Eastern cultures prioritize family cohesion and collective harmony in relationships, emphasizing long-term commitment and interdependence; Western cultures value individualism, personal freedom, and open communication, often fostering more flexible relationship dynamics. Explore this article to uncover deeper insights into how these cultural differences shape romantic and familial bonds.
Table of Comparison
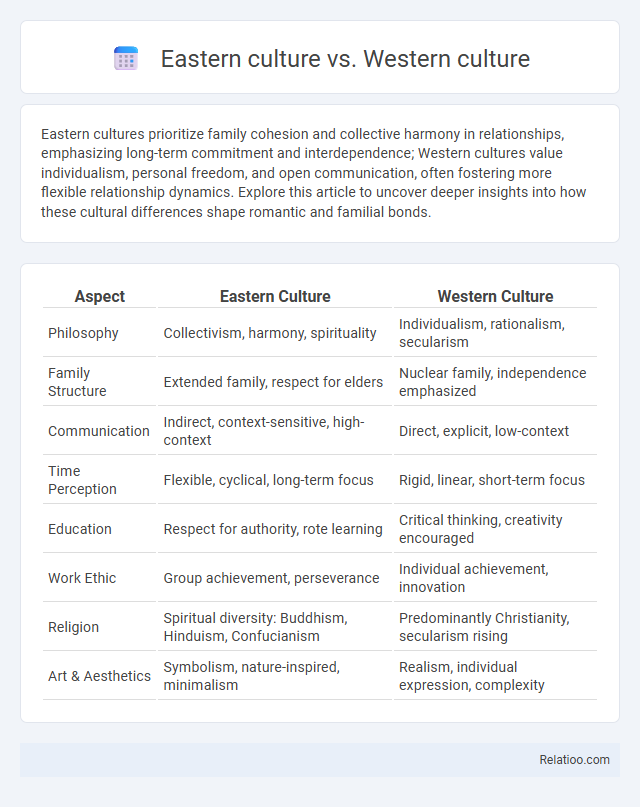
| Aspect | Eastern Culture | Western Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Collectivism, harmony, spirituality | Individualism, rationalism, secularism |
| Family Structure | Extended family, respect for elders | Nuclear family, independence emphasized |
| Communication | Indirect, context-sensitive, high-context | Direct, explicit, low-context |
| Time Perception | Flexible, cyclical, long-term focus | Rigid, linear, short-term focus |
| Education | Respect for authority, rote learning | Critical thinking, creativity encouraged |
| Work Ethic | Group achievement, perseverance | Individual achievement, innovation |
| Religion | Spiritual diversity: Buddhism, Hinduism, Confucianism | Predominantly Christianity, secularism rising |
| Art & Aesthetics | Symbolism, nature-inspired, minimalism | Realism, individual expression, complexity |
Origins and Historical Background
Eastern culture originates from ancient civilizations in Asia, such as China, India, and Japan, deeply rooted in philosophies like Confucianism, Buddhism, and Hinduism that emphasize community, harmony, and spirituality. Western culture traces its origins to Greco-Roman antiquity, the Renaissance, and the Enlightenment, fostering values of individualism, scientific inquiry, and democratic principles. Your understanding of any cultural background benefits from recognizing these distinct historical contexts, which shape societal norms, traditions, and worldviews.
Philosophical Foundations
Eastern culture emphasizes interconnectedness, harmony, and collective well-being rooted in philosophies such as Confucianism, Taoism, and Buddhism, which prioritize balance and holistic understanding. Western culture, shaped by Greek philosophy and Enlightenment ideals, values individualism, rationality, and analytical thinking, promoting self-expression and scientific inquiry. Your cultural background shapes how you interpret concepts like identity, morality, and existence through these distinct philosophical foundations.
Family Structure and Social Hierarchy
Eastern culture typically emphasizes extended family structures with strong intergenerational bonds and respect for elders, reinforcing hierarchical roles within both family and society. Western culture generally prioritizes nuclear family units, promoting individualism and egalitarian relationships that challenge traditional social hierarchies. Cultural background profoundly shapes family dynamics and social hierarchy, influencing values around authority, communal responsibility, and personal autonomy across different societies.
Approaches to Education and Learning
Eastern culture emphasizes collective learning, respect for authority, and rote memorization, fostering discipline and mastery of foundational knowledge. Western culture prioritizes critical thinking, creativity, and individual expression, encouraging interactive participation and inquiry-based learning. Cultural background shapes educational approaches by influencing values, teaching methods, and student-teacher dynamics, reflecting diverse perceptions of knowledge and learning objectives.
Communication Styles and Language
Eastern culture emphasizes indirect communication, valuing context, harmony, and nonverbal cues, while Western culture favors direct, explicit language that prioritizes clarity and individual expression. Communication in Eastern societies often relies on high-context interactions where meaning is derived from shared experiences and subtle signals, contrasting with the low-context, straightforward approach prevalent in Western cultures. Cultural backgrounds shape language use significantly, influencing how people interpret messages, manage conflicts, and establish relationships across diverse social and professional settings.
Attitudes Toward Individualism and Collectivism
Eastern culture emphasizes collectivism, valuing group harmony, family loyalty, and community interdependence, which shapes social behavior and decision-making processes. Western culture prioritizes individualism, promoting personal freedom, self-expression, and autonomy, influencing legal systems, education, and workplace dynamics. Cultural background plays a crucial role in shaping attitudes toward individualism and collectivism, affecting communication styles, conflict resolution, and identity construction across societies.
Religion and Spiritual Beliefs
Eastern culture predominantly embraces religions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Taoism, emphasizing spiritual harmony, meditation, and reincarnation. Western culture is largely influenced by Christianity, valuing doctrines like salvation, moral judgment, and an afterlife in heaven or hell. Cultural background shapes individual worldviews by integrating these religious and spiritual beliefs into social norms, rituals, and ethical frameworks.
Art, Music, and Literature
Eastern culture emphasizes spiritual themes and harmony with nature in art, music, and literature, often reflecting ancient philosophies like Confucianism and Taoism. Western culture typically prioritizes individualism and innovation, shown in diverse artistic movements, dynamic musical expressions, and a rich literary tradition spanning classical to contemporary genres. Cultural background shapes these practices by influencing the values, techniques, and narratives passed through generations, creating distinct yet occasionally overlapping aesthetic and thematic elements.
Work Ethic and Professional Relationships
Eastern culture often emphasizes collectivism, respect for hierarchy, and long-term commitment in work ethic, fostering strong loyalty and harmony in professional relationships. Western culture typically values individualism, innovation, and direct communication, promoting personal achievement and transparent interactions in the workplace. Cultural background significantly shapes these dynamics, influencing attitudes toward teamwork, authority, and conflict resolution across diverse professional environments.
Perspectives on Modernization and Globalization
Eastern culture often emphasizes community harmony and tradition, shaping perspectives on modernization as a process that should integrate innovation with cultural values. Western culture typically views modernization as rapid technological progress and individualism, promoting globalization as an opportunity for economic expansion and cultural exchange. Your understanding of these cultural backgrounds can enhance cross-cultural communication by appreciating how modernization and globalization impact societies differently.
Infographic: Eastern culture vs Western culture
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com