Justice ensures fairness through impartial judgment, while mercy offers compassion by tempering strict penalties with forgiveness. Explore how balancing justice and mercy shapes ethical decisions and human relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
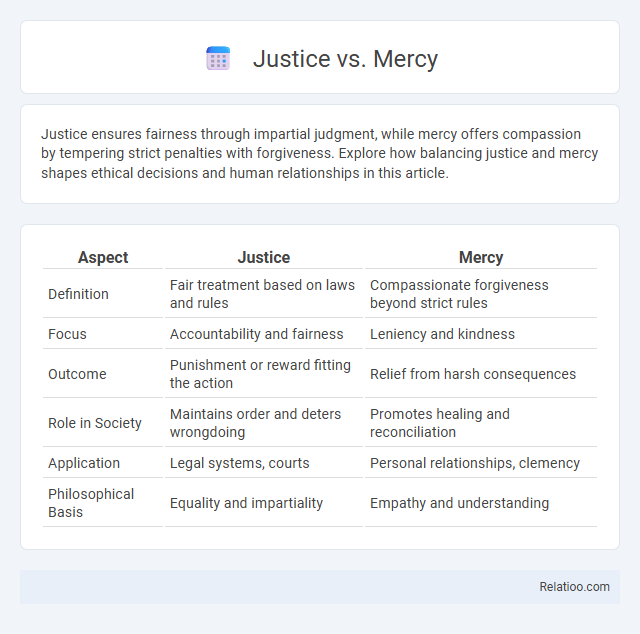
| Aspect | Justice | Mercy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fair treatment based on laws and rules | Compassionate forgiveness beyond strict rules |
| Focus | Accountability and fairness | Leniency and kindness |
| Outcome | Punishment or reward fitting the action | Relief from harsh consequences |
| Role in Society | Maintains order and deters wrongdoing | Promotes healing and reconciliation |
| Application | Legal systems, courts | Personal relationships, clemency |
| Philosophical Basis | Equality and impartiality | Empathy and understanding |
Understanding the Concepts: Justice and Mercy
Justice represents the principle of fairness, emphasizing the consistent application of laws and consequences to maintain social order. Mercy involves compassion and leniency, offering forgiveness or reduced punishment based on individual circumstances and humanity. Both concepts intersect in moral philosophy by balancing strict adherence to rules with empathy to achieve ethical decision-making.
Historical Perspectives on Justice and Mercy
Historical perspectives on justice emphasize strict adherence to laws and societal order, often prioritizing retribution and fairness in punishment. Mercy, historically viewed through religious and philosophical lenses, introduces compassion and leniency, sometimes challenging rigid justice systems to consider human fallibility and forgiveness. Your understanding of these concepts must balance the sometimes conflicting demands of moral values, which guide how justice and mercy should be applied in a society.
Philosophical Foundations: Justice vs Mercy
Justice is grounded in the principle of fairness, emphasizing the consistent application of rules and the equitable distribution of rewards and punishments within society. Mercy introduces compassion as a counterbalance to strict justice, allowing leniency and forgiveness based on contextual factors and individual circumstances. Philosophical debates explore how justice upholds social order through impartiality while mercy embodies humanity by addressing moral nuances beyond rigid legalistic frameworks.
Justice in Modern Legal Systems
Justice in modern legal systems serves as the foundation for ensuring fairness, equality, and the rule of law, emphasizing impartiality and the protection of individual rights. Your understanding of justice reflects society's commitment to accountability and the consistent application of laws to maintain social order. While mercy offers compassion and moral value provides ethical guidance, justice remains the structured mechanism through which legal decisions are made and enforced.
The Role of Mercy in Society
Mercy plays a crucial role in society by tempering strict justice with compassion, allowing for forgiveness and rehabilitation rather than solely punishment. It fosters social harmony and resilience by acknowledging human fallibility and promoting second chances. Your sense of morality is enriched when mercy balances justice, creating a more empathetic and just community.
Ethical Dilemmas: When Justice Clashes with Mercy
Ethical dilemmas arise when justice demands strict adherence to laws and moral codes, while mercy calls for compassion and forgiveness based on individual circumstances. The conflict between justice and mercy often highlights the complexity of moral values, where rigid punishment may clash with humanity's need for understanding and rehabilitation. Balancing these principles requires careful ethical judgment to ensure fairness without undermining empathy or societal order.
Justice and Mercy in Religious Teachings
Justice in religious teachings emphasizes fairness, accountability, and the upholding of divine laws, ensuring that individuals receive what they rightfully deserve according to sacred texts. Mercy, often portrayed as compassion and forgiveness, allows for leniency and grace, reflecting the benevolent nature of the divine in many faiths such as Christianity and Islam. Your understanding of these concepts can deepen spiritual growth by balancing strict justice with compassionate mercy, aligning actions with moral values rooted in faith traditions.
Balancing Justice and Mercy: Case Studies
Balancing justice and mercy requires carefully evaluating each case's unique circumstances to uphold moral values while ensuring fairness and compassion. Case studies involving criminal sentencing often highlight the tension between strict legal punishments and leniency based on mitigating factors, demonstrating the complexity in applying equitable justice. Courts that integrate restorative justice principles illustrate effective models where mercy complements justice, fostering rehabilitation and societal healing without compromising accountability.
The Impact of Justice and Mercy on Social Harmony
Justice ensures social harmony by upholding fairness, accountability, and the rule of law, which cultivates trust and stability within communities. Mercy complements justice by allowing compassion and forgiveness, reducing resentment and promoting reconciliation among conflicting parties. Balancing justice and mercy enhances moral values in society, fostering a more cohesive and peaceful social environment.
Striving for Equilibrium: Integrating Justice and Mercy
Striving for equilibrium between justice and mercy involves harmonizing fair consequences with compassionate understanding to uphold moral values in decision-making. Balancing justice ensures accountability and societal order, while mercy introduces forgiveness that acknowledges human imperfection, fostering ethical growth and reconciliation. This integration promotes a nuanced moral framework that respects both the law and empathy, enhancing social cohesion and individual dignity.
Infographic: Justice vs Mercy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com