Anxious attachment is characterized by a strong desire for closeness paired with fear of abandonment, while avoidant attachment involves discomfort with intimacy and a tendency to maintain emotional distance. Explore this article to understand how these attachment styles impact relationship dynamics and ways to foster healthier connections.
Table of Comparison
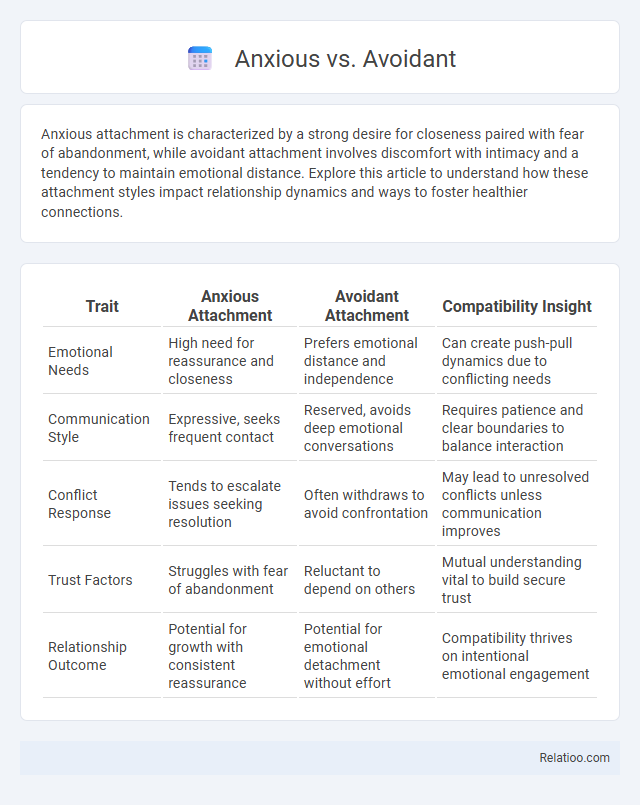
| Trait | Anxious Attachment | Avoidant Attachment | Compatibility Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional Needs | High need for reassurance and closeness | Prefers emotional distance and independence | Can create push-pull dynamics due to conflicting needs |
| Communication Style | Expressive, seeks frequent contact | Reserved, avoids deep emotional conversations | Requires patience and clear boundaries to balance interaction |
| Conflict Response | Tends to escalate issues seeking resolution | Often withdraws to avoid confrontation | May lead to unresolved conflicts unless communication improves |
| Trust Factors | Struggles with fear of abandonment | Reluctant to depend on others | Mutual understanding vital to build secure trust |
| Relationship Outcome | Potential for growth with consistent reassurance | Potential for emotional detachment without effort | Compatibility thrives on intentional emotional engagement |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Anxious vs. Avoidant
Anxious attachment style is characterized by a heightened need for closeness and fear of abandonment, leading to clinginess and emotional dependence in relationships. Avoidant attachment style involves discomfort with intimacy and a tendency to maintain emotional distance to protect oneself from vulnerability. Understanding these contrasting attachment behaviors helps explain patterns of interaction and emotional regulation in adult relationships.
Key Traits of Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a strong desire for closeness paired with fear of abandonment, often leading to heightened sensitivity to relationship cues and emotional vulnerability. Individuals with this attachment style tend to seek constant reassurance and may exhibit clinginess or worry about their partner's commitment. This contrasts with avoidant attachment, which involves emotional distance and discomfort with intimacy, and secure attachment, marked by confidence and balanced interpersonal connections.
Characteristics of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a strong desire for independence and discomfort with closeness or emotional intimacy, leading individuals to suppress their feelings and avoid relying on others. People with this style often prioritize self-sufficiency, may appear distant or emotionally unavailable, and struggle to trust or seek support in relationships. Your understanding of avoidant attachment helps in recognizing patterns that hinder deep connection and promotes healthier interpersonal dynamics.
Root Causes of Anxious and Avoidant Behaviors
Anxious attachment often stems from inconsistent caregiving during childhood, leading to heightened sensitivity to rejection and a pervasive fear of abandonment. Avoidant attachment typically originates from emotional unavailability or neglect by primary caregivers, causing individuals to suppress emotions and maintain distance in relationships. Understanding these root causes is crucial for addressing maladaptive patterns and fostering healthier interpersonal connections.
How Anxious Attachment Impacts Relationships
Anxious attachment significantly influences relationships by causing individuals to seek constant reassurance and fear abandonment, leading to heightened emotional sensitivity and dependence on their partners. This attachment style often results in overanalyzing interactions and misinterpreting neutral behaviors as rejection, which can create cycles of conflict and insecurity. The persistent need for closeness combined with anxiety about the partner's availability often challenges relationship stability and satisfaction.
The Effects of Avoidant Attachment in Love
Avoidant attachment in love often leads to emotional distance and difficulty expressing intimacy, causing partners to feel rejected or unimportant. Individuals with avoidant attachment may suppress their feelings and prioritize independence, which can result in misunderstandings and unstable relationships. Over time, this attachment style can undermine emotional connection, increasing the risk of relationship dissatisfaction and breakup.
Signs You Have an Anxious or Avoidant Attachment Style
Signs of an anxious attachment style include constant worry about relationships, fear of abandonment, and a strong need for reassurance from partners. Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance, difficulty trusting others, and discomfort with closeness or dependency. Recognizing these patterns helps in understanding relationship dynamics and improving emotional connections.
Common Challenges in Anxious–Avoidant Relationships
Anxious and avoidant attachment styles often create a cycle of pursuit and withdrawal, where your need for closeness clashes with your partner's desire for distance, leading to frequent misunderstandings and emotional frustration. Common challenges include difficulty in establishing trust, inconsistent communication patterns, and heightened sensitivity to rejection or abandonment. Navigating these dynamics requires recognizing each attachment style's fears and developing healthier ways to connect and communicate.
Healing and Managing Attachment Style Differences
Healing attachment style differences involves understanding the unique patterns of anxious and avoidant behaviors in relationships. Strategies such as self-awareness, emotional regulation, and open communication help reduce insecurity and build trust between partners with differing attachment styles. Therapeutic approaches like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) provide effective tools for managing conflicts and fostering secure attachment bonds.
Building Secure Attachment: Practical Steps Forward
Building secure attachment involves recognizing and addressing anxious and avoidant attachment patterns through consistent emotional availability and effective communication. You can foster trust by developing empathy, setting healthy boundaries, and practicing vulnerability within relationships. These practical steps enhance emotional regulation and create a foundation for lasting security and connection.
Infographic: Anxious vs Avoidant
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com