Empathic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing the feelings of another, while reflective listening focuses on accurately paraphrasing and clarifying the speaker's message. Explore the differences and benefits of these listening techniques in this article.
Table of Comparison
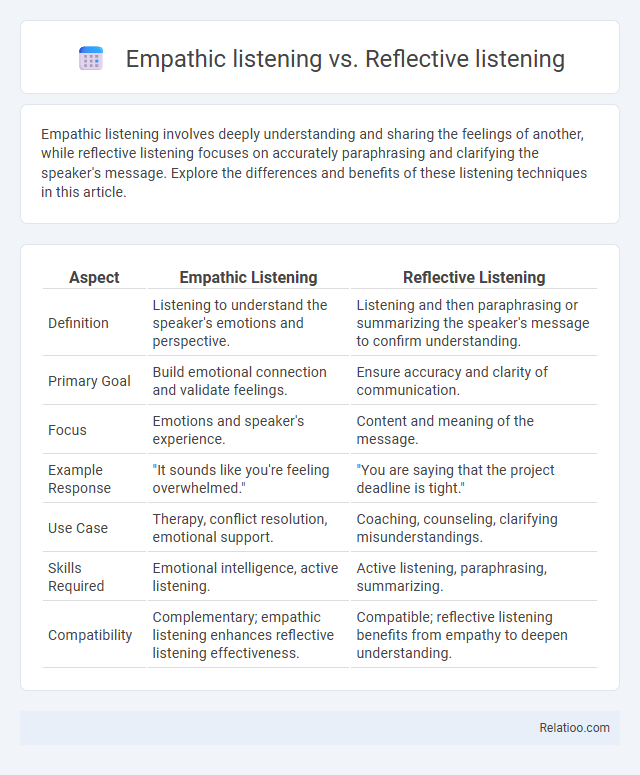
| Aspect | Empathic Listening | Reflective Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Listening to understand the speaker's emotions and perspective. | Listening and then paraphrasing or summarizing the speaker's message to confirm understanding. |
| Primary Goal | Build emotional connection and validate feelings. | Ensure accuracy and clarity of communication. |
| Focus | Emotions and speaker's experience. | Content and meaning of the message. |
| Example Response | "It sounds like you're feeling overwhelmed." | "You are saying that the project deadline is tight." |
| Use Case | Therapy, conflict resolution, emotional support. | Coaching, counseling, clarifying misunderstandings. |
| Skills Required | Emotional intelligence, active listening. | Active listening, paraphrasing, summarizing. |
| Compatibility | Complementary; empathic listening enhances reflective listening effectiveness. | Compatible; reflective listening benefits from empathy to deepen understanding. |
Introduction to Empathic and Reflective Listening
Empathic listening involves fully understanding and sharing another person's feelings, fostering deep emotional connections. Reflective listening focuses on accurately paraphrasing and clarifying the speaker's message to ensure mutual understanding. Both techniques enhance communication by promoting active engagement and validating the speaker's experience.
Defining Empathic Listening
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, creating a genuine emotional connection that fosters trust and openness. Unlike reflective listening, which primarily focuses on mirroring the speaker's words and content to ensure clarity, empathic listening prioritizes recognizing and validating the speaker's emotions. Your ability to practice empathic listening enhances communication by making others feel truly heard and valued beyond just their verbal expressions.
Defining Reflective Listening
Reflective listening involves actively understanding and mirroring the speaker's emotions and content to confirm comprehension and promote clarity. Unlike empathic listening, which primarily focuses on feeling and validating emotions, reflective listening emphasizes restating or paraphrasing the speaker's message to ensure accurate communication. This technique enhances mutual understanding and fosters a deeper connection in interpersonal interactions.
Key Differences Between Empathic and Reflective Listening
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing the speaker's emotions, creating a strong emotional connection, while reflective listening centers on accurately paraphrasing or summarizing the speaker's words to ensure clarity and comprehension. Your ability to practice empathic listening builds trust and rapport by validating feelings, whereas reflective listening focuses on confirming understanding without necessarily engaging emotionally. Key differences lie in empathic listening's emphasis on emotional resonance versus reflective listening's goal of cognitive accuracy and feedback.
Benefits of Empathic Listening
Empathic listening fosters deep emotional connections by fully understanding and validating Your feelings, which can improve trust and communication in relationships. Unlike reflective listening that mainly focuses on paraphrasing and clarifying, empathic listening enhances emotional support and helps in resolving conflicts effectively. Benefits of empathic listening include increased emotional intelligence, reduced misunderstandings, and stronger interpersonal bonds.
Benefits of Reflective Listening
Reflective listening enhances your communication by promoting clarity and deeper understanding through accurately restating the speaker's message. This technique reduces misunderstandings and builds trust, fostering stronger relationships in personal and professional settings. Benefits of reflective listening include improved conflict resolution, increased empathy, and greater emotional validation for the speaker.
Core Skills Required for Each Listening Style
Empathic listening requires deep emotional awareness and the ability to understand and share the feelings of another, focusing on compassion and unconditional positive regard. Reflective listening centers on accurately paraphrasing and summarizing the speaker's message, requiring strong attention to verbal and non-verbal cues to clarify meaning and ensure mutual understanding. Your effective communication improves when you hone core skills like active presence, emotional attunement, and precise feedback tailored to each listening style.
Common Scenarios for Empathic vs Reflective Listening
Empathic listening often occurs in emotionally charged situations like counseling or personal conversations where understanding feelings is crucial, while reflective listening is common in conflict resolution and coaching to clarify and confirm messages. Your ability to distinguish between these styles enhances communication by responding to emotions with empathy or summarizing to ensure comprehension. Both listening types improve connection, but empathic listening focuses on emotional validation and reflective listening on accurate feedback.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Empathic listening often faces the challenge of being mistaken for sympathy, leading to emotional over-involvement instead of understanding. Reflective listening is frequently misunderstood as mere repetition, which can hinder true engagement and may frustrate the speaker. Both approaches require skill to balance active attention and emotional resonance, avoiding common pitfalls like misinterpretation or ineffective communication.
Choosing the Right Listening Approach
Choosing the right listening approach depends on the communication goal and context: empathic listening focuses on fully understanding and sharing the emotional experience of the speaker, fostering deep connection and trust; reflective listening involves paraphrasing or summarizing the speaker's words to confirm understanding and clarify meaning, promoting accurate comprehension and problem-solving; selective listening, contrasting with both, filters information based on interest or relevance, which may limit effective communication in sensitive or complex conversations.
Infographic: Empathic listening vs Reflective listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com