Maintaining a healthy relationship requires balancing independence and dependence, where each partner supports personal growth while fostering mutual trust and connection. Explore this article to understand how to navigate independence and dependence for a stronger, more fulfilling relationship.
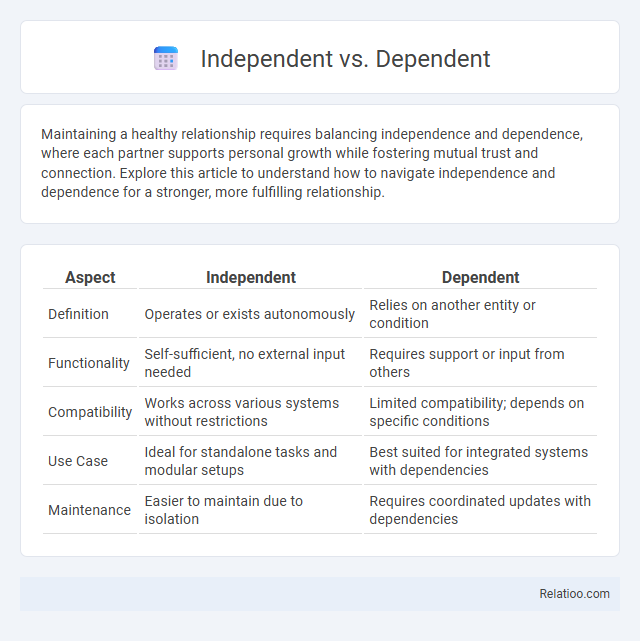
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Independent | Dependent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Operates or exists autonomously | Relies on another entity or condition |
| Functionality | Self-sufficient, no external input needed | Requires support or input from others |
| Compatibility | Works across various systems without restrictions | Limited compatibility; depends on specific conditions |
| Use Case | Ideal for standalone tasks and modular setups | Best suited for integrated systems with dependencies |
| Maintenance | Easier to maintain due to isolation | Requires coordinated updates with dependencies |
Understanding Independent and Dependent Variables
Independent variables represent factors or conditions manipulated to observe their effect on dependent variables, which are the outcomes measured in an experiment. Emotional needs influence how Your behavior or responses might vary, acting as potential dependent variables affected by changes in external or internal independent variables. Clear understanding of these distinctions allows precise control and interpretation of experimental results, bridging the analysis of emotional and behavioral data.
Key Differences Between Independent and Dependent
Independent needs emphasize self-sufficiency, personal growth, and the ability to fulfill desires without relying on others, whereas dependent needs involve seeking support, guidance, or validation from external sources to feel secure or complete. Emotional needs intersect both types but specifically relate to the requirement for affection, understanding, and psychological connection, which can be fulfilled independently through self-awareness or dependently through relationships. Recognizing these distinctions aids in fostering emotional intelligence, healthy boundaries, and balanced interpersonal dynamics.
The Role of Independent Variables in Research
Independent variables play a crucial role in research by serving as the factors manipulated to observe their effect on dependent variables, which represent the outcome or response in the study. Emotional needs, often included as independent variables in psychological research, help explain variations in human behavior by influencing dependent variables such as stress levels or decision-making. Understanding the distinction and interaction between independent, dependent, and emotional needs enables researchers to design experiments that accurately measure cause-and-effect relationships within diverse contexts.
How Dependent Variables Are Measured
Dependent variables in research are measured through quantitative methods such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies to objectively capture changes influenced by independent variables. Accurate measurement involves selecting valid scales, ensuring reliability, and consistently applying data collection procedures tailored to the specific emotional or behavioral needs studied. Your ability to analyze these dependent variable outcomes informs the strength and direction of relationships within complex psychological or social frameworks.
Examples of Independent vs Dependent Variables
Independent variables represent factors that you manipulate or control in an experiment, such as temperature settings or fertilizer types, while dependent variables are the outcomes measured, like plant growth or test scores. Emotional needs, unlike these variables, relate to psychological requirements for support, security, and belonging that influence behavior but are not directly manipulated in scientific studies. Understanding the difference helps you design better experiments and analyze how changing one element affects another.
Identifying Variables in Real-World Scenarios
Independent needs refer to personal goals and self-sufficiency, dependent needs involve reliance on others for support, while emotional needs center around feelings of connection and validation. Identifying variables in real-world scenarios requires analyzing factors such as social context, individual personality traits, and situational stressors that influence whether a need is independent, dependent, or emotional. Understanding these variables helps tailor interventions and support systems effectively across diverse environments.
The Importance of Variables in Experiments
Understanding independent, dependent, and emotional needs variables is crucial for designing effective experiments. Independent variables represent the conditions manipulated by researchers to observe their effects on dependent variables, which are the outcomes measured. Emotional needs variables influence participants' responses, requiring careful control to ensure valid and reliable data interpretation.
Common Mistakes When Distinguishing Variables
Common mistakes in distinguishing independent, dependent, and emotional needs stem from confusing variables with feelings or outcomes, leading to inaccurate analysis in research or personal contexts. Your understanding improves by clearly identifying the independent variable as the cause, the dependent variable as the effect or outcome, and emotional need as a psychological factor influencing behavior but not a measurable variable. Misclassification often results in flawed conclusions and ineffective interventions, highlighting the importance of precise variable differentiation.
Best Practices for Using Independent and Dependent Variables
Independent variables represent factors you manipulate to observe effects, while dependent variables are the outcomes measured in response; emotional needs often influence how these variables interact in psychological studies. Best practices include clearly defining and isolating independent variables to ensure accurate measurement of dependent variables and using validated scales to capture emotional needs reliably. Your research will benefit from controlling for emotional factors to reduce bias and enhance the validity of experimental results.
Frequently Asked Questions About Independent vs Dependent
Independent needs focus on self-sufficiency and personal goals, while dependent needs involve relying on others for support and resources. Emotional needs encompass feelings of connection, security, and validation essential for mental well-being. Frequently asked questions about independent vs dependent needs often address balancing autonomy with interpersonal support and recognizing when emotional dependence becomes unhealthy.
Infographic: Independent vs Dependent
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com