A partner shares emotional connection and commitment without legal bonds, while a spouse involves formal marriage and associated legal rights. Explore the key differences and implications of partner versus spouse in this article.
Table of Comparison
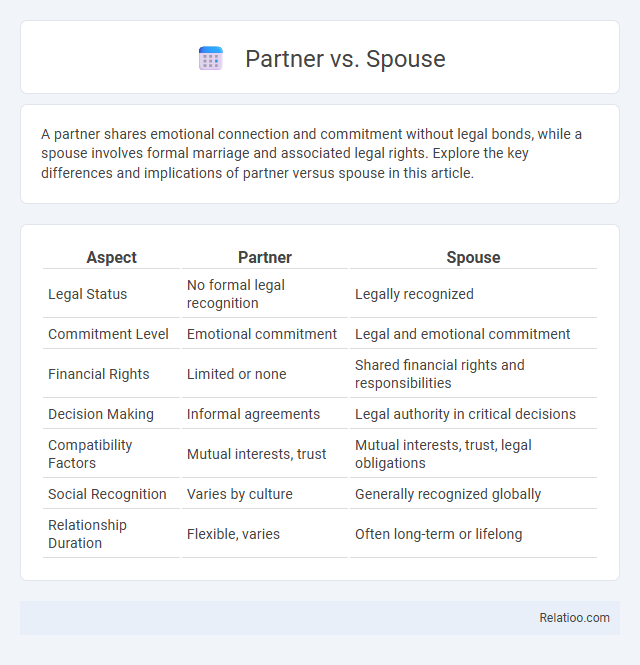
| Aspect | Partner | Spouse |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Status | No formal legal recognition | Legally recognized |
| Commitment Level | Emotional commitment | Legal and emotional commitment |
| Financial Rights | Limited or none | Shared financial rights and responsibilities |
| Decision Making | Informal agreements | Legal authority in critical decisions |
| Compatibility Factors | Mutual interests, trust | Mutual interests, trust, legal obligations |
| Social Recognition | Varies by culture | Generally recognized globally |
| Relationship Duration | Flexible, varies | Often long-term or lifelong |
Understanding the Terms: Partner vs Spouse
A partner generally refers to a significant other involved in a committed relationship without necessarily implying legal marriage, while a spouse specifically denotes a person legally married to another. Role expectations differ as partners may share responsibilities based on mutual agreement, whereas spouses often have societal and legal obligations tied to marriage. Understanding these distinctions is essential for clear communication about relationship dynamics and expectations.
Legal Definitions and Recognition
Legal definitions of partner and spouse vary significantly across jurisdictions, with "spouse" typically referring to individuals legally married under recognized matrimonial laws, conferring specific rights and responsibilities such as inheritance and tax benefits. "Partner" may denote a broader category including domestic partners or civil union participants, often lacking the full legal recognition or protections granted to spouses, though some regions provide comparable legal status through registered partnerships. Role expectations in legal contexts depend on these definitions, affecting the scope of rights related to decision-making, property, and social benefits.
Social Perceptions and Cultural Differences
Social perceptions of partner, spouse, and role expectations vary significantly across cultures, shaping your relationship dynamics and societal acceptance. In many Western societies, a partner may be seen as an equal companion without formal obligations, while a spouse carries legal and social duties often tied to traditional gender roles. Cultural differences influence how these roles are interpreted, with some cultures emphasizing collective family responsibilities for spouses and others prioritizing individual autonomy for partners.
Relationship Commitment Levels
Partner and spouse represent distinct relationship commitment levels; a partner typically denotes a significant other in a committed relationship without legal or formal recognition, while a spouse indicates marital status with legal and social obligations. Role expectations for partners often involve emotional support, shared decision-making, and cohabitation flexibility, whereas spouses generally face more structured roles including legal responsibilities, financial interdependence, and societal expectations. Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating relationship dynamics and aligning mutual commitment goals effectively.
Rights and Responsibilities
Partner, spouse, and role expectations each carry distinct rights and responsibilities shaped by legal, social, and personal contexts. Your rights as a spouse often include legal recognition, inheritance entitlements, and decision-making authority in healthcare, whereas partners may share similar responsibilities but lack formal legal protections. Role expectations influence duties such as financial support, emotional care, and household management, requiring clear communication to balance mutual obligations effectively.
Impact on Family Dynamics
Partner, spouse, and role expectations significantly shape family dynamics by influencing communication patterns, decision-making, and emotional support structures. Your role as a spouse often involves formal commitments and societal expectations that can affect conflict resolution and parenting styles differently than those with partners without legal or cultural recognition. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate family interactions with greater empathy and adaptability, fostering healthier relationships overall.
Financial Considerations
Partner financial roles often emphasize shared expenses and joint investment strategies without the legal obligations binding spouses. Spouses typically face statutory financial responsibilities such as alimony, joint tax filings, and inheritance rights that affect financial planning and asset division. Role expectations in relationships influence budgeting priorities, risk tolerance, and decision-making authority, shaping how finances are managed between partners and spouses.
Navigating Healthcare and Benefits
Navigating healthcare and benefits requires clear understanding of the distinctions between partner, spouse, and role expectation, as your legal rights and eligibility often depend on marital status. Spouses typically have automatic access to healthcare benefits, while partners may need to provide proof of a committed relationship or meet specific criteria established by employers or insurers. Knowing your designated role can streamline access to coverage, reduce delays in medical decision-making, and ensure your healthcare benefits align with your legal entitlements.
Implications for Parenting
Partner, spouse, and role expectations significantly shape parenting dynamics, influencing how responsibilities and emotional support are distributed. Your understanding of these distinctions impacts co-parenting harmony, affecting children's stability and development. Clear communication about role expectations reduces conflict and enhances collaborative parenting efforts.
Choosing the Right Term for Your Relationship
Choosing the right term for your relationship--partner, spouse, or role expectation--depends on the level of legal commitment, personal identification, and social context. "Spouse" specifically refers to a legally married individual, while "partner" offers a more inclusive and flexible description applying to committed couples regardless of marital status. Understanding role expectations within your relationship involves recognizing emotional, legal, and social responsibilities, ensuring the chosen term aligns with both personal values and societal recognition.
Infographic: Partner vs Spouse
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com