Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, longer cycle life, and faster charging compared to lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for electric vehicles and portable electronics. Explore this article to understand the key differences and applications of lithium-ion versus lead-acid batteries.
Table of Comparison
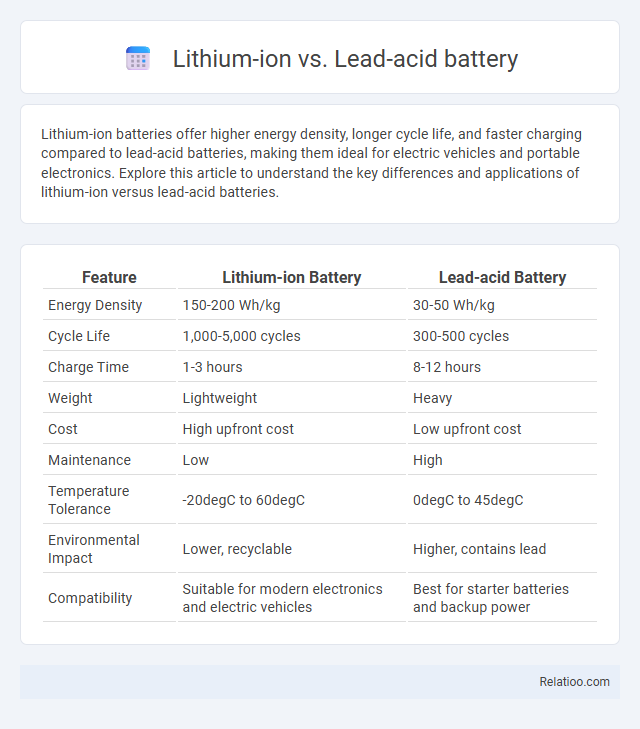
| Feature | Lithium-ion Battery | Lead-acid Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150-200 Wh/kg | 30-50 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | 1,000-5,000 cycles | 300-500 cycles |
| Charge Time | 1-3 hours | 8-12 hours |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Cost | High upfront cost | Low upfront cost |
| Maintenance | Low | High |
| Temperature Tolerance | -20degC to 60degC | 0degC to 45degC |
| Environmental Impact | Lower, recyclable | Higher, contains lead |
| Compatibility | Suitable for modern electronics and electric vehicles | Best for starter batteries and backup power |
Introduction to Battery Technologies
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for modern energy storage applications. Lead-acid batteries remain cost-effective and reliable for stationary energy systems and automotive use but suffer from lower energy efficiency and shorter cycle life. Understanding your energy needs helps determine whether the advanced capabilities of lithium-ion or the affordability of lead-acid technology best suits your battery solution.
Overview of Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life compared to lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and efficient energy storage. Your choice of battery impacts overall system performance, with lithium-ion batteries providing faster charging, superior depth of discharge, and reduced maintenance needs. In contrast, lead-acid batteries are heavier, have shorter lifespans, and lower energy efficiency, limiting their suitability for modern high-demand energy solutions.
Overview of Lead-acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are among the oldest rechargeable battery technologies, widely used for energy storage due to their reliability and low cost. They offer moderate energy density and are commonly found in automotive starters and backup power systems, although they are heavier and have shorter cycle life compared to lithium-ion batteries. Understanding your energy needs helps determine whether the durability and affordability of lead-acid batteries align with your specific application requirements.
Energy Density Comparison
Lithium-ion batteries offer significantly higher energy density compared to lead-acid batteries, enabling your devices or vehicles to store more energy in a smaller and lighter package. While lead-acid batteries typically have energy densities around 30-50 Wh/kg, lithium-ion batteries can achieve 150-250 Wh/kg, making them more efficient for energy storage and longer-lasting applications. Choosing lithium-ion technology enhances your overall energy performance and optimizes space utilization for power storage solutions.
Cycle Life and Longevity
Lithium-ion batteries typically offer a significantly longer cycle life compared to lead-acid batteries, often exceeding 2,000 to 5,000 charge cycles versus 500 to 1,000 cycles for lead-acid. The enhanced longevity of lithium-ion batteries translates to more efficient energy storage and better performance over time, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent charging and discharging. Your choice of battery technology directly impacts energy efficiency, total cost of ownership, and system reliability based on cycle life and durability.
Charging Speed and Efficiency
Lithium-ion batteries exhibit significantly faster charging speeds and higher energy efficiency compared to lead-acid batteries, with lithium-ion charging times often reduced by 50-70%. Lead-acid batteries suffer from lower charge acceptance rates and higher energy losses, typically around 20-30% inefficiency, whereas lithium-ion batteries maintain efficiencies above 90%. The superior energy density and charge retention of lithium-ion technology make it more suitable for applications demanding rapid recharge cycles and optimal energy utilization.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries, resulting in better cost efficiency over time despite a higher initial investment. Lead-acid batteries have lower upfront costs but require more frequent replacements and maintenance, increasing total ownership costs. Your decision should weigh immediate affordability against long-term savings and energy performance to optimize overall budget and reliability.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste generation. However, lithium-ion batteries involve complex recycling processes due to hazardous materials, while lead-acid batteries benefit from well-established, efficient recycling systems with over 95% material recovery rates. You can minimize environmental impact by choosing batteries with robust recycling programs and prioritizing sustainable disposal methods.
Safety and Risk Factors
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries, but they carry risks such as thermal runaway and fire hazards if damaged or improperly handled. Lead-acid batteries, while safer and more stable due to their robust design, pose environmental risks related to acid leaks and heavy metal contamination. Your choice should weigh the increased energy efficiency of lithium-ion against the safer, more environmentally manageable profile of lead-acid batteries.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Application
Selecting the right battery depends on energy density, cycle life, and application requirements; lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles. Lead-acid batteries, while heavier and lower in energy capacity, provide cost-effective power storage suited for backup systems and automotive starters. Understanding specific energy demands and budget constraints ensures optimal performance and longevity in energy storage solutions.
Infographic: Lithium-ion vs Lead-acid battery
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com