The Judging personality type prefers structure, planning, and decisiveness in relationships, while the Perceiving type values flexibility, spontaneity, and adaptability. Discover how understanding these differences can improve your connection in this article.
Table of Comparison
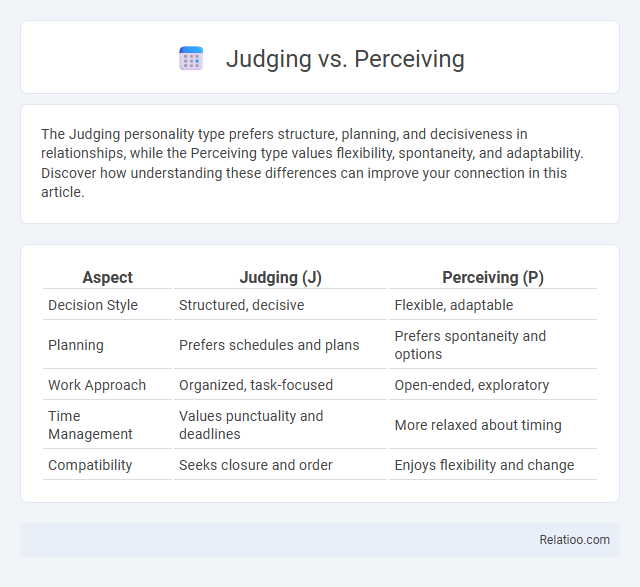
| Aspect | Judging (J) | Perceiving (P) |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Style | Structured, decisive | Flexible, adaptable |
| Planning | Prefers schedules and plans | Prefers spontaneity and options |
| Work Approach | Organized, task-focused | Open-ended, exploratory |
| Time Management | Values punctuality and deadlines | More relaxed about timing |
| Compatibility | Seeks closure and order | Enjoys flexibility and change |
Understanding Judging and Perceiving
Judging and Perceiving are key personality traits in the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator that influence how individuals approach structure and decision-making, with Judging types preferring organization and closure while Perceiving types favor flexibility and spontaneity. Understanding these traits helps improve social compatibility by aligning expectations in communication and lifestyle preferences, reducing conflicts between planners and adapters. Recognizing whether someone leans toward Judging or Perceiving fosters better teamwork, relationship dynamics, and mutual respect through tailored interaction styles.
Origins of Judging and Perceiving in Personality Theory
Judging and Perceiving originate from Carl Jung's personality theory, representing how individuals prefer to organize their external world--Judging types seek structure and decisiveness, while Perceiving types favor flexibility and spontaneity. These preferences underpin social compatibility by influencing how you interact and align with others' approaches to planning, decision-making, and adaptability. Understanding the roots of these traits enhances your ability to navigate social dynamics and improve interpersonal harmony.
Core Characteristics of Judging Types
Judging types exhibit strong organizational skills, preference for structure, and decisive decision-making, which often lead to efficient time management and goal-oriented behavior. Your ability to plan ahead and set clear priorities promotes order and predictability, fostering stability in social interactions. These core characteristics align well with others who appreciate commitment and reliability, enhancing social compatibility within structured environments.
Key Traits of Perceiving Types
Perceiving types in the Myers-Briggs framework exhibit adaptability, spontaneity, and a preference for keeping options open, thriving in dynamic social environments that value flexibility. These individuals often approach social compatibility by being open-minded, curious, and responsive to changing social cues, which fosters harmonious interactions with diverse personality types. Their key trait of embracing uncertainty allows them to navigate complex social situations fluidly, making them approachable and engaging partners in both personal and professional contexts.
Judging vs Perceiving: Decision-Making Styles
Judging and Perceiving represent distinct decision-making styles within personality frameworks, where Judging types prefer structured, planned approaches with clear deadlines, while Perceiving types favor flexibility, spontaneity, and adapting to changes. These contrasting traits influence social compatibility by affecting how individuals handle commitments, problem-solving, and responsiveness to others' expectations. Understanding these differences enables smoother interactions, as recognizing a preference for Judging's decisiveness or Perceiving's openness fosters effective communication and collaborative decision-making.
Communication Differences Between Judgers and Perceivers
Judgers prefer structured, planned communication, valuing clarity and decisiveness, while Perceivers favor spontaneous, flexible interactions that allow for exploration and adaptability. Your approach to communication impacts social compatibility, as Judgers may find Perceivers too unpredictable, and Perceivers may see Judgers as rigid or controlling. Understanding these differences enhances mutual respect and smoother exchanges in personal and professional relationships.
How Judging and Perceiving Impact Work and Relationships
Judging personalities prefer structure and clear plans, leading to efficient project completion and reliable meeting of deadlines in work environments. Perceiving types thrive on flexibility and adaptability, fostering creativity and open communication but sometimes causing challenges in time management and consistency. In relationships, Judging individuals seek stability and predictability, while Perceiving partners value spontaneity, affecting compatibility and requiring conscious balance for harmony.
Common Misunderstandings About Judgers and Perceivers
Judgers often face the misconception that they are rigid and inflexible, when in fact they value structure and timely decisions which can enhance social compatibility by providing predictability. Perceivers are frequently misunderstood as indecisive or disorganized, yet their adaptability and openness typically foster more spontaneous and dynamic social interactions. Misinterpreting these traits can lead to unnecessary conflicts, highlighting the importance of recognizing how Judging and Perceiving preferences uniquely influence social harmony.
Tips for Harmonizing Judger-Perceiver Interactions
Judger-Perceiver interactions thrive when both parties respect each other's approach to time and structure, with Judgers valuing plans and deadlines while Perceivers prefer flexibility and spontaneity. You can enhance social compatibility by establishing clear communication and setting boundaries that allow for both organization and adaptability, ensuring mutual understanding. Encouraging open dialogue about expectations and embracing compromise helps balance the Judger's need for order with the Perceiver's desire for freedom.
Embracing Both Judging and Perceiving in Personal Growth
Balancing Judging and Perceiving traits fosters adaptive personal growth by integrating structured decision-making with open-minded flexibility. Embracing this duality enhances social compatibility, allowing individuals to navigate diverse interpersonal dynamics and respond effectively to changing environments. Cultivating both preferences supports holistic development and improves communication across varied social contexts.
Infographic: Judging vs Perceiving
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com