longer range and better penetration through walls but suffers from higher interference due to its crowded frequency with devices like microwaves and Bluetooth. In contrast, the 5 GHz band provides faster data rates and less congestion, making it ideal for high-bandwidth activities such as HD streaming and gaming. Users should choose 2.4 GHz for wider coverage and 5 GHz for improved performance in less obstructed environments.
Speed Comparison: 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz
The 5 GHz frequency band provides faster data transfer rates compared to the 2.4 GHz band due to its higher bandwidth and reduced interference from common household devices. While 2.4 GHz offers greater range and better penetration through walls, 5 GHz excels in delivering increased speed, often reaching up to 1300 Mbps, ideal for high-bandwidth activities such as gaming and HD video streaming. Speed performance on 5 GHz can be hindered by physical obstructions, making 2.4 GHz preferable in larger, obstacle-rich environments despite its lower maximum throughput.
Coverage Range: Which Band Reaches Farther?
The 2.4 GHz frequency band provides a broader coverage range and better signal penetration through walls and obstacles compared to the 5 GHz band, making it ideal for larger spaces or areas with many obstructions. The 5 GHz band offers faster data rates but covers a shorter distance due to higher frequency attenuation, which limits its effective range. Your choice depends on whether extended coverage or higher speed performance is more crucial for your wireless network setup.
Interference and Signal Stability Issues
2.4 GHz frequency often experiences more interference from common household devices like microwaves and Bluetooth gadgets, leading to less stable signals. 5 GHz frequency offers less congestion and higher data rates but has a shorter range and weaker penetration through walls, impacting signal stability in larger spaces. Your choice between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz should consider the balance between interference susceptibility and the need for consistent, reliable connectivity.
Device Compatibility With 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
Devices compatible with 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi benefit from broader range and better penetration through walls, ideal for older or budget hardware that supports legacy standards like 802.11b/g/n. In contrast, devices that support 5 GHz offer faster speeds and lower interference but have a shorter range, commonly found in modern routers and smartphones with 802.11ac or 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) standards. Choosing between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies depends on device compatibility, with many dual-band devices automatically switching to optimize performance based on signal strength and network congestion.
Best Use Cases for 2.4 GHz
The 2.4 GHz frequency band offers better range and penetration through walls, making it ideal for larger spaces and environments with multiple obstacles. You should choose 2.4 GHz for devices that require stable connectivity over long distances, such as smart home gadgets and basic web browsing. While it has lower data speeds compared to 5 GHz, the 2.4 GHz band excels in crowded or interference-prone areas due to its wider coverage.
Best Use Cases for 5 GHz
5 GHz frequency offers faster speeds and less interference compared to 2.4 GHz, making it ideal for high-bandwidth activities like streaming HD videos or online gaming. Your devices benefit from better performance in environments with many competing Wi-Fi networks since 5 GHz experiences less congestion. Choosing 5 GHz is optimal for close-range connections in homes or offices where speed and low latency are priorities.
How to Switch Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
Switching between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wireless bands depends on your router settings and device compatibility. Access your router's network settings via its IP address, then select the wireless or Wi-Fi section to enable dual-band mode or choose a preferred band for connection. On devices, navigate to Wi-Fi settings and connect to the specific SSID associated with either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band for optimized network performance.
Choosing the Right Wi-Fi Band for Your Needs
Choosing the right Wi-Fi band between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz depends on your device usage and environment. The 2.4 GHz band offers longer range and better penetration through walls, making it ideal for larger homes or areas with many obstacles, while the 5 GHz band provides faster speeds and less interference, perfect for high-bandwidth activities like streaming or gaming in smaller spaces. Understanding your specific needs and the frequency characteristics ensures your Wi-Fi connection is optimized for speed, reliability, and coverage.
Infographic: 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com